|
GAK (gene)
Cyclin G-associated kinase (GAK) is a serine/threonine kinase that in humans is encoded by the ''GAK'' gene. Function In all eukaryotes, the cell cycle is governed by cyclin-dependent protein kinases (CDKs), whose activities are regulated by cyclins and CDK inhibitors in a diverse array of mechanisms that involve the control of phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of Ser, Thr or Tyr residues. Cyclins are molecules that possess a consensus domain called the 'cyclin box.' In mammalian cells, 9 cyclin species have been identified, and they are referred to as cyclins A through I. Cyclin G is a direct transcriptional target of the p53 tumor suppressor gene product and thus functions downstream of p53. GAK is an association partner of cyclin G and CDK5. Cyclin G-associated kinase received its name because it immunoprecipitated with cyclin G though it now appears to not be associated with it. Cyclin G-associated kinase is homologous in function to the protein auxilin which when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine/threonine Kinase
A serine/threonine protein kinase () is a kinase enzyme, in particular a protein kinase, that phosphorylates the OH group of the amino-acid residues serine or threonine, which have similar side chains. At least 350 of the 500+ human protein kinases are serine/threonine kinases (STK). In enzymology, the term ''serine/threonine protein kinase'' describes a class of enzymes in the family of transferases, that transfer phosphates to the oxygen atom of a serine or threonine side chain in proteins. This process is called phosphorylation. Protein phosphorylation in particular plays a significant role in a wide range of cellular processes and is a very important posttranslational modification. The chemical reaction performed by these enzymes can be written as :ATP + a protein \rightleftharpoons ADP + a phosphoprotein Thus, the two substrates of this enzyme are ATP and a protein, whereas its two products are ADP and phosphoprotein. The systematic name of this enzyme class is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal Adhesion
In cell biology, focal adhesions (also cell–matrix adhesions or FAs) are large macromolecular assemblies through which mechanical force and regulatory signals are transmitted between the extracellular matrix (ECM) and an interacting cell. More precisely, focal adhesions are the sub-cellular structures that mediate the regulatory effects (i.e., signaling events) of a cell in response to ECM adhesion. Focal adhesions serve as the mechanical linkages to the ECM, and as a biochemical signaling hub to concentrate and direct numerous signaling proteins at sites of integrin binding and clustering. Structure and function Focal adhesions are integrin-containing, multi-protein structures that form mechanical links between intracellular actin bundles and the extracellular substrate in many cell types. Focal adhesions are large, dynamic protein complexes through which the cytoskeleton of a cell connects to the ECM. They are limited to clearly defined ranges of the cell, at which the pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNAJC6
Putative tyrosine-protein phosphatase auxilin is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''DNAJC6'' gene. Function DNAJC6 belongs to the evolutionarily conserved DNAJ/HSP40 family of proteins, which regulate molecular chaperone activity by stimulating ATPase activity. DNAJ proteins may have up to 3 distinct domains: a conserved 70-amino acid J domain, usually at the N terminus, a glycine/phenylalanine (G/F)-rich region, and a cysteine-rich domain containing 4 motifs resembling a zinc-finger domain (Ohtsuka and Hata, 2000). Structure The protein tyrosine phosphatase domain and C2 domain pair of auxilin, located near the N-terminus of the polypeptide, constitute a superdomain, a tandem arrangement of two or more nominally unrelated domains that form a single heritable unit. The phosphatase domain belongs to the auxilin subfamily Putative tyrosine-protein phosphatase auxilin is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''DNAJC6'' gene. Function DNAJC6 belongs to the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocytosis
Endocytosis is a cellular process in which substances are brought into the cell. The material to be internalized is surrounded by an area of cell membrane, which then buds off inside the cell to form a vesicle containing the ingested material. Endocytosis includes pinocytosis (cell drinking) and phagocytosis (cell eating). It is a form of active transport. History The term was proposed by De Duve in 1963. Phagocytosis was discovered by Élie Metchnikoff in 1882. Pathways Endocytosis pathways can be subdivided into four categories: namely, receptor-mediated endocytosis (also known as clathrin-mediated endocytosis), caveolae, pinocytosis, and phagocytosis Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is .... *Clathrin-mediated endocytosis is mediated by the production of smal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PTEN (gene)
Phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) is a phosphatase in humans and is encoded by the ''PTEN'' gene. Mutations of this gene are a step in the development of many cancers, specifically glioblastoma, lung cancer, breast cancer, and prostate cancer. Genes corresponding to PTEN (orthologs) have been identified in most mammals for which complete genome data are available. ''PTEN'' acts as a tumor suppressor gene through the action of its phosphatase protein product. This phosphatase is involved in the regulation of the cell cycle, preventing cells from growing and dividing too rapidly. It is a target of many anticancer drugs. The protein encoded by this gene is a phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate 3-phosphatase. It contains a tensin-like domain as well as a catalytic domain similar to that of the dual specificity protein tyrosine phosphatases. Unlike most of the protein tyrosine phosphatases, this protein preferentially dephosphorylates phosphoinositide substrates. It nega ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N-terminus
The N-terminus (also known as the amino-terminus, NH2-terminus, N-terminal end or amine-terminus) is the start of a protein or polypeptide, referring to the free amine group (-NH2) located at the end of a polypeptide. Within a peptide, the amine group is bonded to the carboxylic group of another amino acid, making it a chain. That leaves a free carboxylic group at one end of the peptide, called the C-terminus, and a free amine group on the other end called the N-terminus. By convention, peptide sequences are written N-terminus to C-terminus, left to right (in LTR writing systems). This correlates the translation direction to the text direction, because when a protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from the N-terminus to the C-terminus, as amino acids are added to the carboxyl end of the protein. Chemistry Each amino acid has an amine group and a carboxylic group. Amino acids link to one another by peptide bonds which form through a dehydration reaction that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clathrin
Clathrin is a protein that plays a major role in the formation of coated vesicles. Clathrin was first isolated and named by Barbara Pearse in 1976. It forms a triskelion shape composed of three clathrin heavy chains and three light chains. When the triskelia interact they form a polyhedral lattice that surrounds the vesicle, hence the protein's name, which is derived from the Latin ''clathrum'' meaning lattice. Coat-proteins, like clathrin, are used to build small vesicles in order to transport molecules within cells. The endocytosis and exocytosis of vesicles allows cells to communicate, to transfer nutrients, to import signaling receptors, to mediate an immune response after sampling the extracellular world, and to clean up the cell debris left by tissue inflammation. The endocytic pathway can be hijacked by viruses and other pathogens in order to gain entry to the cell during infection. Structure The clathrin triskelion is composed of three clathrin heavy chains inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-terminus
The C-terminus (also known as the carboxyl-terminus, carboxy-terminus, C-terminal tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH). When the protein is translated from messenger RNA, it is created from N-terminus to C-terminus. The convention for writing peptide sequences is to put the C-terminal end on the right and write the sequence from N- to C-terminus. Chemistry Each amino acid has a carboxyl group and an amine group. Amino acids link to one another to form a chain by a dehydration reaction which joins the amine group of one amino acid to the carboxyl group of the next. Thus polypeptide chains have an end with an unbound carboxyl group, the C-terminus, and an end with an unbound amine group, the N-terminus. Proteins are naturally synthesized starting from the N-terminus and ending at the C-terminus. Function C-terminal retention signals While the N-terminus of a protein often c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HSPA8
Heat shock 70 kDa protein 8 also known as heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein or Hsc70 or Hsp73 is a heat shock protein that in humans is encoded by the ''HSPA8'' gene on chromosome 11. As a member of the heat shock protein 70 family and a chaperone protein, it facilitates the proper folding of newly translated and misfolded proteins, as well as stabilize or degrade mutant proteins. Its functions contribute to biological processes including signal transduction, apoptosis, autophagy, protein homeostasis, and cell growth and differentiation. It has been associated with an extensive number of cancers, neurodegenerative diseases, cell senescence, and aging. Structure This gene encodes a 70kDa heat shock protein which is a member of the heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) family. As a Hsp70 protein, it has a C-terminal protein substrate-binding domain and an N-terminal ATP-binding domain. The substrate-binding domain consists of two subdomains, a two-layered β-sandwich subdomain (SBDβ) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a basic unit of heredity and the molecular gene is a sequence of nucleotides in DNA that is transcribed to produce a functional RNA. There are two types of molecular genes: protein-coding genes and noncoding genes. During gene expression, the DNA is first copied into RNA. The RNA can be directly functional or be the intermediate template for a protein that performs a function. The transmission of genes to an organism's offspring is the basis of the inheritance of phenotypic traits. These genes make up different DNA sequences called genotypes. Genotypes along with environmental and developmental factors determine what the phenotypes will be. Most biological traits are under the influence of polygenes (many different genes) as well as gen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
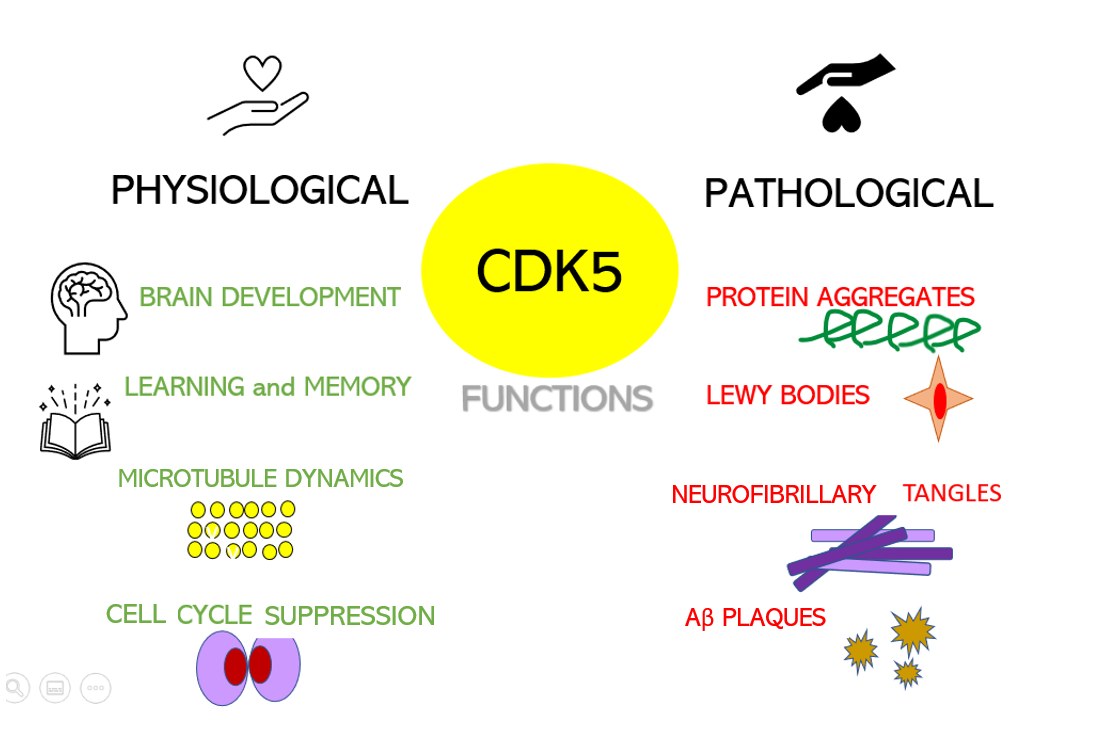
Cyclin-dependent Kinase 5
Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 is a protein, and more specifically an enzyme, that is encoded by the Cdk5 gene. It was discovered 15 years ago, and it is saliently expressed in post-mitotic central nervous system neurons (CNS). The molecule belongs to the cyclin-dependent kinase family. Kinases are enzymes that catalyze reactions of phosphorylation. This process allows the substrate to gain a phosphate group donated by an organic compound known as ATP. Phosphorylations are of vital importance during glycolysis, therefore, making kinases an essential part of the cell due to their role in the metabolism, cell signaling, and many other processes. Structure Cdk5 is a proline-directed serine/threonine kinase, which was first identified as a CDK family member due to its similar structure to CDC2/CDK1 in humans, a protein that plays a crucial role in the regulation of the cell cycle. The gene Cdk5 contains 12 exons in a region that contains around 5000 nucleotides (5kb), as it was det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CCNG1
Cyclin-G1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CCNG1'' gene. Function The eukaryotic cell cycle is governed by cyclin-dependent protein kinases (CDKs) whose activities are regulated by cyclins and CDK inhibitors. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the cyclin family and contains the cyclin box. The encoded protein lacks the protein destabilizing (PEST) sequence that is present in other family members. Transcriptional activation of this gene can be induced by tumor protein p53. Two transcript variants encoding the same protein have been identified for this gene. Interactions CCNG1 has been shown to interact with: * Mdm2, * P16, * P53, and * PPP2R4 Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunit B is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PPP2R4'' gene. Protein phosphatase 2A is one of the four major Ser/Thr phosphatases and is implicated in the negative control of cell gro .... References External links * Further reading < ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |