|
Gene Pyramiding
Gene pyramiding is the simultaneous selection for and/or introduction of multiple genes during plant breeding. Objectives of gene pyramiding includes 1) enhancing trait performance by combining two or more complementary genes, 2) remedying deficits by introgressing genes from other sources, 3) increasing the durability. For example, pyramiding has been successfully demonstrated in ''Oryza sativa'' for rice blast, producing durable multi-race resistance Resistance may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media Comics * Either of two similarly named but otherwise unrelated comic book series, both published by Wildstorm: ** ''Resistance'' (comics), based on the video game of the same title ** ''T ... simultaneously. Pyramiding and Marker Assisted Selection can be combined as Marker-Assisted Pyramiding. Gene stacking can be achieved a few different ways, and pyramiding is one of those methods. References * {{horticulture-stub Plant breeding Agricultural research Agric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Breeding
Plant breeding is the science of changing the traits of plants in order to produce desired characteristics. It has been used to improve the quality of nutrition in products for humans and animals. The goals of plant breeding are to produce crop varieties that boast unique and superior traits for a variety of applications. The most frequently addressed agricultural traits are those related to biotic and abiotic stress tolerance, grain or biomass yield, end-use quality characteristics such as taste or the concentrations of specific biological molecules (proteins, sugars, lipids, vitamins, fibers) and ease of processing (harvesting, milling, baking, malting, blending, etc.). Plant breeding can be performed through many different techniques ranging from simply selecting plants with desirable characteristics for propagation, to methods that make use of knowledge of genetics and chromosomes, to more complex molecular techniques. Genes in a plant are what determine what type of quali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oryza Sativa
''Oryza sativa'', commonly known as Asian rice or indica rice, is the plant species most commonly referred to in English as ''rice''. It is the type of farmed rice whose cultivars are most common globally, and was first domesticated in the Yangtze River basin in China 13,500 to 8,200 years ago. ''Oryza sativa'' belongs to the genus '' Oryza'' of the grass family Poaceae. With a genome consisting of 430 Mbp across 12 chromosomes, it is renowned for being easy to genetically modify and is a model organism for the botany of cereals. Classification ''Oryza sativa'' contains two major subspecies: the sticky, short-grained ''japonica'' or ''sinica'' variety, and the nonsticky, long-grained ' rice variety. ''Japonica'' was domesticated in the Yangtze Valley 9–6,000 years ago, and its varieties can be cultivated in dry fields (it is cultivated mainly submerged in Japan), in temperate East Asia, upland areas of Southeast Asia, and high elevations in South Asia, while ''indica'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
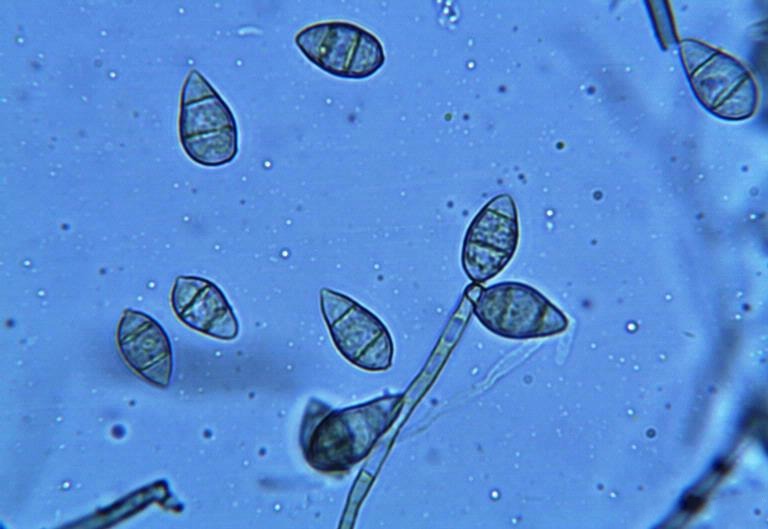
Rice Blast
''Magnaporthe grisea'', also known as rice blast fungus, rice rotten neck, rice seedling blight, blast of rice, oval leaf spot of graminea, pitting disease, ryegrass blast, Johnson spot, neck blast, wheat blast, and Imochi ( Japanese:稲熱) is a plant-pathogenic fungus and model organism that causes a serious disease affecting rice. It is now known that ''M. grisea'' consists of a cryptic species complex containing at least two biological species that have clear genetic differences and do not interbreed. Complex members isolated from '' Digitaria'' have been more narrowly defined as ''M. grisea''. The remaining members of the complex isolated from rice and a variety of other hosts have been renamed ''Magnaporthe oryzae'', within the same ''M. grisea'' complex. Confusion on which of these two names to use for the rice blast pathogen remains, as both are now used by different authors. Members of the ''Magnaporthe grisea'' complex can also infect other agriculturally important cer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plant Disease Resistance
Plant disease resistance protects plants from pathogens in two ways: by pre-formed structures and chemicals, and by infection-induced responses of the immune system. Relative to a susceptible plant, disease resistance is the reduction of pathogen growth on or in the plant (and hence a reduction of disease), while the term disease tolerance describes plants that exhibit little disease damage despite substantial pathogen levels. Disease outcome is determined by the three-way interaction of the pathogen, the plant and the environmental conditions (an interaction known as the disease triangle). Defense-activating compounds can move cell-to-cell and systematically through the plant's vascular system. However, plants do not have circulating immune cells, so most cell types exhibit a broad suite of antimicrobial defenses. Although obvious ''qualitative'' differences in disease resistance can be observed when multiple specimens are compared (allowing classification as “resistant” o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marker-assisted Selection
Marker assisted selection or marker aided selection (MAS) is an indirect selection process where a Trait (biology), trait of interest is selected based on a Biological marker, marker (Morphology (biology), morphological, biochemical or DNA/RNA variation) linked to a trait of interest (e.g. productivity, disease resistance, abiotic stress tolerance, and quality), rather than on the trait itself.Ribaut, J.-M. et al., Genetic basis of physiological traits. In Application of Physiology in Wheat Breeding, CIMMYT, Mexico, 2001.Ribaut, J.-M. and Hoisington, D. A., Marker assisted selection: new tools and strategies. Trends Plant Sci., 1998, 3, 236–239.Rosyara, U.R. 2006. REQUIREMENT OF ROBUST MOLECULAR MARKER TECHNOLOGY FOR PLANT BREEDING APPLICATIONS. Journal of Plant Breed. Gr. 1: 67 – 72click to download/ref> This process has been extensively researched and proposed for Plant breeding, plant and Selective breeding, animal breeding. For example, using MAS to select individuals with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Stacking
Gene stacking is the combination of more than one gene for plant disease resistance, or crop productivity, or other horticultural traits. In plant breeding traditionally that means breeding those genes in, but increasingly also can mean genetic engineering. This can be achieved a few different ways, and gene pyramiding is one of those methods. Stacking of transgenes is yet more difficult than stacking natural genes, but especially in the case of pest resistance genes which require a significant financial investment to insert, is advantageous over other methods. Pathosystems with rapid evolution in the pathogen have long been considered good targets of stacking, to broaden and prolong resistance. Assaying for successful insertion of R gene Resistance genes (R-Genes) are genes in plant genomes that convey plant disease resistance against pathogens by producing R proteins. The main class of R-genes consist of a nucleotide binding domain (NB) and a leucine rich repeat (LRR) d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetics (journal)
''Genetics'' is a monthly scientific journal publishing investigations bearing on heredity, genetics, biochemistry and molecular biology Molecular biology is the branch of biology that seeks to understand the molecular basis of biological activity in and between cells, including biomolecular synthesis, modification, mechanisms, and interactions. The study of chemical and phys .... Genetics is published by the Genetics Society of America. It has a delayed open access policy, and makes articles available online without a subscription after 12 months have elapsed since first publication. Since 2010, it is published online-only.http://www.councilscienceeditors.org/wp-content/uploads/v36n1p14-15_17.pdf George Harrison Shull was the founding editor of ''Genetics'' in 1916. Editors-in-Chief References External linksOfficial website Genetics journals Delayed open access journals English-language journals Publications established in 1916 Online-only journals {{ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586, it is the second oldest university press after Cambridge University Press. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics known as the Delegates of the Press, who are appointed by the vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho. For the last 500 years, OUP has primarily focused on the publication of pedagogical texts a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Reports
''Scientific Reports'' is a peer-reviewed open-access scientific mega journal published by Nature Portfolio, covering all areas of the natural sciences. The journal was established in 2011. The journal states that their aim is to assess solely the scientific validity of a submitted paper, rather than its perceived importance, significance, or impact. In September 2016, the journal became the largest in the world by number of articles, overtaking '' PLOS ONE''. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in the Chemical Abstracts Service, the Science Citation Index Expanded, and selectively in Index Medicus/MEDLINE/PubMed. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor 4.996. Reviewing policy The ''Guide to Referees'' states that to be published, "a paper must be scientifically valid and technically sound in methodology and analysis", and reviewers have to ensure manuscripts "are not assessed based on their perceived impo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Springer Science+Business Media
Springer Science+Business Media, commonly known as Springer, is a German multinational publishing company of books, e-books and peer-reviewed journals in science, humanities, technical and medical (STM) publishing. Originally founded in 1842 in Berlin, it expanded internationally in the 1960s, and through mergers in the 1990s and a sale to venture capitalists it fused with Wolters Kluwer and eventually became part of Springer Nature in 2015. Springer has major offices in Berlin, Heidelberg, Dordrecht, and New York City. History Julius Springer founded Springer-Verlag in Berlin in 1842 and his son Ferdinand Springer grew it from a small firm of 4 employees into Germany's then second largest academic publisher with 65 staff in 1872.Chronology ". Springer Science+Business Media. In 1964, Springer expanded its business internationally, o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Biosafety Research
A biophysical environment is a biotic and abiotic surrounding of an organism or population, and consequently includes the factors that have an influence in their survival, development, and evolution. A biophysical environment can vary in scale from microscopic to global in extent. It can also be subdivided according to its attributes. Examples include the marine environment, the atmospheric environment and the terrestrial environment. The number of biophysical environments is countless, given that each living organism has its own environment. The term ''environment'' can refer to a singular global environment in relation to humanity, or a local biophysical environment, e.g. the UK's Environment Agency. Life-environment interaction All life that has survived must have adapted to the conditions of its environment. Temperature, light, humidity, soil nutrients, etc., all influence the species within an environment. However, life in turn modifies, in various forms, its conditions. So ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EDP Sciences
EDP Sciences (Édition Diffusion Presse Sciences) is an STM publisher that specialises scientific information for specialist and more general audiences (general public, decision-makers, teachers, etc.). EDP produces and publishes international journals, books, conferences, and websites with predominantly scientific and technical content. The company is a joint venture of four French learned societies in science, mathematics, and medicine. History The company was founded in 1920 under the name La Société du ''Journal de Physique'' et ''Le Radium''. It thus took over the publication of the ''Journal de Physique'' (established in 1872) on the occasion of its merger with the journal ''Le Radium'' (established in 1904). Among the founders were the Société Française de Physique and several notable scientists and industrialists: Antoine Béclère, Louis de Broglie, Marie Curie, Paul Langevin, Louis Lumière, Jean Perrin, and Léon Brillouin, as well as patrons such as Albert I, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)