|
Genetically Modified Potato
A genetically modified potato is a potato that has had its genes modified, using genetic engineering. Goals of modification include introducing pest resistance, tweaking the amounts of certain chemicals produced by the plant, and to prevent browning or bruising of the tubers. Varieties modified to produce large amounts of starches may be approved for industrial use only, not for food. Currently marketed varieties Used for food Innate The genetically modified Innate potato was approved by the United States Department of Agriculture in 2014 and the US FDA in 2015. The cultivar was developed by J. R. Simplot Company. It is designed to resist blackspot bruising, browning and to contain less of the amino acid asparagine that turns into acrylamide during the frying of potatoes. Acrylamide is a probable human carcinogen, so reduced levels of it in fried potato foods is desirable. Though, browning does not affect the quality of the potato, it is simply that consumers tend to not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
McDonald's
McDonald's Corporation is an American Multinational corporation, multinational fast food chain store, chain, founded in 1940 as a restaurant operated by Richard and Maurice McDonald, in San Bernardino, California, United States. They rechristened their business as a hamburger stand, and later turned the company into a Franchising, franchise, with the Golden Arches logo being introduced in 1953 at a location in Phoenix, Arizona. In 1955, Ray Kroc, a businessman, joined the company as a franchise agent and proceeded to purchase the chain from the McDonald brothers. McDonald's had its previous headquarters in Oak Brook, Illinois, but moved its global headquarters to Chicago in June 2018. McDonald's is the world's largest restaurant chain by revenue, serving over 69 million customers daily in over 100 countries in more than 40,000 outlets as of 2021. McDonald's is best known for its hamburgers, cheeseburgers and french fries, although their menus include other items like ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge Agricultural Genetics
Cambridge ( ) is a university city and the county town in Cambridgeshire, England. It is located on the River Cam approximately north of London. As of the 2021 United Kingdom census, the population of Cambridge was 145,700. Cambridge became an important trading centre during the Roman and Viking ages, and there is archaeological evidence of settlement in the area as early as the Bronze Age. The first town charters were granted in the 12th century, although modern city status was not officially conferred until 1951. The city is most famous as the home of the University of Cambridge, which was founded in 1209 and consistently ranks among the best universities in the world. The buildings of the university include King's College Chapel, Cavendish Laboratory, and the Cambridge University Library, one of the largest legal deposit libraries in the world. The city's skyline is dominated by several college buildings, along with the spire of the Our Lady and the English Martyrs Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Gatehouse
John is a common English name and surname: * John (given name) * John (surname) John may also refer to: New Testament Works * Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John * First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John * Second Epistle of John, often shortened to 2 John * Third Epistle of John, often shortened to 3 John People * John the Baptist (died c. AD 30), regarded as a prophet and the forerunner of Jesus Christ * John the Apostle (lived c. AD 30), one of the twelve apostles of Jesus * John the Evangelist, assigned author of the Fourth Gospel, once identified with the Apostle * John of Patmos, also known as John the Divine or John the Revelator, the author of the Book of Revelation, once identified with the Apostle * John the Presbyter, a figure either identified with or distinguished from the Apostle, the Evangelist and John of Patmos Other people with the given name Religious figures * John, father of Andrew the Apostle and Saint Peter * Pope Joh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Désirée (potato)
Désirée or Desiree or ''variation'', may refer to: * Désirée (given name), a female given name People * Des'ree (born 1968), British pop/soul vocalist throughout the 1990s * Desiree Barboza, Venezuelan politician * Desireé Bassett (born 1992), American hard rock guitarist * Desiree Burch (born 1979), American comedian and television host. * Désirée Clary (1777–1860), Queen of Sweden, 1818–1844 * Desireé Cousteau (born 1956), American porn star * Desiree Gould (1945–2021), American actress * Desiree Heslop (born 1961), British singer also known by the stage name Princess * Desiree Horton (born 1971), nicknamed "Chopper Chick", Los Angeles helicopter pilot/TV reporter and United States Forest Service helicopter firefighter * Désirée Malonga (born 1981), Afro-Romanian actress and model * Désirée Nosbusch (born 1965), actress and TV host in Germany * Desirée Rogers (born 1959), White House Social Secretary * Desiree Washington (born 1973), beauty pageant con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body of about 32,000 European civil servants. The Commission is divided into departments known as Directorates-General (DGs) that can be likened to departments or ministries each headed by a Director-General who is responsible to a Commissioner. There is one member per member state, but members are bound by their oath of office to represent the general interest of the EU as a whole rather than their home state. The Commission President (currently Ursula von der Leyen) is proposed by the European Council (the 27 heads of state/governments) and elected by the European Parliament. The Council of the European Union then nominates the other members of the Commission in agreement with the nominated President, and the 27 members as a team are then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waxy Potato Starch
Waxy potato starch is a variety of commercially available starch composed almost entirely of amylopectin molecules, extracted from new potato varieties. Standard starch extracted from traditional potato varieties contains both amylose and amylopectin. Waxy potato starch, when gelatinized, has a clearer film, a stickier paste and retrogradates (thickening of starch film or paste during storage) less compared to regular potato starch. Waxy potato starch derivatives are used in textile sizing and food applications. Two types of potato plant varieties are developed using different methods: one using traditional breeding techniques and another using genetic manipulation (GMO). Amylopectin potato (traditional breeding) Through traditional breeding techniques an amylose-free mutant was obtained without genetic manipulation. Since 2005 the first natural potato variety Eliane is being cultivated and marketed by the starch company AVEBE. Amylopectin potato (genetically modified) Genet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
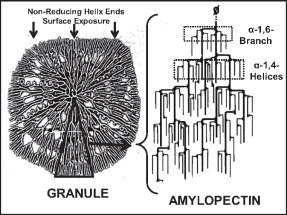
Amylopectin
Amylopectin is a water-insoluble polysaccharide and highly branched polymer of α-glucose units found in plants. It is one of the two components of starch, the other being amylose. Plants store starch within specialized organelles called amyloplasts. To generate energy, the plant hydrolyzes the starch, releasing the glucose subunits. Humans and other animals that eat plant foods also use amylase, an enzyme that assists in breaking down amylopectin, to initiate the hydrolyzation of starch. Starch is made of about 70–80% amylopectin by weight, though it varies depending on the source. For example, it ranges from lower percent content in long-grain rice, amylomaize, and russet potatoes to 100% in glutinous rice, waxy potato starch, and waxy corn. Amylopectin is highly branched, being formed of 2,000 to 200,000 glucose units. Its inner chains are formed of 20–24 glucose subunits. Dissolved amylopectin starch has a lower tendency of retrogradation (a partial recrystallization a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BASF Plant Science
BASF Plant Science is a subsidiary of BASF in which all plant biotechnology activities are consolidated. The company was founded in 1998 and employs approximately 700 people at 6 different locations worldwide. The headquarters of BASF Plant Science is located in Research Triangle Park (North Carolina, USA) and has research sites in the US, Canada, and Europe. The company is mainly developing genetically modified seeds at these locations. Company profile The company genetically modifies crops like maize, soy, cotton, canola, sugarcane, sugar beet, and potatoes "for more efficient agriculture". Together with subsidiaries and partners, as well as in cooperation with universities and research institutions, BASF Plant Science is also developing new procedures and practices in genetic technology. Genetically modified crops by BASF are sold and distributed through biotechnology companies like Monsanto, KWS Saat, Embrapa,Press Release �BASF and Embrapa’s Cultivance soybeans receive a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultivar
A cultivar is a type of cultivated plant that people have selected for desired traits and when propagated retain those traits. Methods used to propagate cultivars include: division, root and stem cuttings, offsets, grafting, tissue culture, or carefully controlled seed production. Most cultivars arise from purposeful human manipulation, but some originate from wild plants that have distinctive characteristics. Cultivar names are chosen according to rules of the International Code of Nomenclature for Cultivated Plants (ICNCP), and not all cultivated plants qualify as cultivars. Horticulturists generally believe the word ''cultivar''''Cultivar'' () has two meanings, as explained in ''Formal definition'': it is a classification category and a taxonomic unit within the category. When referring to a taxon, the word does not apply to an individual plant but to all plants that share the unique characteristics that define the cultivar. was coined as a term meaning "cultivated variety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Thuringiensis
''Bacillus thuringiensis'' (or Bt) is a gram-positive, soil-dwelling bacterium, the most commonly used biological pesticide worldwide. ''B. thuringiensis'' also occurs naturally in the gut of caterpillars of various types of moths and butterflies, as well on leaf surfaces, aquatic environments, animal feces, insect-rich environments, and flour mills and grain-storage facilities. It has also been observed to parasitize other moths such as ''Cadra calidella''—in laboratory experiments working with ''C. calidella'', many of the moths were diseased due to this parasite. During sporulation, many Bt strains produce crystal proteins (proteinaceous inclusions), called delta endotoxins, that have insecticidal action. This has led to their use as insecticides, and more recently to genetically modified crops using Bt genes, such as Bt corn. Many crystal-producing Bt strains, though, do not have insecticidal properties. The subspecies ''israelensis'' is commonly used for control of mosq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bt Toxin
Delta endotoxins (δ-endotoxins) are pore-forming toxins produced by ''Bacillus thuringiensis'' species of bacteria. They are useful for their insecticidal action and are the primary toxin produced by Bt maize/corn. During spore formation the bacteria produce crystals of such proteins (hence the name Cry toxins) that are also known as parasporal bodies, next to the endospores; as a result some members are known as a parasporin. The Cyt (cytolytic) toxin group is a group of delta-endotoxins different from the Cry group. Mechanism of action When an insect ingests these proteins, they are activated by proteolytic cleavage. The N-terminus is cleaved in all of the proteins and a C-terminal extension is cleaved in some members. Once activated, the endotoxin binds to the gut epithelium and causes cell lysis by the formation of cation-selective channels, which leads to death. For many years there was no clarity as to the relationship between aminopeptidase N and Bt toxins. Althou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)