|
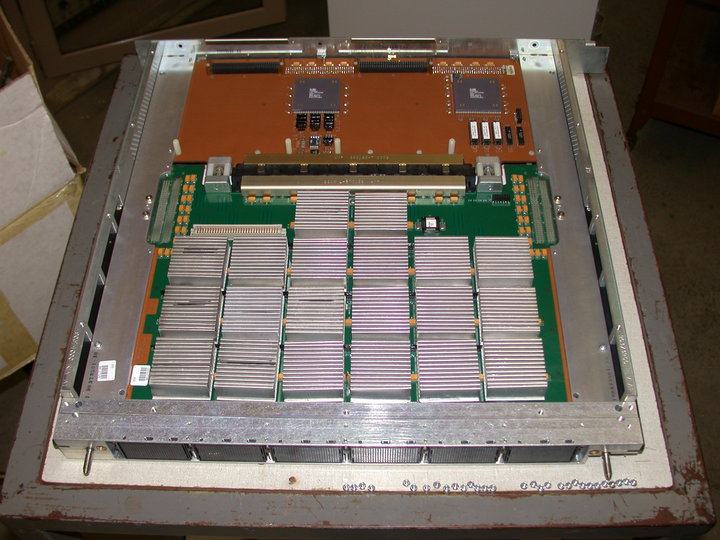
Fujitsu VP2000
The VP2000 was the second series of vector supercomputers from Fujitsu. Announced in December 1988, they replaced Fujitsu's earlier FACOM VP Model E Series. The VP2000 was succeeded in 1995 by the VPP300, a massively parallel supercomputer with up to 256 vector processors. The VP2000 was similar in many ways to their earlier designs, and in turn to the Cray-1, using a register-based vector processor for performance. For additional performance the vector units supported a special multiply-and-add instruction that could retire two results per clock cycle. This instruction "chain" is particularly common in many supercomputer applications. Another difference is that the main scalar units of the processor ran at half the speed of the vector unit. According to Amdahl's Law computers tend to run at the speed of their slowest unit, and in this case unless the program spent most of its time in the vector units, the slower scalar performance would make it 1/2 the performance of a Cray-1 at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vector Processor
In computing, a vector processor or array processor is a central processing unit (CPU) that implements an instruction set where its instructions are designed to operate efficiently and effectively on large one-dimensional arrays of data called ''vectors''. This is in contrast to scalar processors, whose instructions operate on single data items only, and in contrast to some of those same scalar processors having additional single instruction, multiple data (SIMD) or SWAR Arithmetic Units. Vector processors can greatly improve performance on certain workloads, notably numerical simulation and similar tasks. Vector processing techniques also operate in video-game console hardware and in graphics accelerators. Vector machines appeared in the early 1970s and dominated supercomputer design through the 1970s into the 1990s, notably the various Cray platforms. The rapid fall in the price-to-performance ratio of conventional microprocessor designs led to a decline in vector supercom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amdahl Corporation
Amdahl Corporation was an information technology company which specialized in IBM mainframe-compatible computer products, some of which were regarded as supercomputers competing with those from Cray Research. Founded in 1970 by Gene Amdahl, a former IBM computer engineer best known as chief architect of System/360, it was a wholly owned subsidiary of Fujitsu since 1997. The company was located in Sunnyvale, California. From its first machine in 1975, Amdahl's business was to provide mainframe computers that were plug-compatible with contemporary IBM mainframes, but offering higher reliability, running somewhat faster, and costing somewhat less. They often had additional practical advantages as well, in terms of size, power requirements, of being air-cooled instead of requiring a chilled water supply. This offered a price/performance ratio superior to the IBM lineup, and made Amdahl one of the few real competitors to "Big Blue" in the very high-margin computer market segment. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NEC SX
is a Japanese multinational information technology and electronics corporation, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo. The company was known as the Nippon Electric Company, Limited, before rebranding in 1983 as NEC. It provides IT and network solutions, including cloud computing, artificial intelligence (AI), Internet of things (IoT) platform, and telecommunications equipment and software to business enterprises, communications services providers and to government agencies, and has also been the biggest PC vendor in Japan since the 1980s when it launched the PC-8000 series. NEC was the world's fourth-largest PC manufacturer by 1990. Its semiconductors business unit was the world's largest semiconductor company by annual revenue from 1985 to 1992, the second largest in 1995, one of the top three in 2000, and one of the top 10 in 2006. NEC spun off its semiconductor business to Renesas Electronics and Elpida Memory. Once Japan's major electronics company, NEC has largely withdrawn from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cray Y-MP
The Cray Y-MP was a supercomputer sold by Cray Research from 1988, and the successor to the company's X-MP. The Y-MP retained software compatibility with the X-MP, but extended the address registers from 24 to 32 bits. High-density VLSI ECL technology was used and a new liquid-cooling system was devised. The Y-MP ran the Cray UNICOS operating system. The Y-MP could be equipped with two, four or eight vector processors, with two functional units each and a clock cycle time of 6 ns (167 MHz). Peak performance was thus 333 megaflops per processor. Main memory comprised 128, 256 or 512 MB of SRAM. The original Y-MP (otherwise known as the Y-MP Model D) was housed in a chassis similar to the horseshoe-shaped X-MP, but with an extra rectangular cabinet added in the middle (containing the CPU boards), thus forming a "Y" shape in plan view. The system could be configured with one or two ''Model D'' IOSs (Input/Output Subsystems) and an optional Solid State Disk (SSD) of 256 MB ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vectorizing Compiler
Automatic vectorization, in parallel computing, is a special case of automatic parallelization, where a computer program is converted from a scalar implementation, which processes a single pair of operands at a time, to a vector implementation, which processes one operation on multiple pairs of operands at once. For example, modern conventional computers, including specialized supercomputers, typically have vector operations that simultaneously perform operations such as the following four additions (via SIMD or SPMD hardware): :\begin c_1 & = a_1 + b_1 \\ c_2 & = a_2 + b_2 \\ c_3 & = a_3 + b_3 \\ c_4 & = a_4 + b_4 \end However, in most programming languages one typically writes loops that sequentially perform additions of many numbers. Here is an example of such a loop, written in C: for (i = 0; i < n; i++) c = a + b [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C (programming Language)
C (''pronounced like the letter c'') is a General-purpose language, general-purpose computer programming language. It was created in the 1970s by Dennis Ritchie, and remains very widely used and influential. By design, C's features cleanly reflect the capabilities of the targeted CPUs. It has found lasting use in operating systems, device drivers, protocol stacks, though decreasingly for application software. C is commonly used on computer architectures that range from the largest supercomputers to the smallest microcontrollers and embedded systems. A successor to the programming language B (programming language), B, C was originally developed at Bell Labs by Ritchie between 1972 and 1973 to construct utilities running on Unix. It was applied to re-implementing the kernel of the Unix operating system. During the 1980s, C gradually gained popularity. It has become one of the measuring programming language popularity, most widely used programming languages, with C compilers avail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operating System
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs. Time-sharing operating systems schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also include accounting software for cost allocation of processor time, mass storage, printing, and other resources. For hardware functions such as input and output and memory allocation, the operating system acts as an intermediary between programs and the computer hardware, although the application code is usually executed directly by the hardware and frequently makes system calls to an OS function or is interrupted by it. Operating systems are found on many devices that contain a computer from cellular phones and video game consoles to web servers and supercomputers. The dominant general-purpose personal computer operating system is Microsoft Windows with a market share of around 74.99%. macOS by Apple Inc. is in second place (14.84%), and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supercomputer
A supercomputer is a computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second ( FLOPS) instead of million instructions per second (MIPS). Since 2017, there have existed supercomputers which can perform over 1017 FLOPS (a hundred quadrillion FLOPS, 100 petaFLOPS or 100 PFLOPS). For comparison, a desktop computer has performance in the range of hundreds of gigaFLOPS (1011) to tens of teraFLOPS (1013). Since November 2017, all of the world's fastest 500 supercomputers run on Linux-based operating systems. Additional research is being conducted in the United States, the European Union, Taiwan, Japan, and China to build faster, more powerful and technologically superior exascale supercomputers. Supercomputers play an important role in the field of computational science, and are used for a wide range of computationally intensive tasks in var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unix
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others. Initially intended for use inside the Bell System, AT&T licensed Unix to outside parties in the late 1970s, leading to a variety of both academic and commercial Unix variants from vendors including University of California, Berkeley (Berkeley Software Distribution, BSD), Microsoft (Xenix), Sun Microsystems (SunOS/Solaris (operating system), Solaris), Hewlett-Packard, HP/Hewlett Packard Enterprise, HPE (HP-UX), and IBM (IBM AIX, AIX). In the early 1990s, AT&T sold its rights in Unix to Novell, which then sold the UNIX trademark to The Open Group, an industry consortium founded in 1996. The Open Group allows the use of the mark for certified operating systems that comply with the Single UNIX Specification (SUS). Unix systems are chara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amdahl's Law
In computer architecture, Amdahl's law (or Amdahl's argument) is a formula which gives the theoretical speedup in latency of the execution of a task at fixed workload that can be expected of a system whose resources are improved. It states that "the overall performance improvement gained by optimizing a single part of a system is limited by the fraction of time that the improved part is actually used". It is named after computer scientist Gene Amdahl, and was presented at the American Federation of Information Processing Societies (AFIPS) Spring Joint Computer Conference in 1967. Amdahl's law is often used in parallel computing to predict the theoretical speedup when using multiple processors. For example, if a program needs 20 hours to complete using a single thread, but a one-hour portion of the program cannot be parallelized, therefore only the remaining 19 hours' () execution time can be parallelized, then regardless of how many threads are devoted to a parallelized execution ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |