|
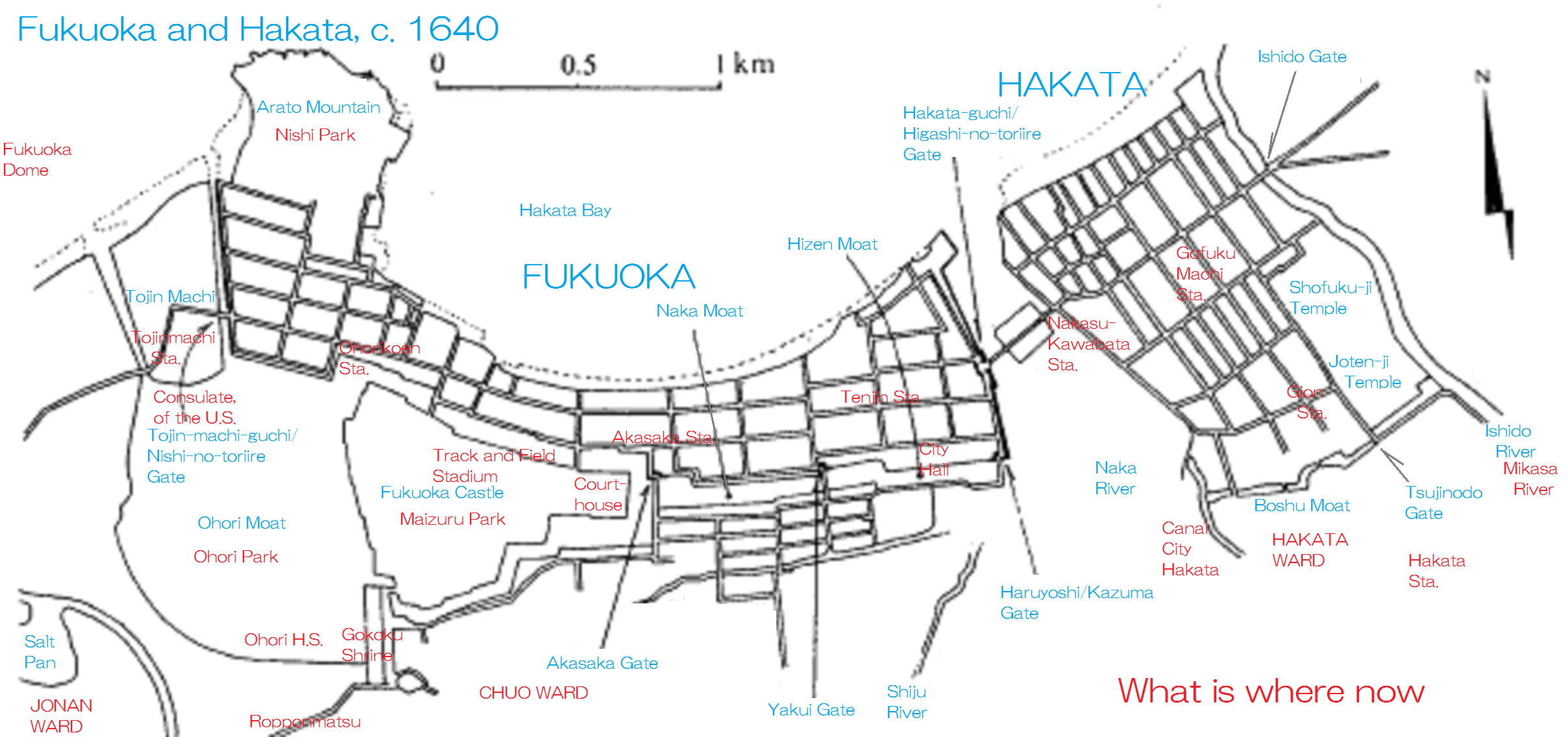
Fukuoka Castle
is a Japanese castle located in Chūō-ku, Fukuoka, Japan. It is also known as Maizuru Castle (舞鶴城 Maizuru-jō) or Seki Castle (石城 Seki-jō). Completed in the early Edo period for ''tozama daimyō'' Kuroda Nagamasa, it has been decreed a historic site by the Japanese government. The castle lies in the centre of Fukuoka, on top of Fukusaki hill. The , Naka-gawa in Japanese, acts as a natural moat on the eastern side of the castle, while the western side uses a mudflat as a natural moat. Hakata, a ward with a bustling port, is located on the opposite side of the Naka River to the east. The castle town was established on the northern side, facing the sea. Much of the castle grounds has been converted to Maizuru Park, which houses several sports facilities, a courthouse, and an art museum. Heiwadai Baseball Stadium, the past home field of the Nishitetsu Lions and the Fukuoka Daiei Hawks, was also located on the castle grounds. Some of the castle's gates as well as its tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heiwadai Stadium
was a ballpark located in the Fukuoka, Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan. From 1950 to 1978, it served as the home ballpark of the Nishitetsu Lions, a team in Nippon Professional Baseball's (NPB) Pacific League. It also briefly served as the home stadium for NPB teams the Nishi Nippon Pirates in 1950 and the Fukuoka Daiei Hawks from 1989 to 1992. The stadium hosted 1,904 official NPB games in its almost 58-year history. The stadium was built in 1949 in Maizuru Park, the former site of Fukuoka Castle, by converting a soccer field at Heiwadai Athletic Stadium into a ballpark. For NPB's inaugural season, the Central League's newly created Nishi Nippon Pirates used Heiwadai Stadium as its home. Additionally, the PL's newly created Nishitetsu Clippers used it as a semi-home. After Nishi Nippon's first and only season, the team merged with the Clippers to form the Nishitetsu Lions who made Heiwadai their full-time home starting in the 1951 season. When it was built, the stadium's stan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fukuoka Castle 2006 01
is the sixth-largest city in Japan, the second-largest port city after Yokohama, and the capital city of Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan. The city is built along the shores of Hakata Bay, and has been a center of international commerce since ancient times. The area has long been considered the gateway to the country, as it is the nearest point among Japan's main islands to the Asian mainland. Although humans occupied the area since the Jomon period, some of the earliest settlers of the Yayoi period arrived in the Fukuoka area. The city rose to prominence during the Yamato period. Because of the cross-cultural exposure, and the relatively great distance from the social and political centers of Kyoto, Osaka, and later, Edo (Tokyo), Fukuoka gained a distinctive local culture and dialect that has persisted to the present. Fukuoka is the most populous city on Kyūshū island, followed by Kitakyushu. It is the largest city and metropolitan area west of Keihanshin. The city was design ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kōrokan
The were guest houses for foreign ambassadors, traveling monks, and merchants that existed in Japan during the Heian period and earlier. These guest houses existed in Kyoto, Osaka, and Fukuoka. Only the location of the ''kōrokan'' in Fukuoka is known with precision today; its ruins were discovered on the grounds of Maizuru Castle Park in 1987. The word was coined in the Heian period by using the first two characters from the Chinese name 鴻臚寺 for Han dynasty and Qi dynasty temples charged with the responsibility of hosting foreign dignitaries. Though the word is Heian in origin, the ''kōrokan'' in Fukuoka and Osaka were already in use in the Asuka period. Tsukushi Kōrokan (Fukuoka) The guest house in Fukuoka is called in Heian sources, after the name of Tsukushi Province, which is part of Fukuoka Prefecture today. The Nihon Shoki mentions that Prince Kim Sang-nim of Silla was entertained at in 688, an early reference to the facility. The Buddhist monk Ennin noted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Katō Kiyomasa
was a Japanese ''daimyō'' of the Azuchi–Momoyama and Edo periods. His court title was Higo-no-kami. His name as a child was ''Yashamaru'', and first name was ''Toranosuke''. He was one of Hideyoshi's Seven Spears of Shizugatake. Biography Kiyomasa was born in what is now Nakamura-ku, Nagoya (situated in contemporary Aichi District, Owari Province) to Katō Kiyotada. Kiyotada's wife, Ito, was a cousin of Toyotomi Hideyoshi's mother. Kiyotada died while his son, Kiyomasa (then known as Toranosuke), was still young. Soon after, Toranosuke entered into Hideyoshi's service, and in 1576, at age 15, was granted a stipend of 170 ''koku''. In 1582, he fought in Hideyoshi's army at the Battle of Yamazaki, and later in 1583 at the Battle of Shizugatake. Owing to his achievement in that battle, he became known as one of the Seven Spears of Shizugatake and was rewarded with 3,000 additional ''koku''. In 1584, Kiyomasa took part in the Battle of Komaki and Nagakute against the Tokuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyūshū
is the third-largest island of Japan's five main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands ( i.e. excluding Okinawa). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surrounding islands. Kyushu has a land area of and a population of 14,311,224 in 2018. In the 8th-century Taihō Code reforms, Dazaifu was established as a special administrative term for the region. Geography The island is mountainous, and Japan's most active volcano, Mount Aso at , is on Kyushu. There are many other signs of tectonic activity, including numerous areas of hot springs. The most famous of these are in Beppu, on the east shore, and around Mt. Aso in central Kyushu. The island is separated from Honshu by the Kanmon Straits. Being the nearest island to the Asian continent, historically it is the gateway to Japan. The total area is which makes it the 37th largest island in the world. It's slightly larger than Taiwan island . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osaka Castle
is a Japanese castle in Chūō-ku, Osaka, Japan. The castle is one of Japan's most famous landmarks and it played a major role in the unification of Japan during the sixteenth century of the Azuchi-Momoyama period. Layout The main tower of Osaka Castle is situated on a plot of land roughly one square kilometre. It is built on two raised platforms of landfill supported by sheer walls of cut rock, using a technique called burdock piling, each overlooking a moat. The central castle building is five stories on the outside and eight stories on the inside, and built atop a tall stone foundation to protect its occupants from attackers. The Main Tower is surrounded by a series of moats and defensive fortifications. The castle has 2 moats (an inner & outer). The inner castle moat lies within the castle grounds, and consists of 2 types: a wet (northern-easterly) and dry (south-westerly). Outer moat meanwhile surrounds the entire castle premise, denotes the castle's outer limits, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edo Castle
is a flatland castle that was built in 1457 by Ōta Dōkan in Edo, Toshima District, Musashi Province. In modern times it is part of the Tokyo Imperial Palace in Chiyoda, Tokyo and is therefore also known as . Tokugawa Ieyasu established the Tokugawa shogunate there, and it was the residence of the ''shōgun'' and the headquarters of the military government during the Edo period (1603-1867) in Japanese history. After the resignation of the ''shōgun'' and the Meiji Restoration, it became the Tokyo Imperial Palace. Some moats, walls and ramparts of the castle survive to this day. However, the grounds were more extensive during the Edo period, with Tokyo Station and the Marunouchi section of the city lying within the outermost moat. It also encompassed Kitanomaru Park, the Nippon Budokan Hall and other current landmarks of the surrounding area. History The warrior Edo Shigetsugu built his residence in what is now the ''Honmaru'' and ''Ninomaru'' part of Edo Castle, around t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keichō
was a after ''Bunroku'' and before ''Genna''. This period spanned from October 1596 to July 1615. The reigning emperors were and . Change of era * 1596 : The era name was changed to ''Keichō'' to mark the passing of various natural disasters. The preceding era ended and a new one commenced on October 27 of the 5th ''Bunroku''. Events of the ''Keichō'' era * 1596 (''Keichō 1''): ''Keichō'' Invasion (invasion of Korea). * September 18, 1598 (''Keichō 3, 18th day of the 8th month''): Toyotomi Hideyoshi died in his Fushimi Castle at the age of 63.Titsingh p. 405./ref> * October 21, 1600 (''Keichō 5, 15th day of the 9th month''): Battle of Sekigahara. The Tokugawa clan and its allies decisively vanquish all opposition. * January 15, 1602 (''Keichō 7, 24th day of the 11th month''): A fire at the Hōkō-ji temple complex in Kyoto was caused by careless workmen; and the great image of the buddha and the structure housing the statue (the Daibutsu-den) were consumed by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kobayakawa Takakage
was a samurai and daimyō (feudal lord) during the Sengoku period and Azuchi–Momoyama period. He was the third son of Mōri Motonari who was adopted by the Kobayakawa clan and became its 14th clan head. He merged the two branches of the Kobayakawa, the Takehara-Kobayakawa clan (竹原小早川氏) and Numata-Kobayakawa clan (沼田小早川氏). He became an active commander of the Mōri army and he with his brother Kikkawa Motoharu became known as the “''Mōri Ryōkawa''", or “''Mōri's Two Rivers''" (毛利両川). As head of the Kobayakawa clan, he expanded the clan's territory in the Chūgoku region (western Honshū), and fought for the Mōri clan in all their campaigns At first he opposed Oda Nobunaga and Toyotomi Hideyoshi but later swore loyalty and became a retainer of Hideyoshi who awarded him domains in Iyo Province on Shikoku and Chikuzen Province on Kyūshū, totalling 350,000 ''koku''. Hideyoshi gave him the title ''Chûnagon'' also appointed him to the Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tachibana Akitoshi , a wild citrus fruit native to Japan
{{disambiguation ...
The term has at least two different meanings, and has been used in several contexts. People * – a clan of ''kuge'' (court nobles) prominent in the Nara and Heian periods (710–1185) * – a clan of ''daimyō'' (feudal lords) prominent in the Muromachi, Sengoku and Edo periods (1333–1868) *Tachibana (surname) Other *Tachibana-class destroyer, a class Japanese warships during World War II *, two destroyers of the Imperial Japanese Navy *Tachibana, Fukuoka, a former town in Fukuoka Prefecture *Tachibana Station, a railway station in Hyogo Prefecture *Tachibana castle, a castle which formerly stood atop Tachibana Mountain *Tachibana orange The tachibana orange (''Citrus tachibana,'' or ''Citrus reticulata tachibana'') is a variety of mandarin orange, a citrus fruit. They grow wild in the forests of Japan and are referred to in the poetry of the early Japanese and Ryukyu Islands ki ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Han (Japan)
( ja, 藩, "domain") is a Japanese historical term for the estate of a daimyo in the Edo period (1603–1868) and early Meiji period (1868–1912). Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"Han"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 283. or (daimyo domain) served as a system of ''de facto'' administrative divisions of Japan alongside the ''de jure'' provinces until they were abolished in the 1870s. History Pre-Edo period The concept of originated as the personal estates of prominent warriors after the rise of the Kamakura Shogunate in 1185, which also saw the rise of feudalism and the samurai noble warrior class in Japan. This situation existed for 400 years during the Kamakura Shogunate (1185–1333), the brief Kenmu Restoration (1333–1336), and the Ashikaga Shogunate (1336–1573). became increasingly important as ''de facto'' administrative divisions as subsequent Shoguns stripped the Imperial provinces () and their officials of their legal powers. Edo period Toyotomi Hideyoshi, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Najima Castle
is a hilltop castle, located in Fukuoka City, Fukuoka Prefecture, Japan. Today, only its ruins still stand. History Najima Castle was located on a peninsula projecting into Hakata Bay on the north of the estuary of the Tatara River. The castle fundamentally consisted of the hon-maru or primary kuruwa, the ni-no-maru or secondary kuruwa, and the san-no-maru or tertiary kuruwa, respectively ranging from west to east, and extending for over 900 meters or 2953 ft. The hon-maru, presumably the highest place in the castle, is now about 25 meters or 82 ft. above sea level.福岡市埋蔵文化財調査報告書第318集『名島城跡I』(福岡市教育委員会、1993年)第2図/Fukuoka City Excavation Report Vol.318 "The site of Najima Castle I", Fukuoka City Board of Education, Fig.2 The castle was built by Kobayakawa Takakage, an illustrious Japanese general, in the late 16th century. However, it turned out to be undesirable as the administrative center of the han o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |