|
Fried- Und Freudenreiche Hinfarth
("With peace and joy"), BuxWV 76, is the common name for a piece of funeral music composed by Dieterich Buxtehude as an homage to his father in 1674. The composer named the work (Departure enriched by Peace and Joy) when he published it the same year. It is a bundle of two compositions, the earlier , BuxWV 76a, a setting of Luther's hymn composed in 1671 reflecting the death of Menno Hanneken, and the elegy (Song of mourning, lament), BuxWV 76b, an aria in seven stanzas. The incipit of the elegy, "", translates roughly to "Even if death must separate us". It is one of few compositions published during Buxtehude's lifetime. History In 1671, Buxtehude composed funeral music on the death of , a superintendent and minister at the Marienkirche in Lübeck, where Buxtehude performed his concert series, the ''Abendmusiken''. Buxtehude composed a canon, ''Divertisons nous'' (BuxWV 124), written in an album of Menno's son and dated 1670, showing that he had good relations with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dieterich Buxtehude
Dieterich Buxtehude (; ; born Diderik Hansen Buxtehude; c. 1637 – 9 May 1707) was a Danish organist and composer of the Baroque period, whose works are typical of the North German organ school. As a composer who worked in various vocal and instrumental idioms, Buxtehude's style greatly influenced other composers, such as Johann Sebastian Bach. Buxtehude is considered one of the most important composers of the 17th century. Life Early years in Denmark He is thought to have been born with the name Diderich Buxtehude.Snyder, Kerala J. Dieterich Buxtehude: Organist in Lübeck. New York: Schirmer Books, 1987. His parents were Johannes (Hans Jensen) Buxtehude and Helle Jespersdatter. His father originated from Oldesloe in the Duchy of Holstein, which at that time was a part of the Danish realms in Northern Germany. Scholars dispute both the year and country of Dieterich's birth, although most now accept that he was born in 1637 in Helsingborg, Skåne at the time part of De ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cantus Firmus
In music, a ''cantus firmus'' ("fixed melody") is a pre-existing melody forming the basis of a polyphonic composition. The plural of this Latin term is , although the corrupt form ''canti firmi'' (resulting from the grammatically incorrect treatment of ''cantus'' as a second- rather than a fourth-declension noun) can also be found. The Italian is often used instead: (and the plural in Italian is ). History The term first appears in theoretical writings early in the 13th century (e.g., Boncampagno da Signa, ''Rhetorica novissima'', 1235). The earliest polyphonic compositions almost always involved a cantus firmus, typically a Gregorian chant, although by convention the term is not applied to music written before the 14th century. The earliest surviving polyphonic compositions, in the ''Musica enchiriadis'' (around 900 AD), contain the chant in the top voice, and the newly composed part underneath; however, this usage changed around 1100, after which the cantus firmus typicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ricercar Consort
The Ricercar Consort is a Belgian instrumental ensemble founded in 1980 together with the Ricercar record label of Jérôme Lejeune. The founding members were violinist François Fernandez, organist Bernard Foccroulle, and viola da gamba player Philippe Pierlot. The initial repertoire was focussed on the German Baroque, and the Consort was closely identified with the series ''Deutsche Barock Kantaten''. In recordings and concerts, the Consort was joined by baroque specialist singers including; Greta De Reyghere, Agnès Mellon, countertenors Henri Ledroit, James Bowman, tenor Guy de Mey, and bass Max van Egmond, as well as the cornett player Jean Tubéry. The consort is associated with the ''Festival Bach en Vallée Mosane'' held in the valley of the Meuse. Recordings < ...
|
St John Passion
The ''Passio secundum Joannem'' or ''St John Passion'' (german: Johannes-Passion, link=no), BWV 245, is a Passion or oratorio by Johann Sebastian Bach, the older of the surviving Passions by Bach. It was written during his first year as director of church music in Leipzig and was first performed on April 7, 1724, at Good Friday Vespers at the St. Nicholas Church. The structure of the work falls in two halves, intended to flank a sermon. The anonymous libretto draws on existing works (notably by Barthold Heinrich Brockes) and is compiled from recitatives and choruses narrating the Passion of Christ as told in the Gospel of John, ariosos and arias reflecting on the action, and chorales using hymn tunes and texts familiar to a congregation of Bach's contemporaries. Compared with the ''St Matthew Passion'', the ''St John Passion'' has been described as more extravagant, with an expressive immediacy, at times more unbridled and less "finished". The work is most often heard toda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
St John Passion Structure
The structure of the ''St John Passion'' (german: Johannes-Passion, link=no), BWV 245, a sacred oratorio by Johann Sebastian Bach, is "carefully designed with a great deal of musico-theological intent". Some main aspects of the structure are shown in tables below. The original Latin title translates to "Passion according to John". Bach's large choral composition in two parts on German text, written to be performed in a Lutheran service on Good Friday, is based on the Passion, as told in two chapters from the Gospel of John ( and ) in the translation by Martin Luther, with two short interpolations from the Gospel of Matthew (in the earliest version, one is from the Gospel of Matthew and one from the Gospel of Mark). During the vespers service, the two parts of the work were performed before and after the sermon. Part I covers the events until Peter's denial of Jesus, Part II concludes with the burial of Jesus. The Bible text is reflected in contemporary poetry and in chorales t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
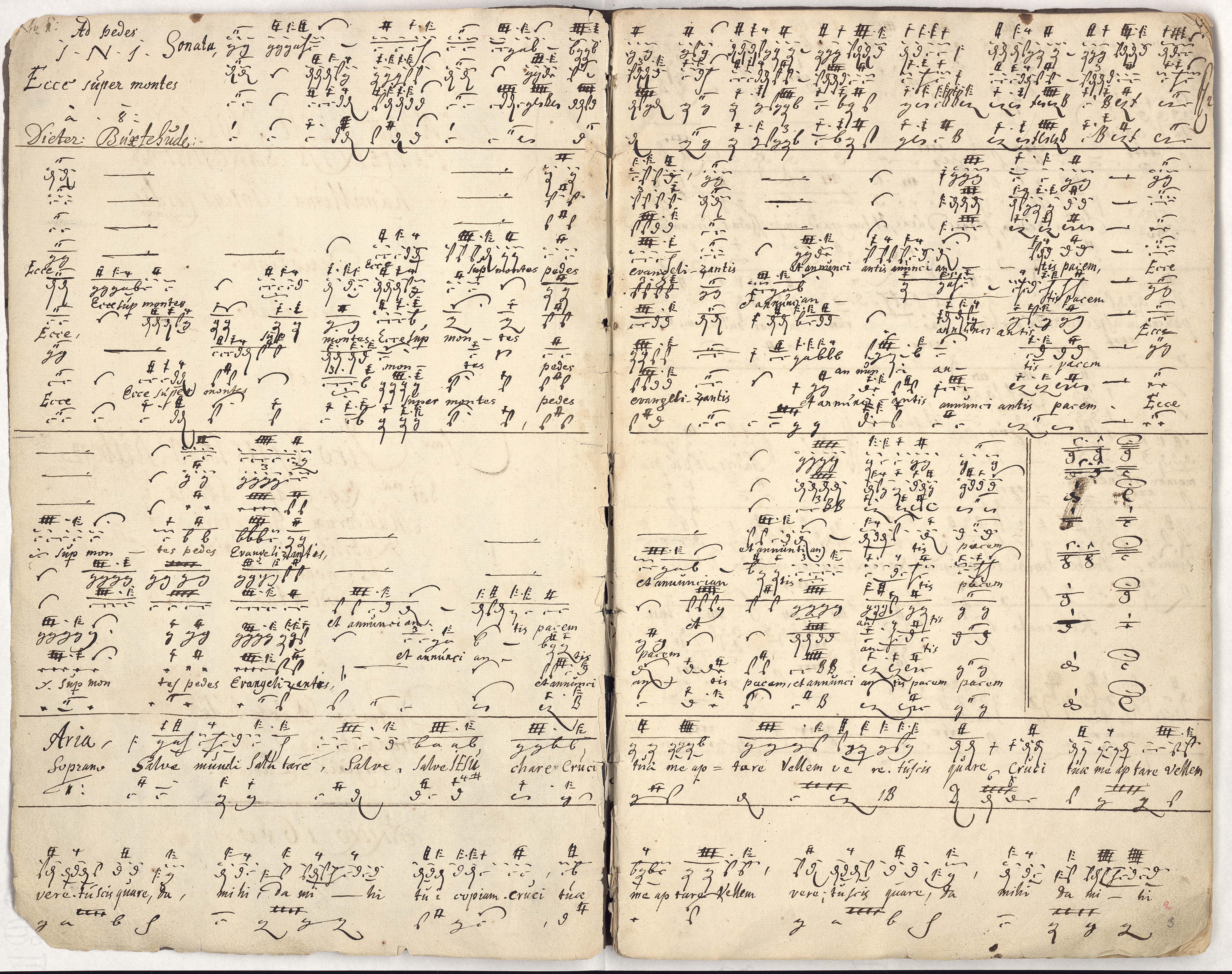
Membra Jesu Nostri
''Membra Jesu nostri'', BuxWV 75, is a cycle of seven cantatas composed in 1680 by Dieterich Buxtehude and dedicated to Gustaf Düben. More specifically and fully it is, in Buxtehude’s phrase, a ''�devotionedecantata,”'' or “sung devotion,” titled ''Membra Jesu nostri patientis sanctissima'', which translates from the Latin as ''Limbs Most Holy of Our Suffering Jesus''. Regarding genre, the cycle consists in seven concerto-aria cantatas, a form that had emerged in Germany in the 1660s. The stanzas of its main text are drawn from the medieval hymn ''Salve mundi salutare'', also known as the ''Rhythmica oratio'', formerly ascribed to Bernard of Clairvaux but now thought to be by Arnulf of Leuven. Each cantata addresses a part of Jesus’ crucified body: feet, knees, hands, side, breast, heart and face; in each, Biblical words referring to the limb frame verses of the hymn’s text. Structure Each cantata in ''Membra Jesu nostri'' is divided into six sections; an instrume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viol Consort
The viol (), viola da gamba (), or informally gamba, is any one of a family of bowed, fretted, and stringed instruments with hollow wooden bodies and pegboxes where the tension on the strings can be increased or decreased to adjust the pitch of each of the strings. Frets on the viol are usually made of gut, tied on the fingerboard around the instrument's neck, to enable the performer to stop the strings more cleanly. Frets improve consistency of intonation and lend the stopped notes a tone that better matches the open strings. Viols first appeared in Spain in the mid-to-late 15th century, and were most popular in the Renaissance and Baroque (1600–1750) periods. Early ancestors include the Arabic ''rebab'' and the medieval European vielle,Otterstedt, Annette. ''The Viol: History of an Instrument. ''Kassel: Barenreiter;-Verlag Karl Votterle GmbH & Co; 2002. but later, more direct possible ancestors include the Venetian ''viole'' and the 15th- and 16th-century Spanish ''vihuela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viol
The viol (), viola da gamba (), or informally gamba, is any one of a family of bowed, fretted, and stringed instruments with hollow wooden bodies and pegboxes where the tension on the strings can be increased or decreased to adjust the pitch of each of the strings. Frets on the viol are usually made of gut, tied on the fingerboard around the instrument's neck, to enable the performer to stop the strings more cleanly. Frets improve consistency of intonation and lend the stopped notes a tone that better matches the open strings. Viols first appeared in Spain in the mid-to-late 15th century, and were most popular in the Renaissance and Baroque (1600–1750) periods. Early ancestors include the Arabic '' rebab'' and the medieval European vielle,Otterstedt, Annette. ''The Viol: History of an Instrument. ''Kassel: Barenreiter;-Verlag Karl Votterle GmbH & Co; 2002. but later, more direct possible ancestors include the Venetian ''viole'' and the 15th- and 16th-century Spanish ''vihue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Düben Collection
The Düben collection is a collection of musical manuscripts named after the original collector, Gustaf Düben, held in the Uppsala University Library. It includes much 17th-century baroque music, in particular the only surviving copies of many works by Dieterich Buxtehude. Chronology The collection was compiled starting in the 1640s by Gustaf Düben, and by subsequent members of the family, who held positions at the Swedish Court Chapel. It was ultimately bequeathed to the Uppsala University Library in 1732. Owing to the music it contained being by then mostly out of fashion, it remained there, in neglect but intact, for most of the 18th and 19th centuries. It was ultimately catalogued in the 1880s by librarian Anders Lagerberg, and, upon being noticed by a visiting German musician from Lübeck, gained the attention of musicologists due to it containing copies of previously unknown works by Buxtehude, and later due to its overall significance in assessing 17th-century music histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kerala J
Kerala ( ; ) is a state on the Malabar Coast of India. It was formed on 1 November 1956, following the passage of the States Reorganisation Act, by combining Malayalam-speaking regions of the erstwhile regions of Cochin, Malabar, South Canara, and Thiruvithamkoor. Spread over , Kerala is the 21st largest Indian state by area. It is bordered by Karnataka to the north and northeast, Tamil Nadu to the east and south, and the Lakshadweep Sea to the west. With 33 million inhabitants as per the 2011 census, Kerala is the 13th-largest Indian state by population. It is divided into 14 districts with the capital being Thiruvananthapuram. Malayalam is the most widely spoken language and is also the official language of the state. The Chera dynasty was the first prominent kingdom based in Kerala. The Ay kingdom in the deep south and the Ezhimala kingdom in the north formed the other kingdoms in the early years of the Common Era (CE). The region had been a prominent spice exporte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basso Continuo
Basso continuo parts, almost universal in the Baroque era (1600–1750), provided the harmonic structure of the music by supplying a bassline and a chord progression. The phrase is often shortened to continuo, and the instrumentalists playing the continuo part are called the ''continuo group''. Forces The composition of the continuo group is often left to the discretion of the performers (or, for a large performance, the conductor), and practice varied enormously within the Baroque period. At least one instrument capable of playing chords must be included, such as a harpsichord, organ, lute, theorbo, guitar, regal, or harp. In addition, any number of instruments that play in the bass register may be included, such as cello, double bass, bass viol, or bassoon. In modern performances of chamber works, the most common combination is harpsichord and cello for instrumental works and secular vocal works, such as operas, and organ and cello for sacred music. A double bass may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |