|
Fundal Height
Fundal height, or McDonald's rule, is a measure of the size of the uterus used to assess fetal growth and development during pregnancy. It is measured from the top of the mother's uterus to the top of the mother's pubic symphysis. Fundal height, when expressed in centimeters, roughly corresponds to gestational age in weeks between 16 and 36 weeks for a vertex fetus. When a tape measure is unavailable, finger widths are used to estimate centimeter (week) distances from a corresponding anatomical landmark. However, landmark distances from the pubic symphysis are highly variable depending on body type. In clinical practice, recording the actual fundal height measurement from the palpable top of the uterus to the superior edge of the pubic symphysis is standard practice beginning around 20 weeks gestation. Most caregivers will record their patient's fundal height on every prenatal visit. Measuring the fundal height can be an indicator of proper fetal growth and amniotic fluid developm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fundal Height By Gestational Age
Chlordimeform is an acaricide (pesticide) active mainly against motile forms of mites and ticks and against eggs and early instars of some ''Lepidoptera'' insects. After the International Agency for Research on Cancer reported sufficient evidence that its major metabolite, 4-chloro-''o''-toluidine, was a carcinogen A carcinogen is any substance, radionuclide, or radiation that promotes carcinogenesis (the formation of cancer). This may be due to the ability to damage the genome or to the disruption of cellular metabolic processes. Several radioactive substan ..., its use has ceased and its registration has been withdrawn in most countries. References {{insecticides Amidines Organochloride insecticides Benzene derivatives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrauterine Growth Restriction
Intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), or fetal growth restriction, refers to poor growth of a fetus while in the womb during pregnancy. IUGR is defined by clinical features of malnutrition and evidence of reduced growth regardless of an infant's birth weight percentile. The causes of IUGR are broad and may involve maternal, fetal, or placental complications. At least 60% of the 4 million neonatal deaths that occur worldwide every year are associated with low birth weight (LBW), caused by intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), preterm delivery, and genetic abnormalities, demonstrating that under-nutrition is already a leading health problem at birth. Intrauterine growth restriction can result in a baby being small for gestational age (SGA), which is most commonly defined as a weight below the 10th percentile for the gestational age. At the end of pregnancy, it can result in a low birth weight. Types There are two major categories of IUGR: pseudo IUGR and true IUGR With pseudo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breech Birth
A breech birth is when a baby is born bottom first instead of head first, as is normal. Around 3–5% of pregnant women at term (37–40 weeks pregnant) have a breech baby. Due to their higher than average rate of possible complications for the baby, breech births are generally considered higher risk. Breech births also occur in many other mammals such as dogs and horses, see veterinary obstetrics. Most babies in the breech position are delivered via caesarean section because it is seen as safer than being born vaginally. Doctors and midwives in the developing world often lack many of the skills required to safely assist women giving birth to a breech baby vaginally. Also, delivering all breech babies by caesarean section in developing countries is difficult to implement as there are not always resources available to provide this service. OB-GYNs do not recommend home births if a breech birth is expected, even when attended by a medical professional. Cause With regard to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydatidiform Mole
A molar pregnancy also known as a hydatidiform mole, is an abnormal form of pregnancy in which a non-viable fertilized egg implants in the uterus. A molar pregnancy is a type of gestational trophoblastic disease that used to be known as a ''hydatidiform mole''. A molar pregnancy grows into a mass in the uterus that has swollen chorionic villi that grow in clusters resembling grapes. A molar pregnancy can develop when a fertilized egg does not contain an original maternal nucleus. The products of conception may or may not contain fetal tissue. Molar pregnancies are categorized as partial moles or complete moles, with the word 'mole' being used to denote simply a clump of growing tissue, or a 'growth'. A complete mole is caused by a single sperm (90% of the time) or two (10% of the time) sperm combining with an egg which has lost its DNA. In the first case, the sperm then reduplicates, forming a "complete" 46 chromosome set. The genotype is typically 46,XX (diploid) due to the sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
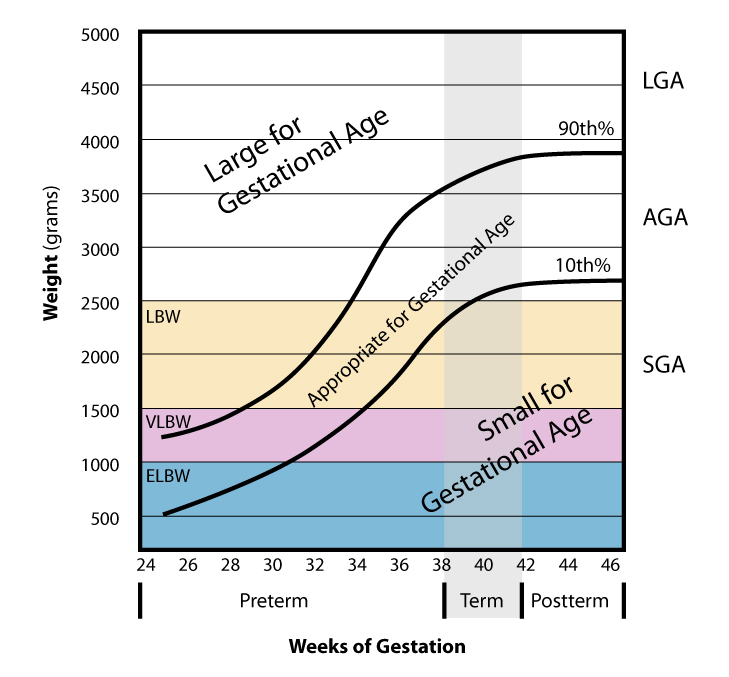
Large For Gestational Age
Large for gestational age (LGA) is a term used to describe infants that are born with an abnormally high weight, specifically in the 90th percentile or above, compared to other babies of the same developmental age. Macrosomia is a similar term that describes excessive birth weight, but refers to an absolute measurement, regardless of gestational age. Typically the threshold for diagnosing macrosomia is a body weight of between , or more, measured at birth, but there are difficulties reaching a universal agreement of this definition. Evaluating an infant for macrosomia or LGA can help identify risks associated with their birth, including labor complications of both the parent and the child, potential long-term health complications of the child, and infant mortality. Signs and symptoms Fetal macrosomia and LGA often do not present with noticeable patient symptoms. Important signs include large fundal height (uterus size) and excessive amniotic fluid (polyhydramnios). Fundal height ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyhydramnios
Polyhydramnios is a medical condition describing an excess of amniotic fluid in the amniotic sac. It is seen in about 1% of pregnancies. It is typically diagnosed when the amniotic fluid index (AFI) is greater than 24 cm. There are two clinical varieties of polyhydramnios: chronic polyhydramnios where excess amniotic fluid accumulates gradually, and acute polyhydramnios where excess amniotic fluid collects rapidly. The opposite to polyhydramnios is oligohydramnios, not enough amniotic fluid. Presentation Associated conditions Fetuses with polyhydramnios are at risk for a number of other problems including cord prolapse, placental abruption, premature birth and perinatal death. At delivery the baby should be checked for congenital abnormalities. Causes In most cases, the exact cause cannot be identified. A single case may have one or more causes, including intrauterine infection (TORCH), rh-isoimmunisation, or chorioangioma of the placenta. In a multiple gestation pregna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a condition in which a woman without diabetes develops high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Gestational diabetes generally results in few symptoms; however, it increases the risk of pre-eclampsia, depression, and of needing a Caesarean section. Babies born to mothers with poorly treated gestational diabetes are at increased risk of macrosomia, of having hypoglycemia after birth, and of jaundice. If untreated, diabetes can also result in stillbirth. Long term, children are at higher risk of being overweight and of developing type 2 diabetes. Gestational diabetes can occur during pregnancy because of insulin resistance or reduced production of insulin. Risk factors include being overweight, previously having gestational diabetes, a family history of type 2 diabetes, and having polycystic ovarian syndrome. Diagnosis is by blood tests. For those at normal risk, screening is recommended between 24 and 28 weeks' gestation. For those at high risk, testin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiple Births
A multiple birth is the culmination of one multiple pregnancy, wherein the mother gives birth to two or more babies. A term most applicable to vertebrate species, multiple births occur in most kinds of mammals, with varying frequencies. Such births are often named according to the number of offspring, as in ''twins'' and ''triplets''. In non-humans, the whole group may also be referred to as a ''litter'', and multiple births may be more common than single births. Multiple births in humans are the exception and can be exceptionally rare in the largest mammals. A multiple pregnancy may be the result of the fertilization of a single egg that then splits to create identical fetuses, or it may be the result of the fertilization of multiple eggs that create fraternal ("non-identical") fetuses, or it may be a combination of these factors. A multiple pregnancy from a single zygote is called ''monozygotic'', from two zygotes is called ''dizygotic'', or from three or more zygotes is calle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twins
Twins are two offspring produced by the same pregnancy.MedicineNet > Definition of TwinLast Editorial Review: 19 June 2000 Twins can be either ''monozygotic'' ('identical'), meaning that they develop from one zygote, which splits and forms two embryos, or ''dizygotic'' ('non-identical' or 'fraternal'), meaning that each twin develops from a separate egg and each egg is fertilized by its own sperm cell. Since identical twins develop from one zygote, they will share the same sex, while fraternal twins may or may not. In rare cases twins can have the same mother and different fathers (heteropaternal superfecundation). In contrast, a fetus that develops alone in the uterus, womb (the much more common case, in humans) is called a ''singleton'', and the general term for one offspring of a multiple birth is a ''multiple''. Unrelated look-alikes whose resemblance parallels that of twins are referred to as doppelgängers. Statistics The human twin birth rate in the United States rose 7 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Small For Gestational Age
Small for gestational age (SGA) newborns are those who are smaller in size than normal for the gestational age, most commonly defined as a weight below the 10th percentile for the gestational age. Causes Being small for gestational age is broadly either: * Being constitutionally small, wherein the state is basically a genetic trait of the baby. * Intrauterine growth restriction, also called "pathological SGA" Diagnosis The condition is determined by birth weight and/or length. A related condition, intrauterine growth restriction, is generally diagnosed by measuring the mother's uterus, with the fundal height being less than it should be for that stage of the pregnancy. If it is suspected, the mother will usually be sent for an ultrasound to confirm. Management Ninety percent of babies born SGA catch up in growth by the time they reach 2 years old. However, all SGA babies should be watched for signs of failure to thrive, hypoglycemia and other conditions common to SGA babies (see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The uterus is a hormone-responsive sex organ that contains glands in its lining that secrete uterine milk for embryonic nourishment. In the human, the lower end of the uterus, is a narrow part known as the isthmus that connects to the cervix, leading to the vagina. The upper end, the body of the uterus, is connected to the fallopian tubes, at the uterine horns, and the rounded part above the openings to the fallopian tubes is the fundus. The connection of the uterine cavity with a fallopian tube is called the uterotubal junction. The fertilized egg is carried to the uterus along the fallopian tube. It will have divided on its journey to form a blastocyst that will implant itself into the lining of the uterus – the endometrium, where it will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligohydramnios
Oligohydramnios is a medical condition in pregnancy characterized by a deficiency of amniotic fluid, the fluid that surrounds the fetus in the abdomen, in the amniotic sac. It is typically diagnosed by ultrasound when the amniotic fluid index (AFI) measures less than 5 cm or when the single deepest pocket (SDP) of amniotic fluid measures less than 2 cm. Amniotic fluid is necessary to allow for normal fetal movement, lung development, and cushioning from uterine compression. Low amniotic fluid can be attributed to a maternal, fetal, placental or idiopathic cause and can result in poor fetal outcomes including death. The prognosis of the fetus is dependent on the etiology, gestational age at diagnosis, and the severity of the oligohydramnios. The opposite of oligohydramnios is polyhydramnios, or an excess of amniotic fluid. Etiology The amount of amniotic fluid available is based on how much fluid is produced and how much is removed from the amniotic sac. In the first trimester, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |