|
Full Summer Pool
A full summer pool or full pool is the water level of a reservoir at normal operating conditions. Water levels During droughts or water shortages, the water level can drop below full summer pool. Additionally, water levels may be lowered during the winter season below full summer pool to accommodate snowmelt or seasonally heavy rains. During periods of heavy rain, the water level in the reservoir may rise above full summer pool to prevent flooding downstream. See also *Cistern *Hydraulic engineering Hydraulic engineering as a sub-discipline of civil engineering is concerned with the flow and conveyance of fluids, principally water and sewage. One feature of these systems is the extensive use of gravity as the motive force to cause the mov ... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Full Summer Pool Reservoirs Hydraulic engineering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reservoir
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation. Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including controlling a watercourse that drains an existing body of water, interrupting a watercourse to form an embayment within it, through excavation, or building any number of retaining walls or levees. In other contexts, "reservoirs" may refer to storage spaces for various fluids; they may hold liquids or gasses, including hydrocarbons. ''Tank reservoirs'' store these in ground-level, elevated, or buried tanks. Tank reservoirs for water are also called cisterns. Most underground reservoirs are used to store liquids, principally either water or petroleum. Types Dammed valleys Dammed reservoirs are artificial lakes created and controlled by a dam A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, and O. Zolina, 2021Water Cycle Changes In Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Masson-Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, United Kingdom and New York, NY, USA, pp. 1055–1210, doi:10.1017/9781009157896.010. This means that a drought is "a moisture deficit relative to the average water availability at a given location and season". A drought can last for days, months or years. Drought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
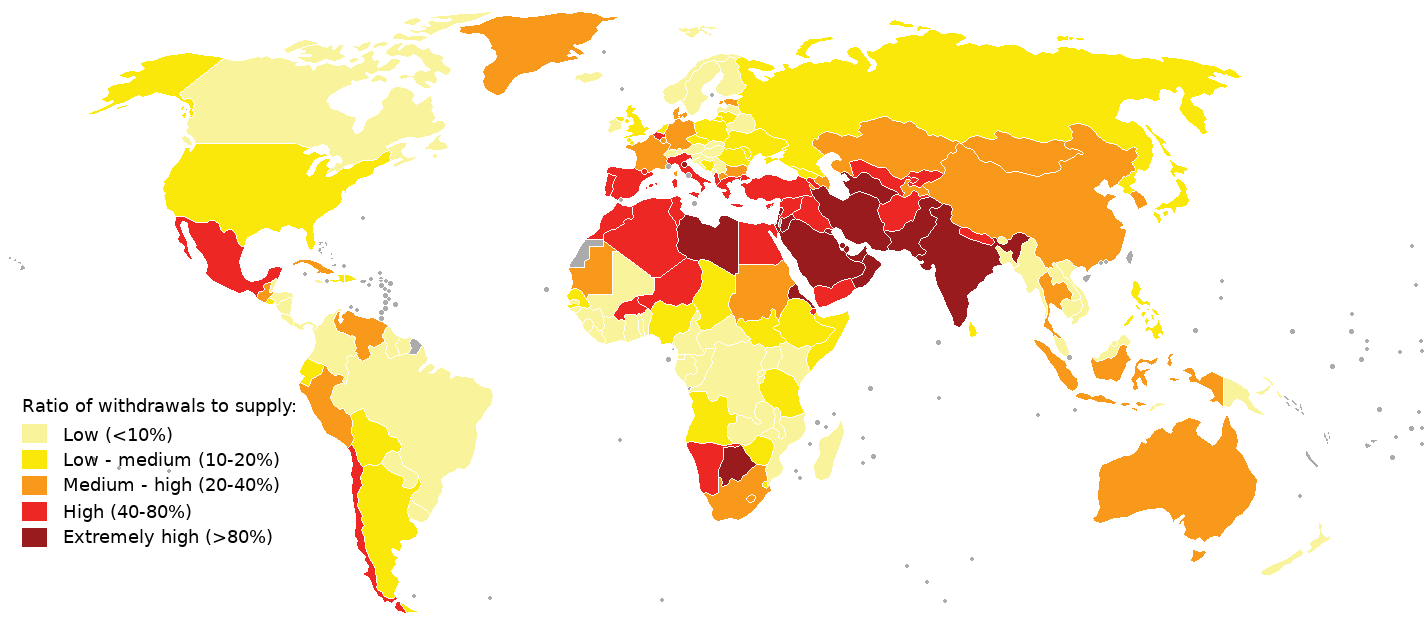
Water Shortage
Water scarcity (closely related to water stress or water crisis) is the lack of fresh water resources to meet the standard water demand. There are two types of water scarcity: physical or economic water scarcity. Physical water scarcity is where there is not enough water to meet all demands, including that needed for ecosystems to function effectively. Arid areas for example Central and West Asia, and North Africa often suffer from physical water scarcity. On the other hand, economic water scarcity is caused by a lack of investment in infrastructure or technology to draw water from rivers, aquifers, or other water sources, or insufficient human capacity to satisfy the demand for water. Much of Sub-Saharan Africa has economic water scarcity. The essence of global water scarcity is the geographic and temporal mismatch between fresh water demand and availability. At the global level and on an annual basis, enough freshwater is available to meet such demand, but spatial and tempora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snowmelt
In hydrology, snowmelt is surface runoff produced from melting snow. It can also be used to describe the period or season during which such runoff is produced. Water produced by snowmelt is an important part of the annual water cycle in many parts of the world, in some cases contributing high fractions of the annual runoff in a watershed. Predicting snowmelt runoff from a drainage basin may be a part of designing water control projects. Rapid snowmelt can cause flooding. If the snowmelt is then frozen, very dangerous conditions and accidents can occur, introducing the need for salt to melt the ice. Energy fluxes related to snowmelt There are several energy fluxes involved in the melting of snow. These fluxes can act in opposing directions, that is either delivering heat to or removing heat from the snowpack. Ground heat flux is the energy delivered to the snowpack from the soil below by conduction. Radiation inputs to the snowpack include net shortwave (solar radiation including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cistern
A cistern (Middle English ', from Latin ', from ', "box", from Greek ', "basket") is a waterproof receptacle for holding liquids, usually water. Cisterns are often built to catch and store rainwater. Cisterns are distinguished from wells by their waterproof linings. Modern cisterns range in capacity from a few litres to thousands of cubic metres, effectively forming covered reservoirs. Origins Early domestic and agricultural use Waterproof lime plaster cisterns in the floors of houses are features of Neolithic village sites of the Levant at, for instance, Ramad and Lebwe, and by the late fourth millennium BC, as at Jawa in northeastern Lebanon, cisterns are essential elements of emerging water management techniques in dry-land farming communities. The Ancient Roman impluvium, a standard feature of the domus house, generally had a cistern underneath. The impluvium and associated structures collected, filtered, cooled, and stored the water, and also cooled and ventilated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulic Engineering
Hydraulic engineering as a sub-discipline of civil engineering is concerned with the flow and conveyance of fluids, principally water and sewage. One feature of these systems is the extensive use of gravity as the motive force to cause the movement of the fluids. This area of civil engineering is intimately related to the design of bridges, dams, channels, canals, and levees, and to both sanitary and environmental engineering. Hydraulic engineering is the application of the principles of fluid mechanics to problems dealing with the collection, storage, control, transport, regulation, measurement, and use of water.Prasuhn, Alan L. ''Fundamentals of Hydraulic Engineering''. Holt, Rinehart, and Winston: New York, 1987. Before beginning a hydraulic engineering project, one must figure out how much water is involved. The hydraulic engineer is concerned with the transport of sediment by the river, the interaction of the water with its alluvial boundary, and the occurrence of scour an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reservoirs
A reservoir (; from French ''réservoir'' ) is an enlarged lake behind a dam. Such a dam may be either artificial, built to store fresh water or it may be a natural formation. Reservoirs can be created in a number of ways, including controlling a watercourse that drains an existing body of water, interrupting a watercourse to form an embayment within it, through excavation, or building any number of retaining walls or levees. In other contexts, "reservoirs" may refer to storage spaces for various fluids; they may hold liquids or gasses, including hydrocarbons. ''Tank reservoirs'' store these in ground-level, elevated, or buried tanks. Tank reservoirs for water are also called cisterns. Most underground reservoirs are used to store liquids, principally either water or petroleum. Types Dammed valleys Dammed reservoirs are artificial lakes created and controlled by a dam constructed across a valley, and rely on the natural topography to provide most of the basin of the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |