|
Fry Model Railway
The Casino Model Railway Museum at Malahide, Ireland (previously called the Fry Model Railway) is the display home for the Fry Model Collection in the refurbished Casino cottage building in central Malahide. It opened to the public on 22 January 2020. The railway and collection was moved from its previous home in Malahide Castle in 2010. The collection originated from the work of Cyril Fry who had created the collection to run on his layout at his cottage in Churchtown, Dublin. History The layout and collection was created by the railway engineer and draughtsman Cyril Fry, an employee of Inchicore Works, and his family. The collection of models passed to Dublin Tourism in the 1970s, following Mr Fry's death. Following work by retired CIÉ craftsman Thomas Tighe at Inchicore Works a new model railway was moved to Malahide Castle in 1988, which operated with models made by other modellers, with the Fry collection on display in viewing cases. Move from Malahide Castle The e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malahide
Malahide ( ; ) is an affluent coastal settlement in Fingal, County Dublin, Ireland, situated north of Dublin city. It has a village centre surrounded by suburban housing estates, with a population of over 17,000. Malahide Castle dates from the 12th century and is surrounded by a large park, part of which incorporates an international cricket ground. The area also features a sandy beach, a marina, and a variety of sporting clubs. Etymology The modern name Malahide comes from "Mullach Íde", possibly meaning "the hill of Íde" or "Íde's sand-hill"; it could also mean "Sand-hills of the Hydes" (from Mullac h-Íde), in turn probably referring to a Norman family from the Donabate area. According to the Placenames Database of Ireland the name Malahide is possibly derived from the Irish "Baile Átha Thíd" meaning "the town of the ford of Thíd", which may have been a ford at the mouth of the Gaybrook Stream, on the road to Swords. Malahide Bay was anciently called ''Inber Domnann'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
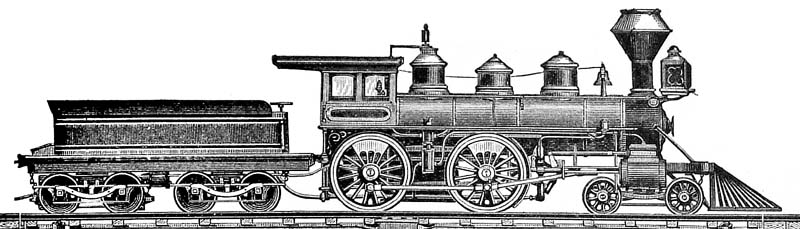
Hibernia (locomotive)
''Hibernia'' was a steam locomotive designed by Richard Roberts and built by Sharp, Roberts and Company in 1834 for the Dublin and Kingstown Railway (D&KR). The locomotive had vertical cylinders driving via bell cranks. History Procurement The D&KR left it until August 1833 before inviting nine firms to tender for 6 identical engines to enable part swapping to be delivered by 1 May 1834, the seven firms replying indicating timescales were short given the infancy of locomotive engineering with manufacturers on a steep learning curve. The D&KR engaged John Urpeth Rastrick who had been judge at the 1830 Rainhill Trials to visit the manufacturers. Rastrick visited six as well as the L&MR works and delivered to board a specification which strongly matched the L&MR No. 32 ''Experiment'' from Sharp, Roberts and Co. D&KR's Bergin visited the L&MR and expressed concerns over ''Experiment's'' unique features, vibrations and fuel consumption. The D&KR's consultant engineer Charles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GS&WR Class 900
The Great Southern and Western Railway (GS&WR) Class 900 consisted of a pair of 4-8-0T locomotives designed by E.A. Watson and introduced in 1915 and 1924 as a heavy shunter and banker for use on the relatively severe gradient from Kingsbridge to Clondalkin. Design The locomotives were unique as being the only locomotives with eight-coupled driving wheels on the Irish gauge, though Watson had chosen to dismiss drawings for at 0-8-2T prepared under his predecessor R. E. L. Maunsell. The cylinders drove the leading coupled driving axle. Some components were common with GS&WR Class 362 and 368. Operation They were noted as being prone to derailment on sidings which could have sharp curves and be poorly ballasted, though thin flanges on the middle driving wheels combined with a long wheelbase and additional weight on the leading axle may equally have been factors. Engine 900 was later converted to a -6-2Tby removing the coupling rods to the rear driving wheels. Engine 901 wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GS&WR Class 500
The Great Southern and Western Railway (GS&WR) Class 500 were 4-6-0 locomotives intended for mixed-traffic work. The lead member of the class was built in 1924 under the GS&WR, the remaining two in 1926 under the amalgamated grouping of the Great Southern Railways (GSR). Design The locomotive was designed by J. R. Bazin who sought to avoid some issues with the unrebuilt GS&WR 400 Class and was aimed at being a mixed-tyraffic type. Use of a valve travel of and a lap was a significant contributor to the performance of the type. The boiler was interchangeable with the existing GS&WR 400 Class. Service Although a mixed-traffic type the engines could and were often used on passenger services which were the domain of the GS&WR 400 Class. It was pointed out in a 1948 report their smaller wheels made them unsuitable for that work and they should be allocated to goods and night mails. Livery The locomotives were painted in Standard GS&WR/GSR Livery. Model A model by C.R. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-6-0
A 4-6-0 steam locomotive, under the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement, has four leading wheels on two axles in a leading bogie and six powered and coupled driving wheels on three axles with the absence of trailing wheels. In the mid-19th century, this wheel arrangement became the second-most-popular configuration for new steam locomotives in the United States, where this type is commonly referred to as a ten-wheeler.White, John H., Jr. (1968). ''A history of the American locomotive; its development: 1830-1880''. New York, NY: Dover Publications. p. 57. As locomotives pulling trains of lightweight all-wood passenger cars from the 1890 to the 1920s, they were exceptionally stable at near speeds on the New York Central's New York-to-Chicago Water Level Route and on the Reading Railroad's line from Camden to Atlantic City, New Jersey. Overview Tender locomotives During the second half of the nineteenth and first half of the twenti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GS&WR Class 362
The Great Southern and Western Railway (GS&WR) Class 362, also known as class B3, consisted of six locomotives designed by Robert Coey and built between 1905 and 1907 for goods traffic and was the first tender locomotive to utilise the wheel arrangement in Ireland. History The class was designed to be more powerful than his preceding class 355 . It was the first mainline use of the wheel arrangement in Ireland, and an axle loading of under . Chas. S. Lake, in his book ''Locomotives of 1906'' illustrated the type as en example of the becoming considered for other than express passenger usage, the Class 362 with its driving wheels optimised for freight work. The GS&WR selected engine 366 to be displayed at the 1907 Dublin Exhibition. While the designed increase in power was achieved the type did have some operational issues, these included being too long for some turntables, a tendency for rough riding at speed and incidents of derailment due to lack of weight on the forwa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Goulding
William Goulding (15 November 1817 – 8 December 1884) was an Irish Conservative Party politician from Cork. He was a Member of Parliament (MP) from 1876 to 1880. At the general election in February 1874, he was stood unsuccessfully as a candidate in Cork City, where both seats were won by nationalist Repeal Association candidates. After the Home Rule League MP Joseph Ronayne died in May 1876, the nationalist vote at the resulting by-election was split between two candidates for the single seat, and Goulding won the seat in the House of Commons. However, at the 1880 general election, nationalists fielded only two candidates for Cork's two seats, and Goulding was defeated. He stood again at the by-election in February 1884 after the resignation of John Daly, but was defeated again. Two Conservatives candidates contested Cork City at the 1885 general election, and one Unionist candidate stood at the by-election in 1891, but Goulding was the last Conservative or Unionist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-4-0
4-4-0 is a locomotive type with a classification that uses the Whyte notation for the classification of steam locomotives by wheel arrangement and represents the arrangement: four leading wheels on two axles (usually in a leading bogie), four powered and coupled driving wheels on two axles, and a lack of trailing wheels. Due to the large number of the type that were produced and used in the United States, the 4-4-0 is most commonly known as the American type, but the type subsequently also became popular in the United Kingdom, where large numbers were produced.White, John H., Jr. (1968). ''A history of the American locomotive; its development: 1830-1880''. New York: Dover Publications, pp. 46-. Almost every major railroad that operated in North America in the first half of the 19th century owned and operated locomotives of this type. The first use of the name ''American'' to describe locomotives of this wheel arrangement was made by ''Railroad Gazette'' in April 1872. Prior to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GS&WR Class 341
The Great Southern and Western Railway (GS&WR) Class 341 consisted of a single 4-4-0 express passenger locomotive named Sir William Goulding introduced in 1913 for the Dublin—Cork route. Despite being an apparently capable design it was withdrawn in 1928. Design Design was begun by Robert Coey who retired through ill health and completed by Richard Maunsell who was later to design the UK Southern Railway ''Schools'' 4-4-0. Equipped with a large diameter boiler and Schmidt superheater. It was unique for the GS&WR and its successor the GSR in having inside Walschaerts valve gear. This design was at the limit achievable by a 4-4-0 within the axle weight restriction limits and it was weighed regularly to ensure compliance. The only change to the initial design was a later reduction in cylinder diameter Service Due to weight restrictions it served on the Dublin—Cork route only where from 1916 it later shared services with the new EA Watson designed 400 Class 4-6-0 against w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GS&WR Class 47
The Great Southern and Western Railway (GS&WR) Class 47 consisted of twenty locomotives designed by Alexander McDonnell and introduced from 1883. They were intended for branch lines around Cork and for Dublin—Kildare and Dublin-Kilkenny services. Class 47 was preceded by four members of class 28 introduced from about 1879, these having a slightly longer wheelbase. Only one of class 28 remaining into GSR service when it was renumbered 40 and included in GSR Class 47. This was the 100th locomotive built under the Alexander McDonnell period and was temporarily numbered 100 when new. Model There is a detailed O Gauge O scale (or O gauge) is a scale commonly used for toy trains and rail transport modelling. Introduced by German toy manufacturer Märklin around 1900, by the 1930s three-rail alternating current O gauge was the most common model railroad scal ... model of engine 47 in the Fry model railway collection. References {{DEFAULTSORT:GSandWR Class 47 0-4-4BT l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Southern And Western Railway
The Great Southern and Western Railway (GS&WR) was an Irish gauge () railway company in Ireland from 1844 until 1924. The GS&WR grew by building lines and making a series of takeovers, until in the late 19th and early 20th centuries it was the largest of Ireland's "Big Four" railway networks. At its peak the GS&WR had an network, of which were double track. The core of the GS&WR was the Dublin Kingsbridge – main line; Ireland's "Premier Line", and still one of her most important main line railways. The company's headquarters were at Kingsbridge station. At its greatest extent the GS&WR included, in addition to the Dublin – Cork main line, the Dublin – and – Waterford lines and numerous branch lines. Origins There had been earlier attempts to set up main line railways to the south of Ireland but the 1840s efforts of Peter Purcell, a wealthy landowner and mail coach operator, and his associates were ultimately to prove successful with the implementation of a bill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |