|
Fujitsu Micro 16s
The Fujitsu Micro 16s was a business personal computer from Fujitsu that was launched in 1983, around the same time as the launch of the original IBM PC/XT. The Micro 16s used a plug in microprocessor board, and two models were offered, an Intel 8086 and a Zilog Z80 expansion board. Additional expansion boards with the Motorola 68000, Intel 80286 and Zilog Z8000 processors were also planned. Additionally it had a Motorola 6809 co-processor. As operating systems one could choose between Concurrent CP/M-86 with GSX graphic extension, MP/M-86, MS-DOS, CP/M (for the Z80 board) and Unix. It could support up to four 320 KB 5.25-inch floppy disk drives, and a hard disk of up to 20 MB. It had advanced color graphics with 640x200 resolution with 8 colors per pixel, based on a Motorola 6845 The Motorola 6845, or MC6845, is a display controller that was widely used in 8-bit computers during the 1980s. Originally intended for designs based on the Motorola 6800 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fujitsu
is a Japanese multinational information and communications technology equipment and services corporation, established in 1935 and headquartered in Tokyo. Fujitsu is the world's sixth-largest IT services provider by annual revenue, and the largest in Japan, in 2021. The hardware offerings from Fujitsu are mainly of personal and enterprise computing products, including x86, SPARC and mainframe compatible server products, although the corporation and its subsidiaries also offer a diversity of products and services in the areas of data storage, telecommunications, advanced microelectronics, and air conditioning. It has approximately 126,400 employees and its products and services are available in approximately 180 countries. Fujitsu is listed on the Tokyo Stock Exchange and Nagoya Stock Exchange; its Tokyo listing is a constituent of the Nikkei 225 and TOPIX 100 indices. History 1935 to 2000 Fujitsu was established on June 20, 1935, which makes it one of the oldest operating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphics System Extension
GEM (for Graphics Environment Manager) is an operating environment released by Digital Research (DRI) in 1985 for use with the DOS operating system on Intel 8088 and Motorola 68000 microprocessors. GEM is known primarily as the graphical user interface (GUI) for the Atari ST series of computers, and was also supplied with a series of IBM PC-compatible computers from Amstrad. It was also available for the standard IBM PC, at a time when the 6 MHz IBM PC AT (and the very concept of a GUI) was brand new. It was the core for a small number of DOS programs, the most notable being Ventura Publisher. It was ported to a number of other computers that previously lacked graphical interfaces, but never gained popularity on those platforms. DRI also produced X/GEM for their FlexOS real-time operating system with adaptations for OS/2 Presentation Manager and the X Window System under preparation as well. History GSX In late 1984, GEM started life at DRI as an outgrowth of a more gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Microcomputers
{{disambiguation, geo ...
Early may refer to: History * The beginning or oldest part of a defined historical period, as opposed to middle or late periods, e.g.: ** Early Christianity ** Early modern Europe Places in the United States * Early, Iowa * Early, Texas * Early Branch, a stream in Missouri * Early County, Georgia Other uses * ''Early'' (Scritti Politti album), 2005 * ''Early'' (A Certain Ratio album), 2002 * Early (name) * Early effect, an effect in transistor physics * Early Records, a record label * the early part of the morning See also * Earley (other) Earley is a town in England. Earley may also refer to: * Earley (surname), a list of people with the surname Earley * Earley (given name), a variant of the given name Earlene * Earley Lake, a lake in Minnesota *Earley parser, an algorithm *Earley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
InfoWorld
''InfoWorld'' (abbreviated IW) is an information technology media business. Founded in 1978, it began as a monthly magazine. In 2007, it transitioned to a web-only publication. Its parent company today is International Data Group, and its sister publications include '' Macworld'' and ''PC World''. InfoWorld is based in San Francisco, with contributors and supporting staff based across the United States. Since its founding, ''InfoWorld''s readership has largely consisted of IT and business professionals. ''InfoWorld'' focuses on how-to, analysis, and editorial content from a mixture of experienced technology journalists and working technology practitioners. The site averages 4.6 million monthly page views and 1.1 million monthly unique visitors. History The magazine was founded by Jim Warren in 1978 as ''The Intelligent Machines Journal'' (IMJ). It was sold to IDG in late 1979. On 18 February 1980, the magazine name was changed to ''InfoWorld''. In 1986, the Robert X. Cringel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Creative Computing
''Creative Computing'' was one of the earliest magazines covering the microcomputer revolution. Published from October 1974 until December 1985, the magazine covered the spectrum of hobbyist/home/personal computing in a more accessible format than the rather technically oriented ''Byte (magazine), Byte''. The magazine was created to cover educational-related topics. Early issues include articles on the use of computers in the classroom, various simple programs like madlibs and various programming challenges, mostly in BASIC programming language, BASIC. By the late 1970s, it had moved towards more general coverage as the microcomputer market emerged. Hardware coverage became more common, but type-in programs remained common into the early 1980s. The company published several books, the most successful being ''BASIC Computer Games'', the first million-selling computer book. Their ''Best of Creative Computing'' collections were also popular. ''Creative Computing'' also published so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
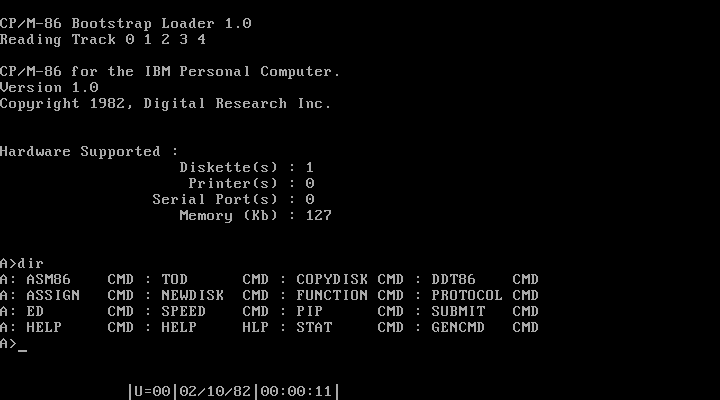
Kanji CP/M-86
CP/M-86 was a version of the CP/M operating system that Digital Research (DR) made for the Intel 8086 and Intel 8088. The system commands are the same as in CP/M-80. Executable files used the relocatable .CMD file format. Digital Research also produced a multi-user multitasking operating system compatible with CP/M-86, MP/M-86, which later evolved into Concurrent CP/M-86. When an emulator was added to provide PC DOS compatibility, the system was renamed Concurrent DOS, which later became Multiuser DOS, of which REAL/32 is the latest incarnation. The FlexOS, DOS Plus, and DR DOS families of operating systems started as derivations of Concurrent DOS as well. History Digital Research's CP/M-86 was originally announced to be released in November 1979, but was delayed repeatedly. When IBM contacted other companies to obtain components for the IBM PC, the as-yet unreleased CP/M-86 was its first choice for an operating system because CP/M had the most applications at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unix
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and others. Initially intended for use inside the Bell System, AT&T licensed Unix to outside parties in the late 1970s, leading to a variety of both academic and commercial Unix variants from vendors including University of California, Berkeley (Berkeley Software Distribution, BSD), Microsoft (Xenix), Sun Microsystems (SunOS/Solaris (operating system), Solaris), Hewlett-Packard, HP/Hewlett Packard Enterprise, HPE (HP-UX), and IBM (IBM AIX, AIX). In the early 1990s, AT&T sold its rights in Unix to Novell, which then sold the UNIX trademark to The Open Group, an industry consortium founded in 1996. The Open Group allows the use of the mark for certified operating systems that comply with the Single UNIX Specification (SUS). Unix systems are chara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CP/M
CP/M, originally standing for Control Program/Monitor and later Control Program for Microcomputers, is a mass-market operating system created in 1974 for Intel 8080/ 85-based microcomputers by Gary Kildall of Digital Research, Inc. Initially confined to single-tasking on 8-bit processors and no more than 64 kilobytes of memory, later versions of CP/M added multi-user variations and were migrated to 16-bit processors. The combination of CP/M and S-100 bus computers became an early standard in the microcomputer industry. This computer platform was widely used in business through the late 1970s and into the mid-1980s. CP/M increased the market size for both hardware and software by greatly reducing the amount of programming required to install an application on a new manufacturer's computer. An important driver of software innovation was the advent of (comparatively) low-cost microcomputers running CP/M, as independent programmers and hackers bought them and shared their crea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MS-DOS
MS-DOS ( ; acronym for Microsoft Disk Operating System, also known as Microsoft DOS) is an operating system for x86-based personal computers mostly developed by Microsoft. Collectively, MS-DOS, its rebranding as IBM PC DOS, and a few operating systems attempting to be compatible with MS-DOS, are sometimes referred to as "DOS" (which is also the generic acronym for disk operating system). MS-DOS was the main operating system for IBM PC compatibles during the 1980s, from which point it was gradually superseded by operating systems offering a graphical user interface (GUI), in various generations of the graphical Microsoft Windows operating system. IBM licensed and re-released it in 1981 as PC DOS 1.0 for use in its PCs. Although MS-DOS and PC DOS were initially developed in parallel by Microsoft and IBM, the two products diverged after twelve years, in 1993, with recognizable differences in compatibility, syntax, and capabilities. Beginning in 1988 with DR-DO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MP/M-86
MP/M (Multi-Programming Monitor Control Program) is a discontinued multi-user version of the CP/M operating system, created by Digital Research developer Tom Rolander in 1979. It allowed multiple users to connect to a single computer, each using a separate terminal. MP/M was a fairly advanced operating system for its era, at least on microcomputers. It included a priority-scheduled multitasking kernel (before such a name was used, the kernel was referred to as the ''nucleus'') with memory protection, concurrent input/output (XIOS) and support for spooling and queueing. It also allowed for each user to run multiple programs, and switch between them. MP/M platforms MP/M-80 The 8-bit system required a 8080 (or Z80) CPU and a minimum of 32 KB of RAM to run, but this left little memory for user applications. In order to support reasonable setups, MP/M allowed for memory to be switched in and out of the machine's "real memory" area. So for instance a program might be load ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concurrent CP/M-86
MP/M (Multi-Programming Monitor Control Program) is a discontinued multi-user version of the CP/M operating system, created by Digital Research developer Tom Rolander in 1979. It allowed multiple users to connect to a single computer, each using a separate terminal. MP/M was a fairly advanced operating system for its era, at least on microcomputers. It included a priority-scheduled multitasking kernel (before such a name was used, the kernel was referred to as the ''nucleus'') with memory protection, concurrent input/output (XIOS) and support for spooling and queueing. It also allowed for each user to run multiple programs, and switch between them. MP/M platforms MP/M-80 The 8-bit system required a 8080 (or Z80) CPU and a minimum of 32 KB of RAM to run, but this left little memory for user applications. In order to support reasonable setups, MP/M allowed for memory to be switched in and out of the machine's "real memory" area. So for instance a program might be loaded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intel 8086
The 8086 (also called iAPX 86) is a 16-bit microprocessor chip designed by Intel between early 1976 and June 8, 1978, when it was released. The Intel 8088, released July 1, 1979, is a slightly modified chip with an external 8-bit data bus (allowing the use of cheaper and fewer supporting ICs),Fewer TTL buffers, latches, multiplexers (although the amount of TTL logic was not drastically reduced). It also permits the use of cheap 8080-family ICs, where the 8254 CTC, 8255 PIO, and 8259 PIC were used in the IBM PC design. In addition, it makes PCB layout simpler and boards cheaper, as well as demanding fewer (1- or 4-bit wide) DRAM chips. and is notable as the processor used in the original IBM PC design. The 8086 gave rise to the x86 architecture, which eventually became Intel's most successful line of processors. On June 5, 2018, Intel released a limited-edition CPU celebrating the 40th anniversary of the Intel 8086, called the Intel Core i7-8086K. History Background In 1972, I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |