|
Frequency Response
In signal processing and electronics, the frequency response of a system is the quantitative measure of the magnitude and phase of the output as a function of input frequency. The frequency response is widely used in the design and analysis of systems, such as audio and control systems, where they simplify mathematical analysis by converting governing differential equations into algebraic equations. In an audio system, it may be used to minimize audible distortion by designing components (such as microphones, amplifiers and loudspeakers) so that the overall response is as flat (uniform) as possible across the system's bandwidth. In control systems, such as a vehicle's cruise control, it may be used to assess system stability, often through the use of Bode plots. Systems with a specific frequency response can be designed using analog and digital filters. The frequency response characterizes systems in the frequency domain, just as the impulse response characterizes systems in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Circuit
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical components (e.g., batteries, resistors, inductors, capacitors, switches, transistors) or a model of such an interconnection, consisting of electrical elements (e.g., voltage sources, current sources, resistances, inductances, capacitances). An electrical circuit is a network consisting of a closed loop, giving a return path for the current. Linear electrical networks, a special type consisting only of sources (voltage or current), linear lumped elements (resistors, capacitors, inductors), and linear distributed elements (transmission lines), have the property that signals are linearly superimposable. They are thus more easily analyzed, using powerful frequency domain methods such as Laplace transforms, to determine DC response, AC response, and transient response. A resistive circuit is a circuit containing only resistors and ideal current and voltage sources. Analysis of resistive circuits is less complicated t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Analog Filter
Analogue filters are a basic building block of signal processing much used in electronics. Amongst their many applications are the separation of an audio signal before application to bass, mid-range, and tweeter loudspeakers; the combining and later separation of multiple telephone conversations onto a single channel; the selection of a chosen radio station in a radio receiver and rejection of others. Passive linear electronic analogue filters are those filters which can be described with linear differential equations (linear); they are composed of capacitors, inductors and, sometimes, resistors (passive) and are designed to operate on continuously varying analogue signals. There are many linear filters which are not analogue in implementation (digital filter), and there are many electronic filters which may not have a passive topology – both of which may have the same transfer function of the filters described in this article. Analogue filters are most often used in wav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fast Fourier Transform
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of a sequence, or its inverse (IDFT). Fourier analysis converts a signal from its original domain (often time or space) to a representation in the frequency domain and vice versa. The DFT is obtained by decomposing a sequence of values into components of different frequencies. This operation is useful in many fields, but computing it directly from the definition is often too slow to be practical. An FFT rapidly computes such transformations by factorizing the DFT matrix into a product of sparse (mostly zero) factors. As a result, it manages to reduce the complexity of computing the DFT from O\left(N^2\right), which arises if one simply applies the definition of DFT, to O(N \log N), where N is the data size. The difference in speed can be enormous, especially for long data sets where ''N'' may be in the thousands or millions. In the presence of round-off error, many FFT algorithm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Spectrum
The power spectrum S_(f) of a time series x(t) describes the distribution of power into frequency components composing that signal. According to Fourier analysis, any physical signal can be decomposed into a number of discrete frequencies, or a spectrum of frequencies over a continuous range. The statistical average of a certain signal or sort of signal (including noise) as analyzed in terms of its frequency content, is called its spectrum. When the energy of the signal is concentrated around a finite time interval, especially if its total energy is finite, one may compute the energy spectral density. More commonly used is the power spectral density (or simply power spectrum), which applies to signals existing over ''all'' time, or over a time period large enough (especially in relation to the duration of a measurement) that it could as well have been over an infinite time interval. The power spectral density (PSD) then refers to the spectral energy distribution that would b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butterworth Response
The Butterworth filter is a type of signal processing filter designed to have a frequency response that is as flat as possible in the passband. It is also referred to as a maximally flat magnitude filter. It was first described in 1930 by the British engineer and physicist Stephen Butterworth in his paper entitled "On the Theory of Filter Amplifiers". Original paper Butterworth had a reputation for solving "impossible" mathematical problems. At the time, filter design required a considerable amount of designer experience due to limitations of the theory then in use. The filter was not in common use for over 30 years after its publication. Butterworth stated that: Such an ideal filter cannot be achieved, but Butterworth showed that successively closer approximations were obtained with increasing numbers of filter elements of the right values. At the time, filters generated substantial ripple in the passband, and the choice of component values was highly interactive. Butterwo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laplace Transform
In mathematics, the Laplace transform, named after its discoverer Pierre-Simon Laplace (), is an integral transform In mathematics, an integral transform maps a function from its original function space into another function space via integration, where some of the properties of the original function might be more easily characterized and manipulated than in ... that converts a Function (mathematics), function of a Real number, real Variable (mathematics), variable (usually t, in the ''time domain'') to a function of a Complex number, complex variable s (in the complex frequency domain, also known as ''s''-domain, or s-plane). The transform has many applications in science and engineering because it is a tool for solving differential equations. In particular, it transforms ordinary differential equations into algebraic equations and convolution into multiplication. For suitable functions ''f'', the Laplace transform is the integral \mathcal\(s) = \int_0^\infty f(t)e^ \, dt. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transfer Function
In engineering, a transfer function (also known as system function or network function) of a system, sub-system, or component is a function (mathematics), mathematical function that mathematical model, theoretically models the system's output for each possible input. They are widely used in electronics and control systems. In some simple cases, this function is a two-dimensional graph (function), graph of an independent scalar (mathematics), scalar input versus the dependent scalar output, called a transfer curve or characteristic curve. Transfer functions for components are used to design and analyze systems assembled from components, particularly using the block diagram technique, in electronics and control theory. The dimensions and units of the transfer function model the output response of the device for a range of possible inputs. For example, the transfer function of a two-port electronic circuit like an amplifier might be a two-dimensional graph of the scalar voltage at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convolution
In mathematics (in particular, functional analysis), convolution is a operation (mathematics), mathematical operation on two function (mathematics), functions ( and ) that produces a third function (f*g) that expresses how the shape of one is modified by the other. The term ''convolution'' refers to both the result function and to the process of computing it. It is defined as the integral of the product of the two functions after one is reflected about the y-axis and shifted. The choice of which function is reflected and shifted before the integral does not change the integral result (see #Properties, commutativity). The integral is evaluated for all values of shift, producing the convolution function. Some features of convolution are similar to cross-correlation: for real-valued functions, of a continuous or discrete variable, convolution (f*g) differs from cross-correlation (f \star g) only in that either or is reflected about the y-axis in convolution; thus it is a cross-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multistage Amplifier
A multistage amplifier is an electronic amplifier consisting of two or more single-stage amplifiers connected together. In this context, a single stage is an amplifier containing only a single transistor (sometimes a pair of transistors) or other active device. The most common reason for using multiple stages is to increase the gain of the amplifier in applications where the input signal is very small, for instance in radio receivers. In these applications a single stage has insufficient gain by itself. In some designs it is possible to obtain more desirable values of other parameters such as input resistance and output resistance. Connection schemes The simplest, and most common, connection scheme is a cascade connection of identical, or similar, stages forming a cascade amplifier. In a cascade connection, the output port of one stage is connected to the input port of the next. Typically, the individual stages are bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) in a common emitt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourier Transform
A Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions into frequency components, which are represented by the output of the transform as a function of frequency. Most commonly functions of time or space are transformed, which will output a function depending on temporal frequency or spatial frequency respectively. That process is also called ''analysis''. An example application would be decomposing the waveform of a musical chord into terms of the intensity of its constituent pitches. The term ''Fourier transform'' refers to both the frequency domain representation and the mathematical operation that associates the frequency domain representation to a function of space or time. The Fourier transform of a function is a complex-valued function representing the complex sinusoids that comprise the original function. For each frequency, the magnitude (absolute value) of the complex value represents the amplitude of a constituent complex sinusoid with that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
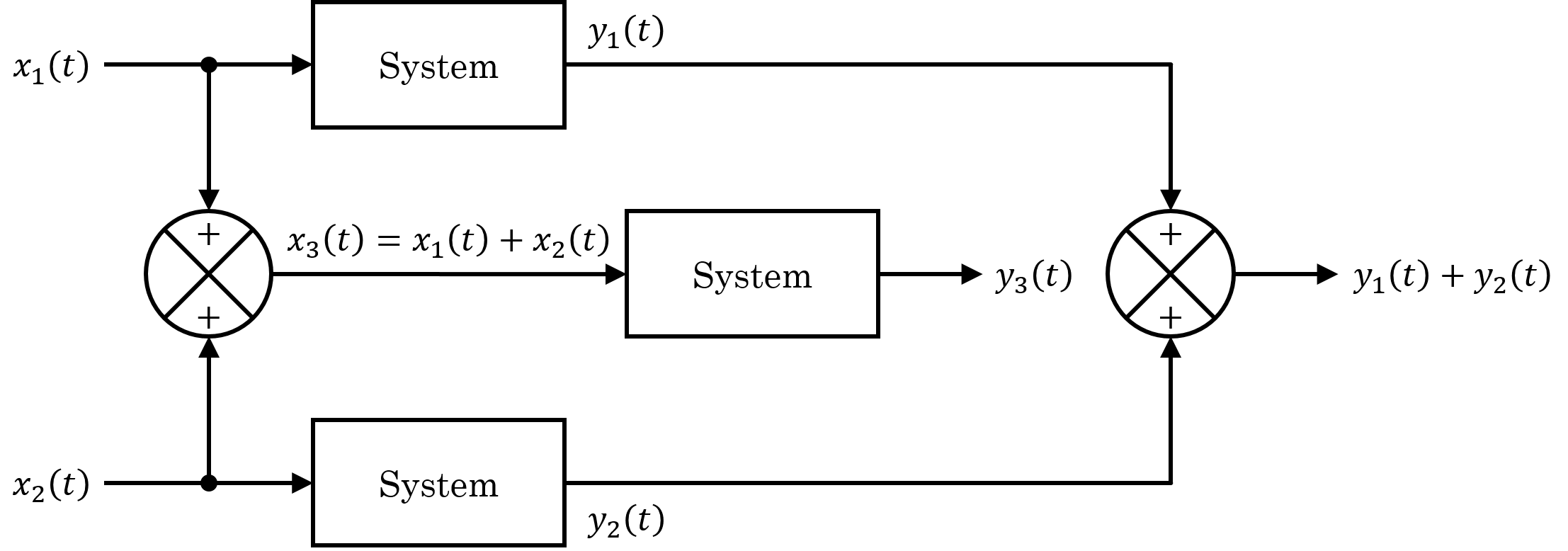
Linear System
In systems theory, a linear system is a mathematical model of a system based on the use of a linear operator. Linear systems typically exhibit features and properties that are much simpler than the nonlinear case. As a mathematical abstraction or idealization, linear systems find important applications in automatic control theory, signal processing, and telecommunications. For example, the propagation medium for wireless communication systems can often be modeled by linear systems. Definition A general deterministic system can be described by an operator, that maps an input, as a function of to an output, a type of black box description. A system is linear if and only if it satisfies the superposition principle, or equivalently both the additivity and homogeneity properties, without restrictions (that is, for all inputs, all scaling constants and all time.) The superposition principle means that a linear combination of inputs to the system produces a linear combination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Domain
Time domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions, physical signals or time series of economic or environmental data, with respect to time. In the time domain, the signal or function's value is known for all real numbers, for the case of continuous time, or at various separate instants in the case of discrete time. An oscilloscope is a tool commonly used to visualize real-world signals in the time domain. A time-domain graph shows how a signal changes with time, whereas a frequency-domain graph shows how much of the signal lies within each given frequency band over a range of frequencies. Though most precisely referring to time in physics, the term ''time domain'' may occasionally informally refer to position in space when dealing with spatial frequencies, as a substitute for the more precise term ''spatial domain''. Origin of term The use of the contrasting terms ''time domain'' and ''frequency domain'' developed in U.S. communication engineering in the late 194 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.gif)