|
Friedrich Albin Hoffmann
Friedrich Albin Hoffmann (13 November 1843, Ruhrort – 13 November 1924, Leipzig) was a German internist. He studied medicine in Würzburg, Tübingen and Berlin, and after graduation (1868), he became an assistant to Friedrich Theodor von Frerichs (1819-1885) in the First Medical Clinic at the University of Berlin. In 1872 he became habilitated for special pathology and therapy (internal medicine), and from 1874 was a professor of internal medicine at the University of Dorpat. From 1886 to 1920 he served as a professor of internal medicine and director of the university polyclinic in University of Leipzig, Leipzig. He was considered an excellent diagnostician, dedicated to histology, histological research in the field of internal medicine. His primary focus dealt with diseases of the bronchi and mediastinum as well as blood diseases, blood and metabolic disorders. With Paul Langerhans (1847-1888), he investigated the "intravital microscopy, intravital storage" of cinnabar in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Albin Hoffmann
Friedrich Albin Hoffmann (13 November 1843, Ruhrort – 13 November 1924, Leipzig) was a German internist. He studied medicine in Würzburg, Tübingen and Berlin, and after graduation (1868), he became an assistant to Friedrich Theodor von Frerichs (1819-1885) in the First Medical Clinic at the University of Berlin. In 1872 he became habilitated for special pathology and therapy (internal medicine), and from 1874 was a professor of internal medicine at the University of Dorpat. From 1886 to 1920 he served as a professor of internal medicine and director of the university polyclinic in University of Leipzig, Leipzig. He was considered an excellent diagnostician, dedicated to histology, histological research in the field of internal medicine. His primary focus dealt with diseases of the bronchi and mediastinum as well as blood diseases, blood and metabolic disorders. With Paul Langerhans (1847-1888), he investigated the "intravital microscopy, intravital storage" of cinnabar in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Diseases
:''This is an incomplete list, which may never be able to satisfy certain standards for completion.'' There are many conditions of or affecting the human hematologic system—the biological system that includes plasma, platelets, leukocytes, and erythrocytes, the major components of blood and the bone marrow. Anemias An anemia is a decrease in number of red blood cells (RBCs) or less than the normal quantity of hemoglobin Hemoglobin (haemoglobin BrE) (from the Greek word αἷμα, ''haîma'' 'blood' + Latin ''globus'' 'ball, sphere' + ''-in'') (), abbreviated Hb or Hgb, is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein present in red blood cells (erythrocyte ... in the blood.MedicineNet.com Definition of Anemia Last Editorial Review: 12/9/2000 Retrieved March 27, 2011 [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Who Named It
''Whonamedit?'' is an online English-language dictionary of medical eponyms and the people associated with their identification. Though it is a dictionary, many eponyms and persons are presented in extensive articles with comprehensive bibliographies. The dictionary is hosted in Norway and maintained by medical historian Ole Daniel Enersen Ole Daniel Enersen (born March 14, 1943, in Oslo, Norway) is a Norwegian climber, photographer, journalist, writer, and medical historian. In 1965 he made the first ascent of the Trollveggen mountain in Romsdalen, Norway, along with Leif Norman .... References External links * Medical websites Medical dictionaries Eponyms {{online-dict-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mononuclear Phagocyte System
In immunology, the mononuclear phagocyte system or mononuclear phagocytic system (MPS) also known as the reticuloendothelial system or macrophage system is a part of the immune system that consists of the phagocytic cells located in reticular connective tissue. The cells are primarily monocytes and macrophages, and they accumulate in lymph nodes and the spleen. The Kupffer cells of the liver and tissue histiocytes are also part of the MPS. The mononuclear phagocyte system and the monocyte macrophage system refer to two different entities, often mistakenly understood as one. "Reticuloendothelial system" is an older term for the mononuclear phagocyte system, but it is used less commonly now, as it is understood that most endothelial cells are not macrophages. The mononuclear phagocyte system is also a somewhat dated concept trying to combine a broad range of cells, and should be used with caution. Cell types and locations The spleen is the second largest unit of the mononuclear ph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludwig Aschoff
Karl Albert Ludwig Aschoff (10 January 1866 – 24 June 1942) was a German physician and pathologist. He is considered to be one of the most influential pathologists of the early 20th century and is regarded as the most important German pathologist after Rudolf Virchow. Early life and education Aschoff was born in Berlin, Prussia on 10 January 1866. He studied medicine at the University of Bonn, University of Strasbourg, and the University of Würzburg. Career After his habilitation in 1894, Ludwig Aschoff was appointed professor for pathology at the University of Göttingen in 1901. Aschoff transferred to the University of Marburg in 1903 to head the department for pathological anatomy. In 1906, he accepted a position as ordinarius at the University of Freiburg, where he remained until his death. Aschoff was interested in the pathology and pathophysiology of the heart. He discovered nodules in the myocardium present during rheumatic fever, the so-called Aschoff bodies. Aschoff ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Capillary System
A capillary is a small blood vessel from 5 to 10 micrometres (μm) in diameter. Capillaries are composed of only the tunica intima, consisting of a thin wall of simple squamous endothelial cells. They are the smallest blood vessels in the body: they convey blood between the arterioles and venules. These microvessels are the site of exchange of many substances with the interstitial fluid surrounding them. Substances which cross capillaries include water, oxygen, carbon dioxide, urea, glucose, uric acid, lactic acid and creatinine. Lymph capillaries connect with larger lymph vessels to drain lymphatic fluid collected in the microcirculation. During early embryonic development, new capillaries are formed through vasculogenesis, the process of blood vessel formation that occurs through a '' de novo'' production of endothelial cells that then form vascular tubes. The term ''angiogenesis'' denotes the formation of new capillaries from pre-existing blood vessels and already present endo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrant (anatomy), right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm. Its other roles in metabolism include the regulation of Glycogen, glycogen storage, decomposition of red blood cells, and the production of hormones. The liver is an accessory digestive organ that produces bile, an alkaline fluid containing cholesterol and bile acids, which helps the fatty acid degradation, breakdown of fat. The gallbladder, a small pouch that sits just under the liver, stores bile produced by the liver which is later moved to the small intestine to complete digestion. The liver's highly specialized biological tissue, tissue, consisting mostly of hepatocytes, regulates a w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Connective Tissue
Connective tissue is one of the four primary types of animal tissue, along with epithelial tissue, muscle tissue, and nervous tissue. It develops from the mesenchyme derived from the mesoderm the middle embryonic germ layer. Connective tissue is found in between other tissues everywhere in the body, including the nervous system. The three meninges, membranes that envelop the brain and spinal cord are composed of connective tissue. Most types of connective tissue consists of three main components: elastic and collagen fibers, ground substance, and cells. Blood, and lymph are classed as specialized fluid connective tissues that do not contain fiber. All are immersed in the body water. The cells of connective tissue include fibroblasts, adipocytes, macrophages, mast cells and leucocytes. The term "connective tissue" (in German, ''Bindegewebe'') was introduced in 1830 by Johannes Peter Müller. The tissue was already recognized as a distinct class in the 18th century. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
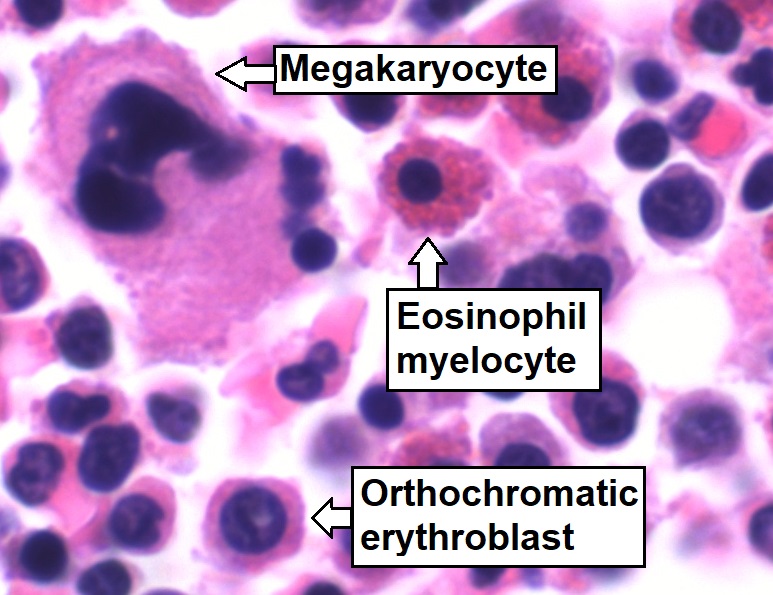
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a semi-solid tissue found within the spongy (also known as cancellous) portions of bones. In birds and mammals, bone marrow is the primary site of new blood cell production (or haematopoiesis). It is composed of hematopoietic cells, marrow adipose tissue, and supportive stromal cells. In adult humans, bone marrow is primarily located in the ribs, vertebrae, sternum, and bones of the pelvis. Bone marrow comprises approximately 5% of total body mass in healthy adult humans, such that a man weighing 73 kg (161 lbs) will have around 3.7 kg (8 lbs) of bone marrow. Human marrow produces approximately 500 billion blood cells per day, which join the systemic circulation via permeable vasculature sinusoids within the medullary cavity. All types of hematopoietic cells, including both myeloid and lymphoid lineages, are created in bone marrow; however, lymphoid cells must migrate to other lymphoid organs (e.g. thymus) in order to complete maturation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Blood Corpuscles
Red blood cells (RBCs), also referred to as red cells, red blood corpuscles (in humans or other animals not having nucleus in red blood cells), haematids, erythroid cells or erythrocytes (from Greek ''erythros'' for "red" and ''kytos'' for "hollow vessel", with ''-cyte'' translated as "cell" in modern usage), are the most common type of blood cell and the vertebrate's principal means of delivering oxygen (O2) to the body tissues—via blood flow through the circulatory system. RBCs take up oxygen in the lungs, or in fish the gills, and release it into tissues while squeezing through the body's capillaries. The cytoplasm of a red blood cell is rich in hemoglobin, an iron-containing biomolecule that can bind oxygen and is responsible for the red color of the cells and the blood. Each human red blood cell contains approximately 270 million hemoglobin molecules. The cell membrane is composed of proteins and lipids, and this structure provides properties essential for physiologi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White Blood Corpuscles
White blood cells, also called leukocytes or leucocytes, are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells. Leukocytes are found throughout the body, including the blood and lymphatic system. All white blood cells have nuclei, which distinguishes them from the other blood cells, the anucleated red blood cells (RBCs) and platelets. The different white blood cells are usually classified by cell lineage (myeloid cells or lymphoid cells). White blood cells are part of the body's immune system. They help the body fight infection and other diseases. Types of white blood cells are granulocytes (neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils), and agranulocytes (monocytes, and lymphocytes (T cells and B cells)). Myeloid cells (myelocytes) include neutrophils, eosinophils, mast cells, basophi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |