|
German Orthography
German orthography is the orthography used in writing the German language, which is largely phonemic. However, it shows many instances of spellings that are historic or analogous to other spellings rather than phonemic. The pronunciation of almost every word can be derived from its spelling once the spelling rules are known, but the opposite is not generally the case. Today, Standard High German orthography is regulated by the (Council for German Orthography), composed of representatives from most German-speaking countries. Alphabet The modern German alphabet consists of the twenty-six letters of the ISO basic Latin alphabet plus four special letters. Basic alphabet 1in Germany 2in Austria Special letters German has four special letters; three are vowels accented with an umlaut () and one is a ligature of and (; called "ess-zed/zee" or "sharp s"), all of which are officially considered distinct letters of the alphabet, and have their own names separat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orthography
An orthography is a set of conventions for writing a language, including norms of spelling, hyphenation, capitalization, word breaks, emphasis, and punctuation. Most transnational languages in the modern period have a writing system, and most of these systems have undergone substantial standardization, thus exhibiting less dialect variation than the spoken language. These processes can fossilize pronunciation patterns that are no longer routinely observed in speech (e.g., "would" and "should"); they can also reflect deliberate efforts to introduce variability for the sake of national identity, as seen in Noah Webster's efforts to introduce easily noticeable differences between American and British spelling (e.g., "honor" and "honour"). Some nations (e.g. France and Spain) have established language academies in an attempt to regulate orthography officially. For most languages (including English) however, there are no such authorities and a sense of 'correct' orthography e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Typographic Ligature
In writing and typography, a ligature occurs where two or more graphemes or letters are joined to form a single glyph. Examples are the characters æ and œ used in English and French, in which the letters 'a' and 'e' are joined for the first ligature and the letters 'o' and 'e' are joined for the second ligature. For stylistic and legibility reasons, 'f' and 'i' are often merged to create 'fi' (where the tittle on the 'i' merges with the hood of the 'f'); the same is true of 's' and 't' to create 'st'. The common ampersand (&) developed from a ligature in which the handwritten Latin letters 'E' and 't' (spelling , Latin for 'and') were combined. History The earliest known script Sumerian cuneiform and Egyptian language, Egyptian hieratic both include many cases of character combinations that gradually evolve from ligatures into separately recognizable characters. Other notable ligatures, such as the Brahmic family, Brahmic abugidas and the Runes, Germanic bind rune, figure pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digraph (orthography)
A digraph or digram (from the grc, δίς , "double" and , "to write") is a pair of characters used in the orthography of a language to write either a single phoneme (distinct sound), or a sequence of phonemes that does not correspond to the normal values of the two characters combined. Some digraphs represent phonemes that cannot be represented with a single character in the writing system of a language, like the English '' sh'' in ''ship'' and ''fish''. Other digraphs represent phonemes that can also be represented by single characters. A digraph that shares its pronunciation with a single character may be a relic from an earlier period of the language when the digraph had a different pronunciation, or may represent a distinction that is made only in certain dialects, like the English '' wh''. Some such digraphs are used for purely etymological reasons, like '' rh'' in English. Digraphs are used in some Romanization schemes, like the '' zh'' often used to represent t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernkastel-Kues
Bernkastel-Kues () is a town on the Middle Moselle in the Bernkastel-Wittlich district in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is a well-known winegrowing centre. The town is a state-recognized health resort (''Erholungsort''), seat of the ''Verbandsgemeinde'' of Bernkastel-Kues and birthplace of one of the most famous German polymaths, the mediaeval churchman and philosopher Nikolaus von Kues (Cusanus). Geography Location Bernkastel-Kues lies in the Moselle valley, roughly from Trier. The greatest elevation is the ''Olymp'' (415 m above sea level), and the lowest point (107 m above sea level) lies on the Moselle's banks. The municipal area totals 23 657 101 m2, of which 7 815 899 m2 is used for agriculture, thereby making Bernkastel-Kues one of the Middle Moselle's biggest towns by land area. Neighbouring municipalities Clockwise from the north, these are Graach, Longkamp, Monzelfeld, Veldenz, Mülheim, Lieser, Maring-Novi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coesfeld
Coesfeld (; Westphalian: ''Koosfeld'') is the capital of the district of Coesfeld in the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia. History Coesfeld received its city rights in 1197, but was first recorded earlier than that in the biography of St. Ludger, patron and first bishop of the diocese of Munster who was born north of Coesfeld in Billerbeck. The day before he died, Ludger spent the night in Coesfeld and heard mass in the morning in the church he founded. He was on his way from his abbey in Essen to Münster. The road he followed passed Coesfeld and Billerbeck, and after preaching in the St. Lambert's church, 26 March 809, he travelled on to Billerbeck, where he died in the evening. The Coesfeld St. Jacobikirche dates from the same period as the city charter. For centuries, Coesfeld was an important stopping place for pilgrims traveling one of the more popular Germanic Jakobi routes (Way of St. James) leading from Warendorf over Münster (via Billerbeck) to Coesfeld, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straelen
Straelen (; Low Rhenish: ''Strale'') is a municipality in the district of Cleves, in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located near the border with the Netherlands, approx. 10 km north-east of Venlo. Twinning : Bayon The Bayon ( km, ប្រាសាទបាយ័ន, ) is a richly decorated Khmer temple related to Buddhism at Angkor in Cambodia. Built in the late 12th or early 13th century as the state temple of the King Jayavarman VII ( km, ព្រះ ... in Meurthe-et-Moselle, since 7 July 1963. ( France ). History Straelen was first mentioned in Latin as Strala in 1063. References External links * Kleve (district) {{Kleve-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaeresis (diacritic)
The diaeresis ( ; is a diacritical mark used to indicate the separation of two distinct vowels in adjacent syllables when an instance of diaeresis (or hiatus) occurs, so as to distinguish from a digraph or diphthong. It consists of two dots placed over a letter, generally a vowel; when that letter is an , the diacritic replaces the tittle: . The diaeresis diacritic indicates that two adjoining letters that would normally form a digraph and be pronounced as one sound, are instead to be read as separate vowels in two syllables. For example, in the spelling "coöperate", the diaeresis reminds the reader that the word has four syllables ''co-op-er-ate'', not three, ''*coop-er-ate''. In British English this usage has been considered obsolete for many years, and in US English, although it persisted for longer, it is now considered archaic as well. Nevertheless, it is still used by the US magazine ''The New Yorker''. In English language texts it is perhaps most familiar in the sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurrent
() is an old form of German-language handwriting based on late medieval cursive writing, also known as ("cursive script"), ("German script") and ''German cursive''. Over the history of its use into the first part of the 20th century, many individual letters acquired variant forms. German writers used both cursive styles, and Latin cursive, in parallel: location, contents, and context of the text determined which script style to use. is a modern script based on that is characterized by simplified letters and vertical strokes. It was developed in 1911 and taught in all German schools as the primary script from 1935 until the beginning of January 1941. Then it was replaced with ("normal German handwriting"), which is sometimes referred to as "Latin writing". Lettering examples File:Lessing Kleist-Brief.jpg, Letter from Lessing to Kleist, 14 March 1758 File:Schein und Sein.jpg, Manuscript by Wilhelm Busch (undated, late 19th century) File:Bielsko-Biała Teatr Polski ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Printing Press
A printing press is a mechanical device for applying pressure to an inked surface resting upon a print medium (such as paper or cloth), thereby transferring the ink. It marked a dramatic improvement on earlier printing methods in which the cloth, paper or other medium was brushed or rubbed repeatedly to achieve the transfer of ink, and accelerated the process. Typically used for texts, the invention and global spread of the printing press was one of the most influential events in the second millennium. In Germany, around 1440, goldsmith Johannes Gutenberg invented the movable-type printing press, which started the Printing Revolution. Modelled on the design of existing screw presses, a single Renaissance movable-type printing press could produce up to 3,600 pages per workday, compared to forty by hand-printing and a few by hand-copying. Gutenberg's newly devised hand mould made possible the precise and rapid creation of metal movable type in large quantities. His two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fronting (phonology)
In phonology, fronting is a sound change in which a vowel or consonant becomes fronted, advanced or pronounced farther to the front of the vocal tract than some reference point. The opposite situation, in which a sound becomes pronounced farther to the back of the vocal tract, is called backing or retraction. Fronting may be triggered by a nearby sound, in which case it is a form of assimilation, or may occur on its own. Examples Assimilation In i-mutation and Germanic umlaut, a back vowel is fronted under the influence of or in a following syllable. This is assimilation. Vowel shifts In the Attic and Ionic dialects of Ancient Greek, Proto-Greek close back were fronted to . This change occurred in all cases and was not triggered by a nearby front consonant or vowel. In Old English and Old Frisian, the back vowels were fronted to in certain cases. For more information, see First a-fronting and Second a-fronting. In many dialects of English, the vowel is fron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
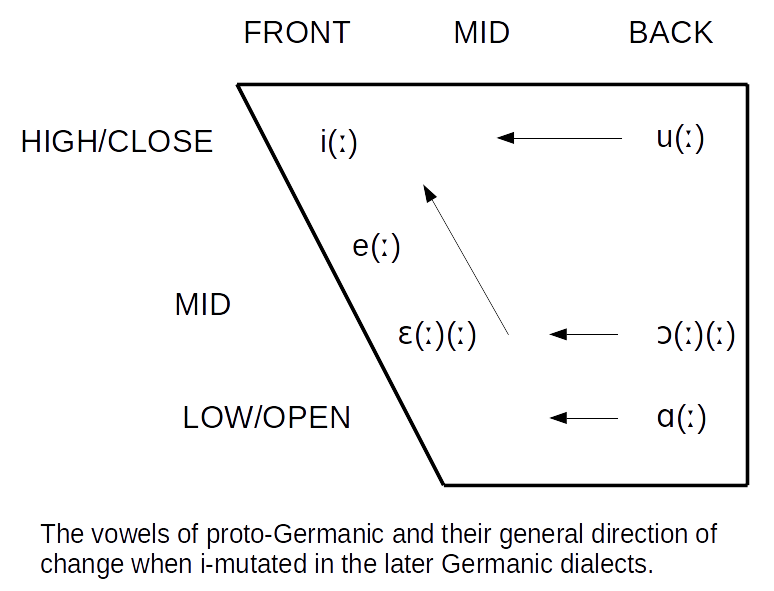
Germanic Umlaut
The Germanic umlaut (sometimes called i-umlaut or i-mutation) is a type of linguistic umlaut in which a back vowel changes to the associated front vowel (fronting) or a front vowel becomes closer to ( raising) when the following syllable contains , , or . It took place separately in various Germanic languages starting around AD 450 or 500 and affected all of the early languages except Gothic. An example of the resulting vowel alternation is the English plural ''foot ~ feet'' (from Proto-Germanic , pl. ). Germanic umlaut, as covered in this article, does not include other historical vowel phenomena that operated in the history of the Germanic languages such as Germanic a-mutation and the various language-specific processes of u-mutation, nor the earlier Indo-European ablaut (''vowel gradation''), which is observable in the conjugation of Germanic strong verbs such as ''sing/sang/sung''. While Germanic umlaut has had important consequences for all modern Germanic lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |