|
Geograpsus Severnsi
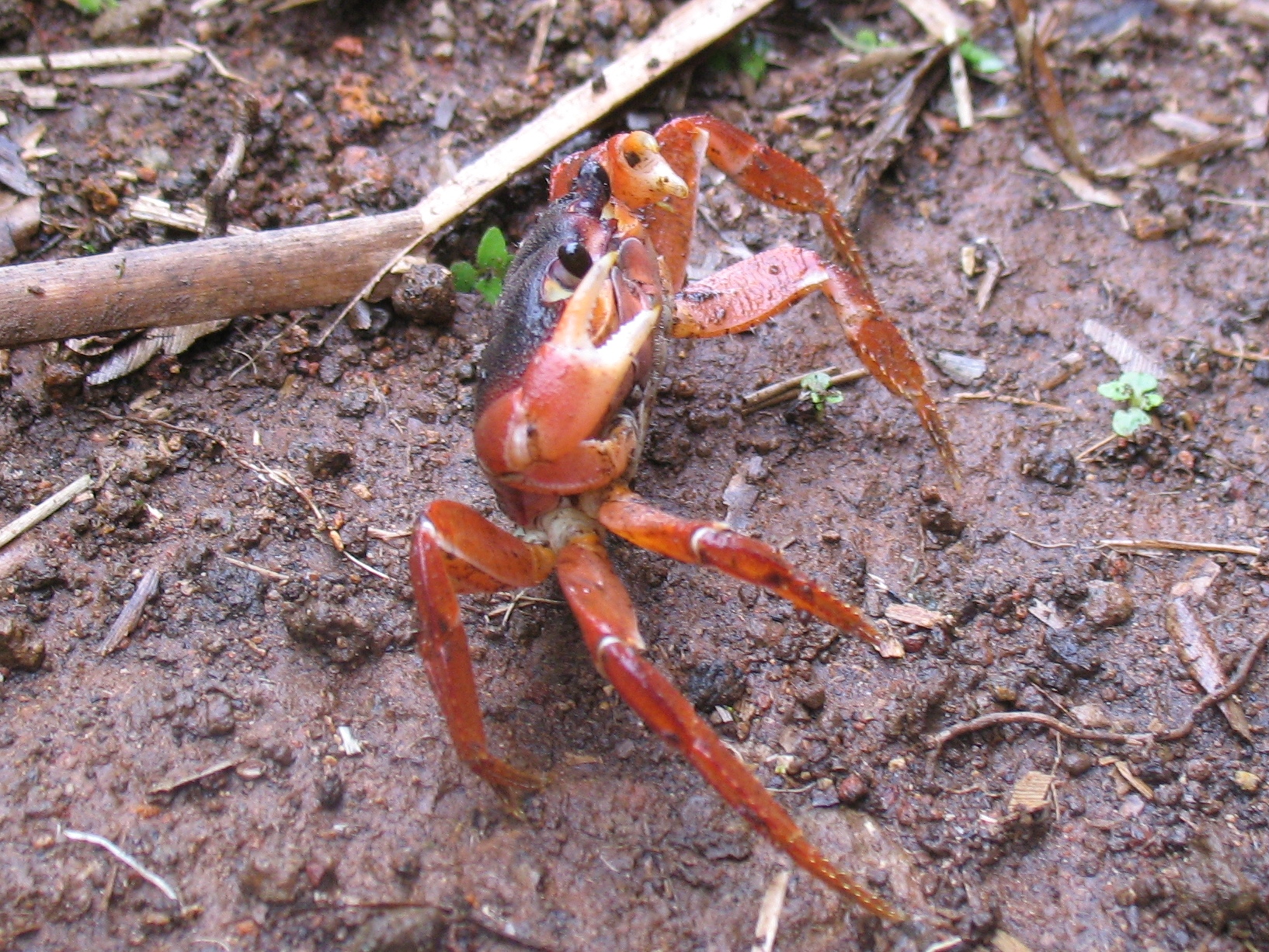
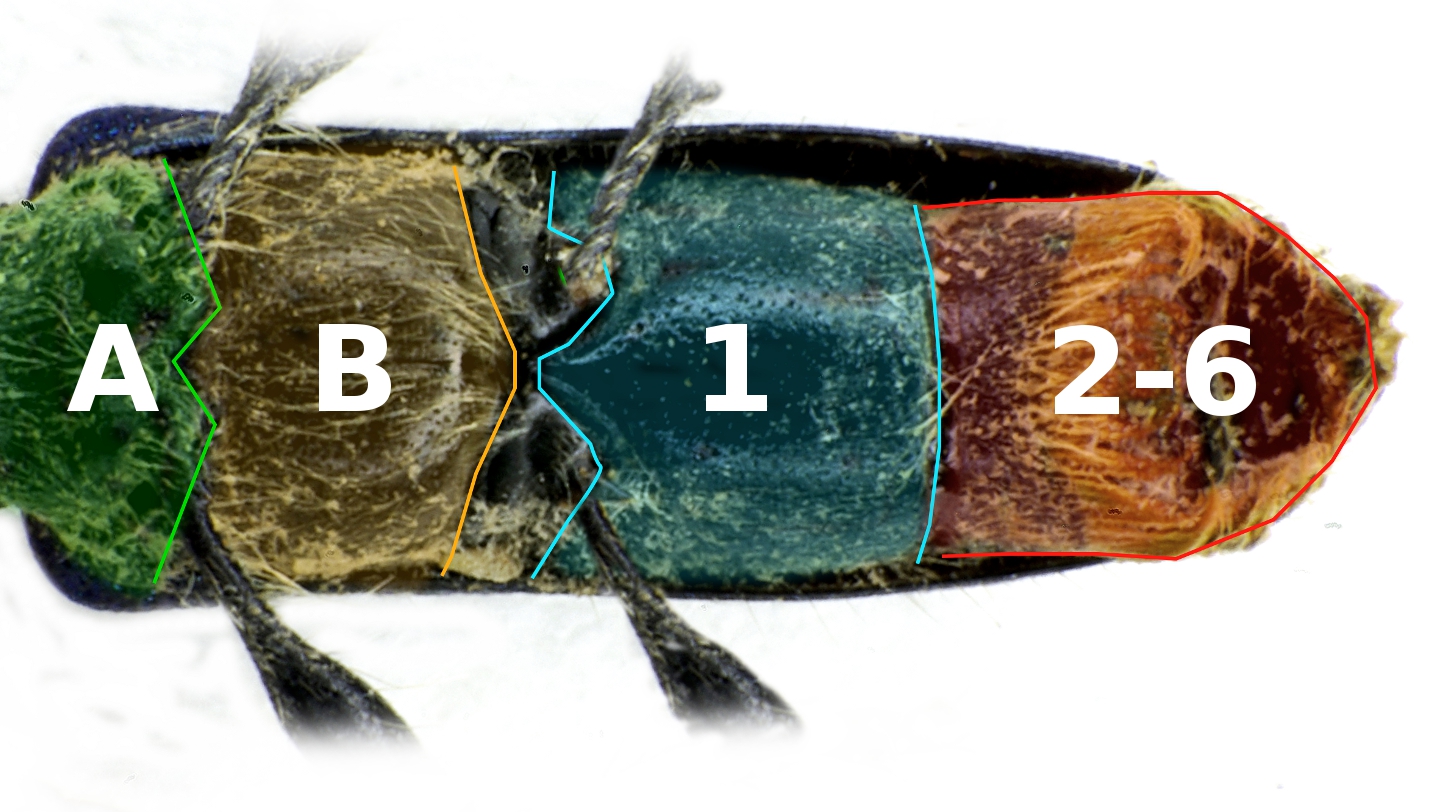
''Geograpsus severnsi'' is an extinct species of land crab from Hawaii. It died out shortly after humans colonized the Hawaiian Islands. It is the first known documented crab to become extinct after the ice age. Distribution Specimens of ''G. severnsi'' have been recovered from several of the Hawaiian high islands, including Hawaii, Maui, Oahu and Kauai. They have been found up to inland, and at altitudes of up to . Its range appears to have overlapped with that of the more coastal '' G. crinipes'', a species which is widespread across the Indo-Pacific. Description ''Geograpsus severnsi'' was probably the largest species in the genus. Based on the size of sternites, its carapace width may have been up to . Its claws were long, and in all the specimens with both claws preserved, the right claw was larger than the left. Most of the known specimens are males, but this is thought to reflect behavioral differences between the sexes, rather than an extreme sex ratio in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holotype
A holotype is a single physical example (or illustration) of an organism, known to have been used when the species (or lower-ranked taxon) was formally described. It is either the single such physical example (or illustration) or one of several examples, but explicitly designated as the holotype. Under the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), a holotype is one of several kinds of name-bearing types. In the International Code of Nomenclature for algae, fungi, and plants (ICN) and ICZN, the definitions of types are similar in intent but not identical in terminology or underlying concept. For example, the holotype for the butterfly '' Plebejus idas longinus'' is a preserved specimen of that subspecies, held by the Museum of Comparative Zoology at Harvard University. In botany, an isotype is a duplicate of the holotype, where holotype and isotypes are often pieces from the same individual plant or samples from the same gathering. A holotype is not necessarily "typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kauai
Kauai, () anglicized as Kauai ( ), is geologically the second-oldest of the main Hawaiian Islands (after Niʻihau). With an area of 562.3 square miles (1,456.4 km2), it is the fourth-largest of these islands and the 21st largest island in the United States. Nicknamed the Garden Isle, Kauai lies 73 miles (117 km) across the Kauai Channel, northwest of Oahu. This island is the site of Waimea Canyon State Park and the Na Pali Coast State Park. The United States Census Bureau defines Kauai as census tracts 401 through 409 of Kauai County, Hawaii, which comprises all of the county except the islands of Kaʻula, Lehua and Niihau. The 2020 United States census population of the island was 73,298. The most populous town is Kapaa. Etymology and language Hawaiian narrative locates the name's origin in the legend of Hawaiiloa, the Polynesian navigator credited with discovery of the Hawaiian Islands. The story relates how he named the island of Kauai after a favorite son; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Omnivore
An omnivore () is an animal that has the ability to eat and survive on both plant and animal matter. Obtaining energy and nutrients from plant and animal matter, omnivores digest carbohydrates, protein, fat, and fiber, and metabolize the nutrients and energy of the sources absorbed. Often, they have the ability to incorporate food sources such as algae, fungi, and bacteria into their diet. Omnivores come from diverse backgrounds that often independently evolved sophisticated consumption capabilities. For instance, dogs evolved from primarily carnivorous organisms ( Carnivora) while pigs evolved from primarily herbivorous organisms (Artiodactyla). Despite this, physical characteristics such as tooth morphology may be reliable indicators of diet in mammals, with such morphological adaptation having been observed in bears. The variety of different animals that are classified as omnivores can be placed into further sub-categories depending on their feeding behaviors. Frugivor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps with the closely related sciences of biogeography, evolutionary biology, genetics, ethology, and natural history. Ecology is a branch of biology, and it is not synonymous with environmentalism. Among other things, ecology is the study of: * The abundance, biomass, and distribution of organisms in the context of the environment * Life processes, antifragility, interactions, and adaptations * The movement of materials and energy through living communities * The successional development of ecosystems * Cooperation, competition, and predation within and between species * Patterns of biodiversity and its effect on ecosystem processes Ecology has practical applications in conservation biology, wetland management, natural resource managemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reproductive Migration
The reproductive system of an organism, also known as the genital system, is the biological system made up of all the anatomical organs involved in sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are also important accessories to the reproductive system. Unlike most organ systems, the sexes of differentiated species often have significant differences. These differences allow for a combination of genetic material between two individuals, which allows for the possibility of greater genetic fitness of the offspring. Reproductive System 2001 Body Guide powered by Adam Animals In mammals, the major organs of the reproductive system include the external ge ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johngarthia Lagostoma
''Johngarthia lagostoma'' is a species of terrestrial crab that lives on Ascension Island and three other islands in the South Atlantic. It grows to a carapace width of on Ascension Island, where it is the largest native land animal. It exists in two distinct colour morphs, one yellow and one purple, with few intermediates. The yellow morph dominates on Ascension Island, while the purple morph is more frequent on Rocas Atoll. The species differs from other '' Johngarthia'' species by the form of the third maxilliped. ''Johngarthia lagostoma'' lives in burrows among vegetation, at altitudes of up to , emerging at night to feed on plant matter and occasionally on animals. From January to March there is an annual migration to the sea to release the planktonic larvae. The species was first described (as ''Gecarcinus lagostoma'') by Henri Milne-Edwards in 1837 from material sent to him by the naturalists Jean René Constant Quoy and Joseph Paul Gaimard, collected by the Fren ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascension Island
Ascension Island is an isolated volcanic island, 7°56′ south of the Equator in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is about from the coast of Africa and from the coast of South America. It is governed as part of the British Overseas Territory of Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan da Cunha, of which the main island, Saint Helena, is around to the southeast. The territory also includes the sparsely populated Tristan da Cunha archipelago, to the south, about halfway to the Antarctic Circle. Named after the day of its recorded discovery, Ascension of Jesus, Ascension Island was an important safe haven as a coaling station to mariners and a refueling stop for commercial airliners back in the days of international air travel by flying boats. Ascension Island was garrisoned by the British Admiralty from 22 October 1815 to 1922. During World War II, it was an important naval and air station, especially providing antisubmarine warfare bases in the Battle of the Atlantic.Victory at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sex Ratio
The sex ratio (or gender ratio) is usually defined as the ratio of males to females in a population. As explained by Fisher's principle, for evolutionary reasons this is typically about 1:1 in species which reproduce sexually. Many species deviate from an even sex ratio, either periodically or permanently. Examples include parthenogenic species, periodically mating organisms such as aphids, some eusocial wasps, bees, ants, and termites. The human sex ratio is of particular interest to anthropologists and demographers. In human societies, sex ratios at birth may be considerably skewed by factors such as the age of mother at birth and by sex-selective abortion and infanticide. Exposure to pesticides and other environmental contaminants may be a significant contributing factor as well. As of 2014, the global sex ratio at birth is estimated at 107 boys to 100 girls (1,000 boys per 934 girls).. Types In most species, the sex ratio varies according to the age profile of the populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carapace
A carapace is a Dorsum (biology), dorsal (upper) section of the exoskeleton or shell in a number of animal groups, including arthropods, such as crustaceans and arachnids, as well as vertebrates, such as turtles and tortoises. In turtles and tortoises, the underside is called the plastron. Crustaceans In crustaceans, the carapace functions as a protective cover over the cephalothorax (i.e., the fused head and thorax, as distinct from the abdomen behind). Where it projects forward beyond the eyes, this projection is called a rostrum (anatomy), rostrum. The carapace is Calcification, calcified to varying degrees in different crustaceans. Zooplankton within the phylum Crustacea also have a carapace. These include Cladocera, ostracods, and Isopoda, isopods, but isopods only have a developed "cephalic shield" carapace covering the head. Arachnids In arachnids, the carapace is formed by the fusion of prosomal tergites into a single Plate (animal anatomy), plate which carries the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sternite
The sternum (pl. "sterna") is the ventral portion of a segment of an arthropod thorax or abdomen. In insects, the sterna are usually single, large sclerites, and external. However, they can sometimes be divided in two or more, in which case the subunits are called sternites, and may also be modified on the terminal abdominal segments so as to form part of the functional genitalia, in which case they are frequently reduced in size and development, and may become internalized and/or membranous. For a detailed explanation of the terminology, see Kinorhynchs have tergal and sternal plates too, though seemingly not homologous with those of arthropods.Sørensen, M. V. et al. Phylogeny of Kinorhyncha based on morphology and two molecular loci. PLoS One 10, 1–33 (2015). Ventrites are externally visible sternites. Usually the first sternite is covered up, so that vertrite numbers do not correspond to sternid numbers. The term is also used in other arthropod groups such as crustaceans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Pacific
The Indo-Pacific is a vast biogeographic region of Earth. In a narrow sense, sometimes known as the Indo-West Pacific or Indo-Pacific Asia, it comprises the tropical waters of the Indian Ocean, the western and central Pacific Ocean, and the seas connecting the two in the general area of Indonesia. It does not include the temperate and polar regions of the Indian and Pacific oceans, nor the Tropical Eastern Pacific, along the Pacific coast of the Americas, which is also a distinct marine realm. The term is especially useful in marine biology, ichthyology, and similar fields, since many marine habitats are continuously connected from Madagascar to Japan and Oceania, and a number of species occur over that range, but are not found in the Atlantic Ocean. The region has an exceptionally high species richness, with the world's highest species richness being found in at its heart in the Coral Triangle, and a remarkable gradient of decreasing species richness radiating outward in al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geograpsus Crinipes
''Geograpsus'' is a genus of crabs in the family Grapsidae, containing four extant species, and one extinct species: *'' Geograpsus crinipes'' (Dana, 1851) *''Geograpsus grayi'' (H. Milne-Edwards, 1853) *''Geograpsus lividus'' (H. Milne-Edwards, 1837) *''Geograpsus stormi ''Geograpsus'' is a genus of crabs in the family Grapsidae, containing four extant species, and one extinct species: *'' Geograpsus crinipes'' (Dana, 1851) *''Geograpsus grayi'' (H. Milne-Edwards, 1853) *''Geograpsus lividus ''Geograpsus liv ...'' De Man, 1895 *† '' Geograpsus severnsi'' Paulay & Starmer, 2011 References Grapsidae {{crab-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)