|
Galileo's Leaning Tower Of Pisa Experiment
Between 1589 and 1592, the Italian scientist Galileo Galilei (then professor of mathematics at the University of Pisa) is said to have dropped two spheres of different masses from the Leaning Tower of Pisa to demonstrate that their time of descent was independent of their mass, according to a biography by Galileo's pupil Vincenzo Viviani, composed in 1654 and published in 1717. The basic premise had already been demonstrated by Italian experimenters a few decades earlier. According to the story, Galileo discovered through this experiment that the objects fell with the same acceleration, proving his prediction true, while at the same time disproving Aristotle's theory of gravity (which states that objects fall at speed proportional to their mass). Most historians consider it to have been a thought experiment rather than a physical test. Background The 6th-century Byzantine Greek philosopher and Aristotelian commentator John Philoponus argued that the Aristotelian assertion that o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pisa Experiment
Pisa ( , or ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, central Italy, straddling the Arno just before it empties into the Ligurian Sea. It is the capital city of the Province of Pisa. Although Pisa is known worldwide for its Leaning Tower of Pisa, leaning tower, the city contains more than twenty other historic churches, several medieval palaces, and bridges across the Arno. Much of the city's architecture was financed from its history as one of the Italian maritime republics. The city is also home to the University of Pisa, which has a history going back to the 12th century, the Scuola Normale Superiore di Pisa, founded by Napoleon in 1810, and its offshoot, the Sant'Anna School of Advanced Studies.Scuola Superiore Sant'Anna di Pisa Information statistics History |
Apollo 15 Feather And Hammer Drop
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label=genitive, , ; , is one of the Olympian deities in classical Greek and Roman religion and Greek and Roman mythology. The national divinity of the Greeks, Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, music and dance, truth and prophecy, healing and diseases, the Sun and light, poetry, and more. One of the most important and complex of the Greek gods, he is the son of Zeus and Leto, and the twin brother of Artemis, goddess of the hunt. Seen as the most beautiful god and the ideal of the ''kouros'' (ephebe, or a beardless, athletic youth), Apollo is considered to be the most Greek of all the gods. Apollo is known in Greek-influenced Etruscan mythology as ''Apulu''. As the patron deity of Delphi (''Apollo Pythios''), Apollo is an oracu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Motu Antiquiora
''De Motu Antiquiora'' ("The Older Writings on Motion"), or simply ''De Motu'', is Galileo Galilei's early written work on motion. It was written largely between 1589 and 1592, but was not published until 1687, after his death. It was never published during his lifetime due to a few uncertainties in his mathematics and certain parts of his understanding. Because it was never published during his life, he never composed a final draft. In the last parts of his work, the writing style changes from an essay to a dialogue between two people who strongly uphold his views. By writing this book in the 16th century, Galileo was on the forefront of investigating the motion of falling bodies. In ''De Motu'', he openly rejects Aristotle's views on the physics of motion and his astronomical views. Galileo opposes him with not only his opinion but with facts he has obtained based on experiment and on observation of celestial bodies.Machamer, Peter"Galileo Galilei" The Stanford Encyclopedia of P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two New Sciences
The ''Discourses and Mathematical Demonstrations Relating to Two New Sciences'' ( it, Discorsi e dimostrazioni matematiche intorno a due nuove scienze ) published in 1638 was Galileo Galilei's final book and a scientific testament covering much of his work in physics over the preceding thirty years. It was written partly in Italian and partly in Latin. After his ''Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems'', the Roman Inquisition had banned the publication of any of Galileo's works, including any he might write in the future. After the failure of his initial attempts to publish ''Two New Sciences'' in France, Germany, and Poland, it was published by Lodewijk Elzevir who was working in Leiden, South Holland, where the writ of the Inquisition was of less consequence (see House of Elzevir). Fra Fulgenzio Micanzio, the official theologian of the Republic of Venice, had initially offered to help Galileo publish in Venice the new work, but he pointed out that publishing the ''T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stillman Drake
Stillman Drake (December 24, 1910 – October 6, 1993) was a Canadian historian of science best known for his work on Galileo Galilei (1569–1642). Drake published over 131 books, articles, and book chapters on Galileo. Including his translations, Drake wrote 16 books on Galileo and contributed to 15 others. Career Drake earned a bachelor’s degree in philosophy and was at UC Berkeley in the early 1930s for graduate mathematics but went to work in the financial sector. In a prelude to scholarly life, Drake was for a time an administrator at the Government Development Bank in San Juan, Puerto Rico. Drake received his first academic appointment in 1967 at the age of 57 as full professor at the University of Toronto after a career as a financial administrator in the World Bank system. Although he had been recruited in the past by Harvard, he demurred in finance until he was attracted to Toronto by the offer made only to stars. During that time he had begun his studies of the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambridge University Press
Cambridge University Press is the university press of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII of England, King Henry VIII in 1534, it is the oldest university press A university press is an academic publishing house specializing in monographs and scholarly journals. Most are nonprofit organizations and an integral component of a large research university. They publish work that has been reviewed by schola ... in the world. It is also the King's Printer. Cambridge University Press is a department of the University of Cambridge and is both an academic and educational publisher. It became part of Cambridge University Press & Assessment, following a merger with Cambridge Assessment in 2021. With a global sales presence, publishing hubs, and offices in more than 40 Country, countries, it publishes over 50,000 titles by authors from over 100 countries. Its publishing includes more than 380 academic journals, monographs, reference works, school and uni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Law Of Falling Bodies
Lection 0 A set of equations describing the trajectories of objects subject to a constant gravitational force under normal Earth-bound conditions. Assuming constant acceleration ''g'' due to Earth’s gravity, Newton's law of universal gravitation simplifies to ''F'' = ''mg'', where ''F'' is the force exerted on a mass ''m'' by the Earth’s gravitational field of strength ''g''. Assuming constant ''g'' is reasonable for objects falling to Earth over the relatively short vertical distances of our everyday experience, but is not valid for greater distances involved in calculating more distant effects, such as spacecraft trajectories. History Galileo was the first to demonstrate and then formulate these equations. He used a ramp to study rolling balls, the ramp slowing the acceleration enough to measure the time taken for the ball to roll a known distance. He measured elapsed time with a water clock, using an "extremely accurate balance" to measure the amount of water.See the work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statics
Statics is the branch of classical mechanics that is concerned with the analysis of force and torque (also called moment) acting on physical systems that do not experience an acceleration (''a''=0), but rather, are in static equilibrium with their environment. The application of Newton's second law to a system gives: : \textbf F = m \textbf a \, . Where bold font indicates a vector that has magnitude and direction. \textbf F is the total of the forces acting on the system, m is the mass of the system and \textbf a is the acceleration of the system. The summation of forces will give the direction and the magnitude of the acceleration and will be inversely proportional to the mass. The assumption of static equilibrium of \textbf a = 0 leads to: : \textbf F = 0 \, . The summation of forces, one of which might be unknown, allows that unknown to be found. So when in static equilibrium, the acceleration of the system is zero and the system is either at rest, or its center of mas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
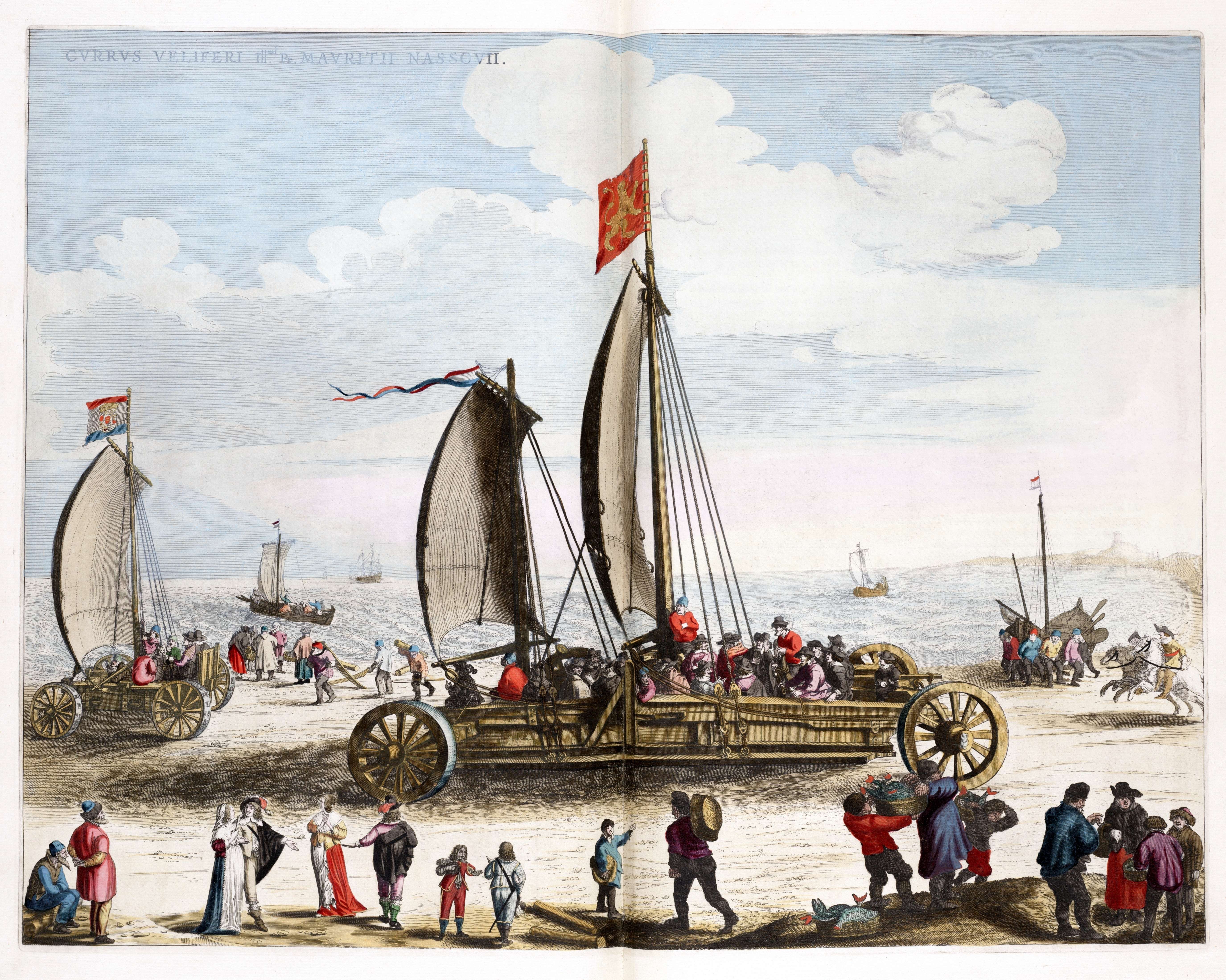
Hugo De Groot
Hugo Grotius (; 10 April 1583 – 28 August 1645), also known as Huig de Groot () and Hugo de Groot (), was a Dutch humanist, diplomat, lawyer, theologian, jurist, poet and playwright. A teenage intellectual prodigy, he was born in Delft and studied at Leiden University. He was imprisoned in Loevestein Castle for his involvement in the intra-Calvinist disputes of the Dutch Republic, but escaped hidden in a chest of books that was transported to Gorinchem. Grotius wrote most of his major works in exile in France. Hugo Grotius was a major figure in the fields of philosophy, political theory and law during the 16th and 17th centuries. Along with the earlier works of Francisco de Vitoria and Alberico Gentili, he laid the foundations for international law, based on natural law in its Protestant side. Two of his books have had a lasting impact in the field of international law: ''De jure belli ac pacis'' 'On the Law of War and Peace''dedicated to Louis XIII of France and the '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Stevin
Simon Stevin (; 1548–1620), sometimes called Stevinus, was a Flemish mathematician, scientist and music theorist. He made various contributions in many areas of science and engineering, both theoretical and practical. He also translated various mathematical terms into Dutch, making it one of the few European languages in which the word for mathematics, '' wiskunde'' ('' wis'' and '' kunde'', i.e., "the knowledge of what is certain"), was not a loanword from Greek but a calque via Latin. He also replaced the word '' chemie'', the Dutch for chemistry, by '' scheikunde'' ("the art of separating"), made in analogy with ''wikt:en:wiskunde#Dutch, wiskunde''. Biography Very little is known with certainty about Simon Stevin's life, and what we know is mostly inferred from other recorded facts.E. J. Dijksterhuis (1970) ''Simon Stevin: Science in the Netherlands around 1600'', The Hague: Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, Dutch original 1943, 's-Gravenhage The exact birth date and the date ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |