|
Generalized Phrase Structure Grammar
Generalized phrase structure grammar (GPSG) is a framework for describing the syntax and semantics of natural languages. It is a type of constraint-based phrase structure grammar. Constraint based grammars are based around defining certain syntactic processes as ungrammatical for a given language and assuming everything not thus dismissed is grammatical within that language. Phrase structure grammars base their framework on constituency relationships, seeing the words in a sentence as ranked, with some words dominating the others. For example, in the sentence "The dog runs", "runs" is seen as dominating "dog" since it is the main focus of the sentence. This view stands in contrast to dependency grammars, which base their assumed structure on the relationship between a single word in a sentence (the sentence head) and its dependents. Origins GPSG was initially developed in the late 1970s by Gerald Gazdar. Other contributors include Ewan Klein, Ivan Sag, and Geoffrey Pullum. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntax
In linguistics, syntax ( ) is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure (constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). Diverse approaches, such as generative grammar and functional grammar, offer unique perspectives on syntax, reflecting its complexity and centrality to understanding human language. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from the ancient Greek word , meaning an orderly or systematic arrangement, which consists of (''syn-'', "together" or "alike"), and (''táxis'', "arrangement"). In Hellenistic Greek, this also specifically developed a use referring to the grammatical order of words, with a slightly altered spelling: . The English term, which first appeared in 1548, is partly borrowed from Latin () and Greek, though the L ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parser
Parsing, syntax analysis, or syntactic analysis is a process of analyzing a string of symbols, either in natural language, computer languages or data structures, conforming to the rules of a formal grammar by breaking it into parts. The term ''parsing'' comes from Latin ''pars'' (''orationis''), meaning part (of speech). The term has slightly different meanings in different branches of linguistics and computer science. Traditional sentence parsing is often performed as a method of understanding the exact meaning of a sentence or word, sometimes with the aid of devices such as sentence diagrams. It usually emphasizes the importance of grammatical divisions such as subject and predicate. Within computational linguistics the term is used to refer to the formal analysis by a computer of a sentence or other string of words into its constituents, resulting in a parse tree showing their syntactic relation to each other, which may also contain semantic information. Some parsing a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammar Frameworks
In linguistics, grammar is the set of rules for how a natural language is structured, as demonstrated by its speakers or writers. Grammar rules may concern the use of clauses, phrases, and words. The term may also refer to the study of such rules, a subject that includes phonology, morphology, and syntax, together with phonetics, semantics, and pragmatics. There are, broadly speaking, two different ways to study grammar: traditional grammar and theoretical grammar. Fluency in a particular language variety involves a speaker internalizing these rules, many or most of which are acquired by observing other speakers, as opposed to intentional study or instruction. Much of this internalization occurs during early childhood; learning a language later in life usually involves more direct instruction. The term ''grammar'' can also describe the linguistic behaviour of groups of speakers and writers rather than individuals. Differences in scale are important to this meaning: for exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Generative Linguistics
Generative grammar is a research tradition in linguistics that aims to explain the cognition, cognitive basis of language by formulating and testing explicit models of humans' subconscious grammatical knowledge. Generative linguists, or generativists (), tend to share certain working assumptions such as the linguistic competence, competence–linguistic performance, performance distinction and the notion that some domain-specific aspects of grammar are partly innate in humans. These assumptions are rejected in non-generative approaches such as usage-based models of language. Generative linguistics includes work in core areas such as syntax, semantics, phonology, psycholinguistics, and language acquisition, with additional extensions to topics including biolinguistics and music cognition. Generative grammar began in the late 1950s with the work of Noam Chomsky, having roots in earlier approaches such as structural linguistics. The earliest version of Chomsky's model was calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head-driven Phrase Structure Grammar
Head-driven phrase structure grammar (HPSG) is a highly lexicalized, constraint-based grammar developed by Carl Pollard and Ivan Sag. It is a type of phrase structure grammar, as opposed to a dependency grammar, and it is the immediate successor to generalized phrase structure grammar. HPSG draws from other fields such as computer science (type system, data type theory and knowledge representation) and uses Ferdinand de Saussure's notion of the sign (linguistics), sign. It uses a uniform formalism and is organized in a modular way which makes it attractive for natural language processing. An HPSG includes principles and grammar rules and lexicon entries which are normally not considered to belong to a grammar. The formalism is based on lexicalism. This means that the lexicon is more than just a list of entries; it is in itself richly structured. Individual entries are marked with types. Types form a hierarchy. Early versions of the grammar were very lexicalized with few grammatica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformational Grammar
In linguistics, transformational grammar (TG) or transformational-generative grammar (TGG) was the earliest model of grammar proposed within the research tradition of generative grammar. Like current generative theories, it treated grammar as a system of formal rules that generate all and only grammatical sentences of a given language. What was distinctive about transformational grammar was that it posited transformation rules that mapped a sentence's deep structure to its pronounced form. For example, in many variants of transformational grammar, the English active voice sentence "Emma saw Daisy" and its passive counterpart "Daisy was seen by Emma" share a common deep structure generated by phrase structure rules, differing only in that the latter's structure is modified by a passivization transformation rule. Basic mechanisms Transformational grammar was a species of generative grammar and shared many of its goals and postulations, including the notion of linguistics as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phrase Structure Grammar
The term phrase structure grammar was originally introduced by Noam Chomsky as the term for grammar studied previously by Emil Post and Axel Thue ( Post canonical systems). Some authors, however, reserve the term for more restricted grammars in the Chomsky hierarchy: context-sensitive grammars or context-free grammars. In a broader sense, phrase structure grammars are also known as ''constituency grammars''. The defining character of phrase structure grammars is thus their adherence to the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation of dependency grammars. History In 1956, Chomsky wrote, "A phrase-structure grammar is defined by a finite vocabulary (alphabet) Vp, and a finite set Σ of initial strings in Vp, and a finite set F of rules of the form: X → Y, where X and Y are strings in Vp." Constituency relation In linguistics, phrase structure grammars are all those grammars that are based on the constituency relation, as opposed to the dependency relation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexical Functional Grammar
Lexical functional grammar (LFG) is a constraint-based grammar framework in theoretical linguistics. It posits several parallel levels of syntactic structure, including a phrase structure grammar representation of word order and constituency, and a representation of grammatical functions such as subject and object, similar to dependency grammar. The development of the theory was initiated by Joan Bresnan and Ronald Kaplan in the 1970s, in reaction to the theory of transformational grammar which was current in the late 1970s. It mainly focuses on syntax, including its relation with morphology and semantics. There has been little LFG work on phonology (although ideas from optimality theory have recently been popular in LFG research). Some recent work combines LFG with Distributed Morphology in Lexical-Realizational Functional Grammar.Ash Asudeh, Paul B. Melchin & Daniel Siddiqi (2021). ''Constraints all the way down: DM in a representational model of grammar''. In ''WCCFL 39 Proc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Head-driven Phrase Structure Grammar
Head-driven phrase structure grammar (HPSG) is a highly lexicalized, constraint-based grammar developed by Carl Pollard and Ivan Sag. It is a type of phrase structure grammar, as opposed to a dependency grammar, and it is the immediate successor to generalized phrase structure grammar. HPSG draws from other fields such as computer science (type system, data type theory and knowledge representation) and uses Ferdinand de Saussure's notion of the sign (linguistics), sign. It uses a uniform formalism and is organized in a modular way which makes it attractive for natural language processing. An HPSG includes principles and grammar rules and lexicon entries which are normally not considered to belong to a grammar. The formalism is based on lexicalism. This means that the lexicon is more than just a list of entries; it is in itself richly structured. Individual entries are marked with types. Types form a hierarchy. Early versions of the grammar were very lexicalized with few grammatica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross-serial Dependencies
In linguistics, cross-serial dependencies (also called crossing dependencies by some authors.) occur when the lines representing the dependency relations between two series of words cross over each other.. They are of particular interest to linguists who wish to determine the syntactic structure of natural language; languages containing an arbitrary number of them are non- context-free. By this fact, Dutch. and Swiss-German. have been proven to be non-context-free. Example As Swiss-German allows verbs and their arguments to be ordered cross-serially, we have the following example, taken from Shieber: That is, "we help Hans paint the house." Notice that the sequential noun phrases ''em Hans'' (''Hans'') and ''es huus'' (''the house''), and the sequential verbs ''hälfed'' (''help'') and ''aastriiche'' (''paint'') both form two separate series of constituents. Notice also that the dative verb ''hälfed'' and the accusative verb ''aastriiche'' take the dative ''em Hans'' a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hilary Was Fond Of ] And [Leslie Despised
Hilary or Hillary may refer to: * Hilary (name), or Hilarie or Hillary, a given name and surname ** Hillary Clinton, American politician ** Edmund Hillary, one of the first to summit Mount Everest * Hillary Coast, Antarctica * Hilary term, the spring term at the Universities of Oxford and Dublin * ''Hikari no Densetsu'', a 1985 manga series, known in Italian as ''Hilary'' * ''Hillary'' (film), a 2020 American documentary film about Hillary Clinton * HMS ''Hilary'' *'' Hilary: the brave world of Hilary Pole'', 1972 book by Dorothy Clarke Wilson * List of storms named Hilary, the name of several storms * Hillary Montes, a mountain range on Pluto See also * Hillery (other) * Saint Hilary (other) * Saint-Hilaire (other) * Ilar (other), Welsh form of the name Hilary * Eleri (other), Welsh form of the name Hilarus * Hillarys, Western Australia Hillarys is a northern coastal suburb of Perth, the capital city of Western Australia, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
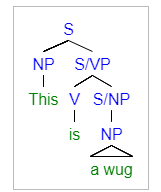
GPSG Syntax Tree Example
Generalized phrase structure grammar (GPSG) is a framework for describing the syntax and semantics of natural languages. It is a type of constraint-based phrase structure grammar. Constraint based grammars are based around defining certain syntactic processes as ungrammatical for a given language and assuming everything not thus dismissed is grammatical within that language. Phrase structure grammars base their framework on constituency relationships, seeing the words in a sentence as ranked, with some words dominating the others. For example, in the sentence "The dog runs", "runs" is seen as dominating "dog" since it is the main focus of the sentence. This view stands in contrast to dependency grammars, which base their assumed structure on the relationship between a single word in a sentence (the sentence head) and its dependents. Origins GPSG was initially developed in the late 1970s by Gerald Gazdar. Other contributors include Ewan Klein, Ivan Sag, and Geoffrey Pullum. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |