|
Germanic Sound Shifts (other)
Germanic sound shifts are the phonological developments (sound changes) from the Proto-Indo-European language (PIE) to Proto-Germanic, in Proto-Germanic itself, and in various Germanic subfamilies and languages. PIE to Proto-Germanic * Germanic spirant law * Grimm's law * Holtzmann's law * Sievers' law * Verner's law * Kluge's law In Proto-Germanic * Germanic a-mutation Germanic subfamilies and languages * Germanic umlaut (all of the early languages except for Gothic) * Great Vowel Shift (English) * High German consonant shift * Ingvaeonic nasal spirant law (attested in Old English, Old Frisian and Old Saxon) * West Germanic gemination See also * Germanic languages * Germanic substrate hypothesis The Germanic substrate hypothesis attempts to explain the purportedly distinctive nature of the Germanic languages within the context of the Indo-European languages. Based on the elements of Common Germanic vocabulary and syntax which do not seem ... Germanic langu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sound Change
A sound change, in historical linguistics, is a change in the pronunciation of a language. A sound change can involve the replacement of one speech sound (or, more generally, one phonetic feature value) by a different one (called phonetic change) or a more general change to the speech sounds that exist (phonological change), such as the merger of two sounds or the creation of a new sound. A sound change can eliminate the affected sound, or a new sound can be added. Sound changes can be environmentally conditioned if the change occurs in only some sound environments, and not others. The term "sound change" refers to diachronic changes, which occur in a language's sound system. On the other hand, " alternation" refers to changes that happen synchronically (within the language of an individual speaker, depending on the neighbouring sounds) and do not change the language's underlying system (for example, the ''-s'' in the English plural can be pronounced differently depending on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic A-mutation
''A''-mutation is a metaphonic process supposed to have taken place in late Proto-Germanic (c. 200). General description In ''a''-mutation, a short high vowel ( or ) was lowered when the following syllable contained a non-high vowel (, or ).Gordon 1957, § 32. Thus, since the change was produced by other vowels besides */a/, the term ''a''-mutation is something of a misnomer. It has also been called "''a''-umlaut", "''a''/''o''-umlaut", "velar umlaut" and, formerly, "Brechung".Lloyd (1966), p. 738. (This last was Grimm's term, but nowadays German ''Brechung'', and its English equivalents ''breaking'' and ''fracture'', are generally restricted in use to other unrelated sound-changes which later affected individual Germanic languages.) :* *''hurną'' > Old English ''horn'' "horn" :* *''wiraz'' > Old English ''wer'' "man" The high vowel was not lowered, however, if intervened between it and the following non-high vowel. An intervening nasal consonant followed by a consonant of a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Languages
The Germanic languages are a branch of the Indo-European language family spoken natively by a population of about 515 million people mainly in Europe, North America, Oceania and Southern Africa. The most widely spoken Germanic language, English, is also the world's most widely spoken language with an estimated 2 billion speakers. All Germanic languages are derived from Proto-Germanic, spoken in Iron Age Scandinavia. The West Germanic languages include the three most widely spoken Germanic languages: English with around 360–400 million native speakers; German language, German, with over 100 million native speakers; and Dutch language, Dutch, with 24 million native speakers. Other West Germanic languages include Afrikaans, an offshoot of Dutch, with over 7.1 million native speakers; Low German, considered a separate collection of Standard language, unstandardized dialects, with roughly 4.35–7.15 million native speakers and probably 6.7–10 million people who can understand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Germanic Gemination
West Germanic gemination was a sound change that took place in all West Germanic languages around the 3rd or 4th century AD. It affected consonants directly followed by , which were generally lengthened or geminated in that position. Because of Sievers' law, only consonants immediately after a short vowel were affected by the process. Overview When followed by , consonants were lengthened (doubled). The consonant , whether original or from earlier through rhotacization, was generally not affected; it occasionally shows gemination in Old High German, but inconsistently and this may be an analogical change. In contrast, the second element of the diphthongs ''iu'' and ''au'' was still underlyingly the consonant at this time, and therefore was lengthened as well. In Proto-Germanic, only appeared at the beginning of a syllable, primarily as the onset of a variety of suffixes and endings. It alternated with its syllabic counterpart in accordance with a phonological rule known as Siev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingvaeonic Nasal Spirant Law
In historical linguistics, the Ingvaeonic nasal spirant law (also called the Anglo-Frisian or North Sea Germanic nasal spirant law) is a description of a phonological development that occurred in the Ingvaeonic dialects of the West Germanic languages. This includes Old English, Old Frisian, and Old Saxon, and to a lesser degree Old Dutch (Old Low Franconian). Overview The sound change affected sequences of vowel + nasal consonant + fricative consonant. ("Spirant" is an older term for "fricative".) The sequences in question are ''-ns-'', ''-mf-'', and ''-nþ-'', preceded by any vowel. The nasal consonant disappeared, sometimes causing nasalization and compensatory lengthening of the vowel before it. The nasalization disappeared relatively soon after in many dialects along the coast, but it was retained long enough to prevent Anglo-Frisian brightening of to . The resulting long nasalized vowel was rounded to in most languages under various circumstances. In Old Saxon on the ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High German Consonant Shift
In historical linguistics, the High German consonant shift or second Germanic consonant shift is a phonological development (sound change) that took place in the southern parts of the West Germanic dialect continuum in several phases. It probably began between the third and fifth centuries and was almost complete before the earliest written records in High German were produced in the eighth century. From Proto-Germanic, the resulting language, Old High German, can be neatly contrasted with the other continental West Germanic languages, which for the most part did not experience the shift, and with Old English, which remained completely unaffected. General description The High German consonant shift altered a number of consonants in the southern German dialects – which includes Standard German, Yiddish, and Luxembourgish – and so explains why many German words have different consonants from the related words in English, Dutch and the Scandinavian languages. The term is sometimes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Vowel Shift
The Great Vowel Shift was a series of changes in the pronunciation of the English language that took place primarily between 1400 and 1700, beginning in southern England and today having influenced effectively all dialects of English. Through this vowel shift, the pronunciation of all Middle English long vowels was changed. Some consonant sounds changed as well, particularly those that became silent; the term ''Great Vowel Shift'' is sometimes used to include these consonantal changes. The standardization of English spelling began in the 15th and 16th centuries, and the Great Vowel Shift is the major reason English spellings now often deviate considerably from how they represent pronunciations. The Great Vowel Shift was first studied by Otto Jespersen (1860–1943), a Danish linguist and Anglicist, who coined the term. Causes The causes of the Great Vowel Shift are unknown and have been a source of intense scholarly debate; as yet, there is no firm consensus. The greatest cha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
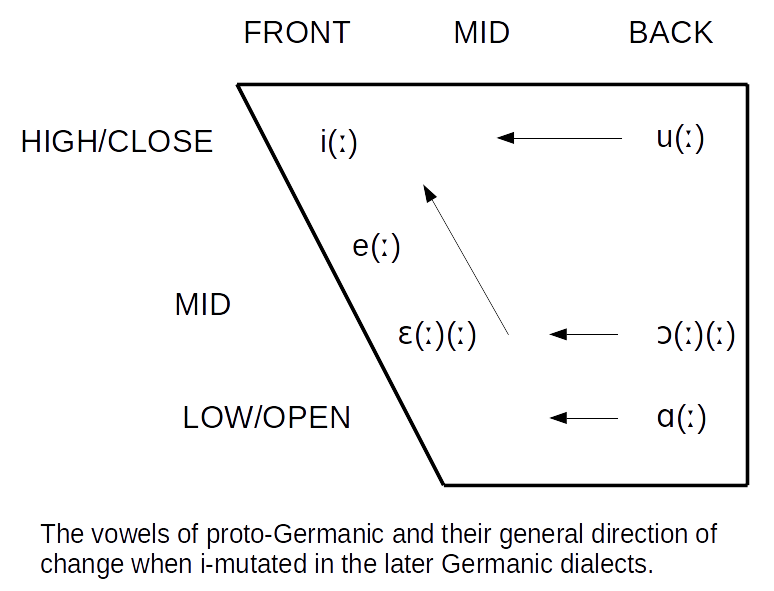
Germanic Umlaut
The Germanic umlaut (sometimes called i-umlaut or i-mutation) is a type of linguistic umlaut in which a back vowel changes to the associated front vowel ( fronting) or a front vowel becomes closer to (raising) when the following syllable contains , , or . It took place separately in various Germanic languages starting around AD 450 or 500 and affected all of the early languages except Gothic. An example of the resulting vowel alternation is the English plural ''foot ~ feet'' (from Proto-Germanic , pl. ). Germanic umlaut, as covered in this article, does not include other historical vowel phenomena that operated in the history of the Germanic languages such as Germanic a-mutation and the various language-specific processes of u-mutation, nor the earlier Indo-European ablaut (''vowel gradation''), which is observable in the conjugation of Germanic strong verbs such as ''sing/sang/sung''. While Germanic umlaut has had important consequences for all modern Germanic languag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kluge's Law
Kluge's law is a controversial Proto-Germanic sound law formulated by Friedrich Kluge. It purports to explain the origin of the Proto-Germanic long consonants ''*kk'', ''*tt'', and ''*pp'' (Proto-Indo-European lacked a phonemic length distinction for consonants) as originating in the assimilation of ''*n'' to a preceding voiced plosive consonant, under the condition that the ''*n'' was part of a suffix which was stressed in the ancestral Proto-Indo-European (PIE). The name "Kluge's law" was coined by Kauffmann (1887) and revived by Frederik Kortlandt (1991). As of 2006, this law has not been generally accepted by historical linguists. The resulting long consonants would subsequently have been shortened, except when they followed a short vowel; this is uncontroversial for ''*ss'' (which has a different origin). Proponents of Kluge's law use this to explain why so many Proto-Germanic roots (especially of strong verbs) end in short ''*p'', ''*t'', or ''*k'' even though their lik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proto-Indo-European Language
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-European exists. Far more work has gone into reconstructing PIE than any other proto-language, and it is the best understood of all proto-languages of its age. The majority of linguistic work during the 19th century was devoted to the reconstruction of PIE or its daughter languages, and many of the modern techniques of linguistic reconstruction (such as the comparative method) were developed as a result. PIE is hypothesized to have been spoken as a single language from 4500 BC to 2500 BC during the Late Neolithic to Early Bronze Age, though estimates vary by more than a thousand years. According to the prevailing Kurgan hypothesis, the original homeland of the Proto-Indo-Europeans may have been in the Pontic–Caspian steppe of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Verner's Law
Verner's law describes a historical sound change in the Proto-Germanic language whereby consonants that would usually have been the voiceless fricatives , , , , , following an unstressed syllable, became the voiced fricatives , , , , . The law was formulated by Karl Verner, and first published in 1877. Problem A seminal insight into how the Germanic languages diverged from their Indo-European ancestor had been established in the early nineteenth century, and had been formulated as Grimm's law. Amongst other things, Grimm's law described how the Proto-Indo-European voiceless stops ', ', ', and regularly changed into Proto-Germanic ( bilabial fricative ), (dental fricative ), (velar fricative ), and (velar fricative ). However, there appeared to be a large set of words in which the agreement of Latin, Greek, Sanskrit, Baltic, Slavic etc. guaranteed Proto-Indo-European ', ' or ', and yet the Germanic reflex was not the expected, unvoiced fricatives , , , but rather their v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sievers' Law
Sievers's law in Indo-European linguistics accounts for the pronunciation of a consonant cluster with a glide ( or ) before a vowel as it was affected by the phonetics of the preceding syllable. Specifically it refers to the alternation between and , and possibly and as conditioned by the weight of the preceding syllable. For instance, Proto-Indo-European (PIE) became Proto-Germanic *''harjaz'', Gothic ''harjis'' "army", but PIE became Proto-Germanic *''hirdijaz'', Gothic ''hairdeis'' "shepherd". It differs from ablaut in that the alternation has no morphological relevance but is phonologically context-sensitive: PIE followed a heavy syllable (a syllable with a diphthong, a long vowel, or ending in more than one consonant), but would follow a light syllable (a short vowel followed by a single consonant). History Discovery This situation was first noticed by the Germanic philologist Eduard Sievers (1859-1932), and his aim was to account for certain phenomena in the Ger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |