|
Gang War In Haiti
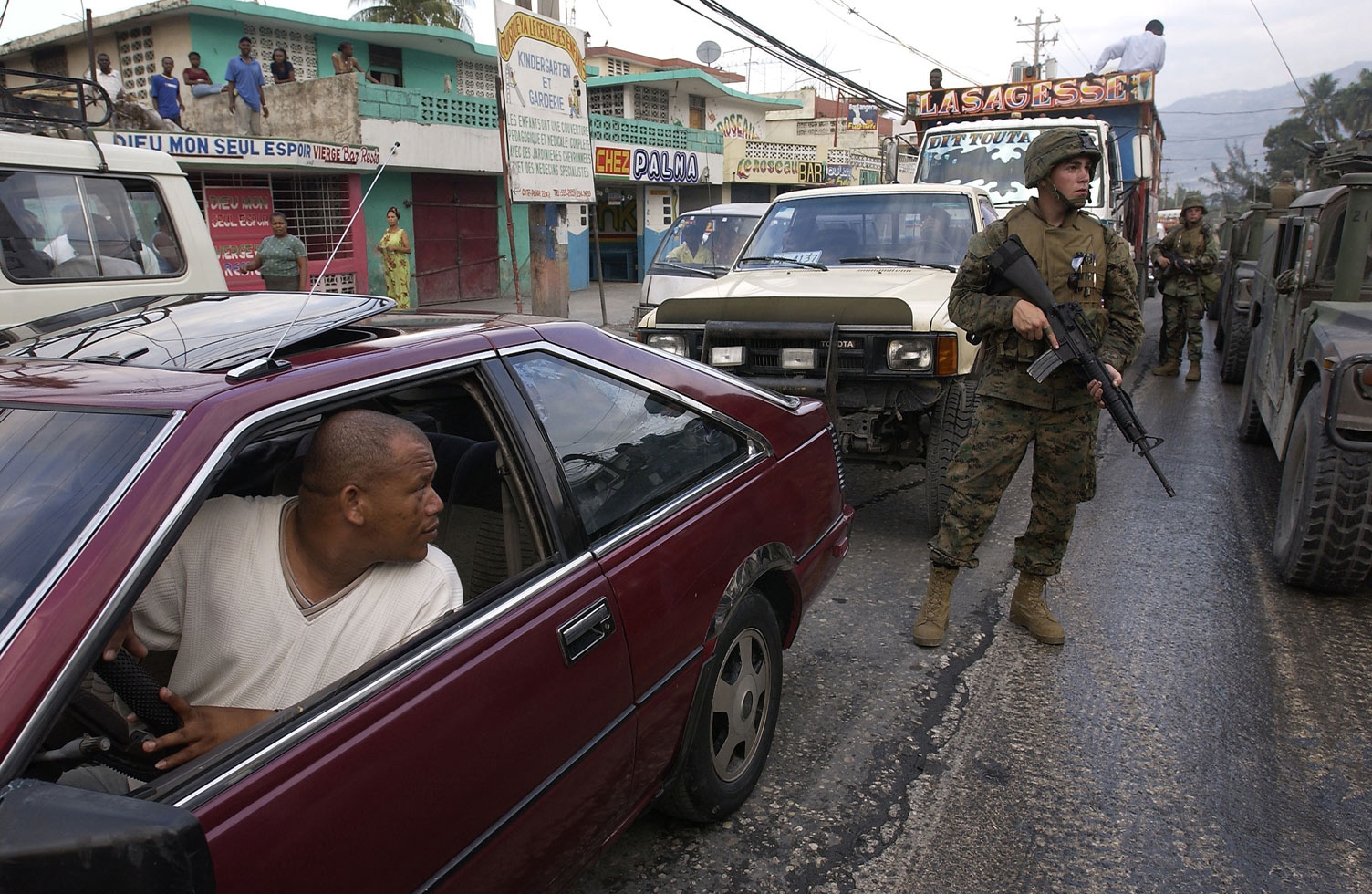
Since 2020, Haiti's capital, Port-au-Prince, is the site of an ongoing gang war between two major criminal groups and their allies: the "Revolutionary Forces of the G9 Family and Allies" (''FRG9'' or ''G9'') and the G-Pep. The Government of Haiti and security forces have struggled to maintain control in Port-au-Prince amid this conflict, with gangs reportedly controlling up to 90% of the city by 2023. In response to the escalating gang fighting, an armed vigilante movement, known as ''bwa kale'' (from French ''bois calé''), also emerged to battle the gangs. On 2 October 2023, United Nations Security Council Resolution 2699 was approved and authorized a Kenya-led " multinational security support mission" to Haiti. Background From the 1950s, non-state armed groups have been firmly established in Haiti. This process began with the establishment of the '' Tonton Macoute'' paramilitaries by Haitian dictator François Duvalier, used to violently suppress dissidents. After the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crime In Haiti
Crime in Haiti is investigated by the Haitian police. Crime by type Murders in Haiti Reliable crime statistics for Haiti is difficult to come by. A comparative analysis of figures from various police/security entities operating throughout Haiti indicates that incidents of crimes tend to be inaccurately or under-reported. Thus, for example, the United Nations office on Drugs and Crime UNODC documented 1,033 murders, for a murder rate of 10.2 per 100,000 people, in 2012, and as few as 486 (5.1 per 100,000 people) in 2007.''Global Study on Homicide''. , 2013. In the 22 months after the ouster of |
Jean-Claude Duvalier
Jean-Claude Duvalier (; 3 July 19514 October 2014), nicknamed "Baby Doc" ( ht, Bebe Dòk), was a Haitian politician who was the President of Haiti from 1971 until he was overthrown by a popular uprising in February 1986. He succeeded his father François "Papa Doc" Duvalier as the ruler of Haiti after his death in 1971. After assuming power, he introduced cosmetic changes to his father's regime and delegated much authority to his advisors. Thousands of Haitians were killed or tortured, and hundreds of thousands fled the country during his presidency. He maintained a notoriously lavish lifestyle (including a state-sponsored US$2million wedding in 1980) while poverty among his people remained the most widespread of any country in the Western Hemisphere. Relations with the United States improved after Duvalier's ascension to the presidency, and later deteriorated under the Carter administration, only to normalize under Ronald Reagan due to the strong anti-communist stance of the Duv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pétion-Ville
Pétion-Ville ( ht, Petyonvil) is a commune and a suburb of Port-au-Prince, Haiti, in the hills east and separate from the city itself on the northern hills of the Massif de la Selle. Founded in 1831 by president Jean-Pierre Boyer, it was named after Alexandre Sabès Pétion (1770–1818), the Haitian general and president later recognized as one of the country's four founding fathers. The district is primarily a residential and touristic area. It had a population of 283,052 at the 2003 Census, which was officially estimated to have reached 376,834 in 2015. Many diplomats, foreign businessmen, and wealthy citizens engage in business and reside in Pétion-Ville. Despite the distance from the capital and the general affluence of the district, the lack of administrative enforcement has led to the formation of shantytowns on the outer edges of the district, as poor locals migrate upward and have settled there in search of job opportunities. On 28 or 29 August 2020, Haitian Lawyer Mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delmas, Haiti
Delmas () is a commune in the Port-au-Prince Arrondissement, in the Ouest department of Haiti. Delmas itself is an urban continuation of the capital city. Delmas is also the location of much of the area's commercial and industrial enterprise. History Delmas was affected by the 12 January 2010 earthquake. On 1 February 2010, electricity was restored for streetlighting in Delmas. Lower Delmas is believed to be the stronghold of Jimmy "Barbecue" Chérizier, whose G9 Family and Allies gang controls most of Lower Delmas. Education *Centre Pédagogique des Frères Unis Centre Pédagogique des Frères Unis is a Christian school (kindergarten, primary and secondary) in Haiti. School colors are white and khaki. History The school was founded in 1988 by Fortune Cherfrère and Eugène Marcel, in Delmas 32 Port-au- ... References Port-au-Prince Populated places in Ouest (department) Communes of Haiti {{Haiti-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economy Of Haiti
Haiti is a free market economy with low labor costs. A republic, it was a French colony before gaining independence in an uprising by its enslaved people. It faced embargoes and isolation after its independence as well as political crises punctuated by foreign interventions and devastating natural disasters. Haiti's estimated population in 2018 was 11,439,646. ''The Economist'' reported in 2010: "Long known as the poorest country in the Western hemisphere, Haiti has stumbled from one crisis to another since the Duvalier ( François Duvalier) years." Haiti has an agricultural economy. Over half of the world's vetiver oil (an essential oil used in high-end perfumes) comes from Haiti. Bananas, cocoa, and mangoes are important export crops. Haiti has also moved to expand to higher-end manufacturing, producing Android-based tablets and current sensors and transformers. Its major trading partner is the United States (US), which provides the country with preferential trade access to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elections In Haiti
Elections in Haiti gives information on election and election results in Haiti. The Constitution of Haiti provides for the election of the President, Parliament, and members of local governing bodies. The current acting president is Ariel Henry, who succeeded acting president Claude Joseph, who in turn assumed office following the assassination of Jovenel Moïse in 2021. 2010-2011 elections The 2010 presidential election took place on 28 November 2010, with a run-off election taking place on 20 March 2011. No candidate received a majority of the vote cast in the first-round election. A second round was scheduled for 20 March 2011 with the two highest vote-getters, Mirlande Manigat and Jude Célestin. Protests claiming fraudulent voting resulted in the electoral commission removing Célestin from the race. This promoted Martelly from his original third-place finish in the first-round, to face Manigat in the run-off. 2010 and following In January 2015, after a series of disp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2018 Port-au-Prince Massacre
On 13 November 2018, a massacre began within the La Saline slums of Port-au-Prince, Haiti. According to reports, 15 to 25 civilians were killed over a 24-hour period. It is alleged that the killings were either due to local gang wars or the actions of Haitian officials attempting to quell anti-corruption protests. Background In October 2017, U.N. peacekeepers ended their mission in Haiti after 13 years. Since the departure of the U.N., the number of gang-controlled areas in the city has apparently grown. The massacre occurred in the middle of various protests within Haiti: Jovenel Moïse was elected president in November 2016, but protestors saw him corrupt. Incident Witness reports state that a police truck carrying uniformed men arrived in Port-au-Prince's La Saline slums at around 3 p.m. on 13 November 2018. The men then opened fire upon civilians, while local gang members killed others with gunfire and machetes. According to witnesses, a human-rights group, at least 21 me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2004 Haitian Coup D'état
A coup d'état in Haiti on 29 February 2004, following several weeks of conflict, resulted in the removal of President Jean-Bertrand Aristide from office. On 5 February 2004, a rebel group, called the National Revolutionary Front for the Liberation and Reconstruction of Haiti, took control of Haiti's fourth-largest city, Gonaïves. By 22 February, the rebels had captured Haiti's second-largest city, Cap-Haïtien and were besieging the capital, Port-au-Prince by the end of February. On the morning of 29 February, Aristide resigned under controversial circumstances and was flown from Haiti by U.S. military/security personnel. He went into exile, being flown directly to the Central African Republic, before eventually settling in South Africa. Aristide afterwards claimed that he had been "kidnapped" by U.S. forces, accusing them of having orchestrated a coup d'état against him, a claim denied by U.S. officials. In 2022, a dozen Haitian and French officials told ''The New York T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MINUSTAH
) , leader_title = Head , leader_name = Sandra Honoré (Special Representative of the Secretary-General) , status = Replaced by MINUJUSTH , formation = 1 June 2004 , websiteUN Peacekeeping: MINUSTAH , parent_organization = UN , , subsidiaries = , footnotes = The United Nations Stabilisation Mission in Haiti (french: Mission des Nations Unies pour la stabilisation en Haïti), also known as MINUSTAH, an |
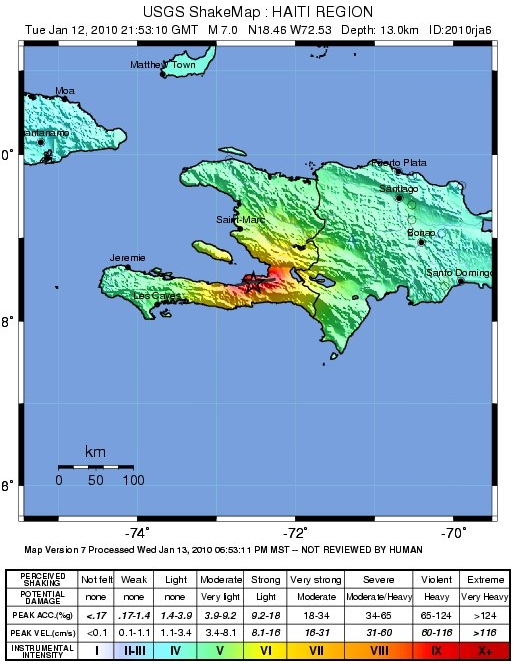
2010 Haiti Earthquake
A disaster, catastrophic Moment magnitude scale, magnitude 7.0 Mw earthquake struck Haiti at 16:53 local time (21:53 UTC) on Tuesday, 12 January 2010. The epicenter was near the town of Léogâne, Ouest (department), Ouest department, approximately west of Port-au-Prince, Haiti's capital. By 24 January, at least 52 aftershocks measuring 4.5 or greater had been recorded. An estimated three million people were affected by the quake. Death toll estimates range from 100,000 to about 160,000 to Haitian government figures from 220,000 to 316,000, although these latter figures are a matter of some dispute. The government of Haiti estimated that 250,000 residential area, residences and 30,000 commercial buildings had collapsed or were severely damaged. The nation's history of External debt of Haiti, national debt, prejudicial trade policies by other countries, and foreign intervention into national affairs contributed to the existing poverty and poor housing conditions that in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vox (website)
''Vox'' () is an American news and opinion website owned by Vox Media. The website was founded in April 2014 by Ezra Klein, Matt Yglesias, and Melissa Bell, and is noted for its concept of explanatory journalism. Vox's media presence also includes a YouTube channel, several podcasts, and a show presented on Netflix. ''Vox'' has been described as left-of-center and progressive. History Prior to founding ''Vox'', Ezra Klein worked for ''The Washington Post'' as the head of Wonkblog, a public policy blog. When Klein attempted to launch a new site using funding from the newspaper's editors, his proposal was turned down and Klein subsequently left ''The Washington Post'' for a position with Vox Media, another communications company, in January 2014. ''The New York Times'' David Carr associated Klein's exit for ''Vox'' with other "big-name journalists" leaving newspapers for digital start-ups, such as Walter Mossberg and Kara Swisher (of '' Recode'', which was later acquired ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel Lewis Foote
Daniel Lewis Foote is an American diplomat and career member of the Senior Foreign Service who was the United States Special Envoy for Haiti from July to September 2021. He formerly served as the United States Ambassador to Zambia. Early life and education A native of Syracuse, New York, Foote graduated from Williamsville East High School in 1981. He attended Columbia University, where he was a member of the school's football and track and field teams and graduated with a Bachelor of Arts degree in economics. Career Foote began his career as a natural gas trader and broker. In 1992, he became a Peace Corps volunteer in Sopachuy, Bolivia. He later taught high school Spanish and coached football and track in Northern California. In 1998, Foote joined the United States Department of State. He held positions at the State Department Operations Center, in the Bureau of European and Eurasian Affairs, at the U.S. Embassy in London, and in the U.S. consulate in Guadalajara, Mexico. He w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |