|
French Frigate Armide (1804)
''Armide'' was a 40-gun frigate of the French Navy, lead ship of her class, and launched in 1804 at Rochefort. She served briefly in the French Navy before the Royal Navy captured her in 1806. She went on to serve in the Royal Navy until 1815 when she was broken up. French service ''Armide'' took part in Allemand's expedition of 1805. On 18 July, she captured and burnt a Prussian cutter to maintain the secrecy of the movements of the fleet, in spite of the neutrality of Prussia at the time. The next day, she captured and burnt her. She then took part in the assault on the ''Calcutta'' convoy, helping engage and capture . In March 1806, under Amable Troude, ''Armide'' helped repel an attack led by Robert Stopford at Les Sables-d'Olonne. Capture During the action of 25 September 1806, , under the command of Commodore Sir Samuel Hood, captured ''Armide'', which was under the command of Captain Jean-Jacques-Jude Langlois, and assisted in the capture of , and . ''Centaur'' los ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Whitcombe
Thomas Whitcombe (possibly 19 May 1763 – c. 1824) was a prominent British marine art, maritime painter of the Napoleonic Wars. Among his work are over 150 actions of the Royal Navy, and he exhibited at the Royal Academy, the British Institution and the Royal Society of British Artists. His pictures are highly sought after today. Life Thomas Whitcombe was born in London between 1752 and 19 May 1763, with the latter date frequently cited. Little is known of his background or training, although speculation based on the locations depicted in his paintings may provide some clues. It is known that he was in Bristol in 1787 and later travelled to the South Coast; there are few ports or harbours from this region that do not feature in his work. In 1789 he toured Wales and in 1813 he travelled to Devon, painting scenes around Plymouth harbour. During his career he also painted scenes showing the Cape of Good Hope, Madeira, Cuba and Cape Horn. Between 1783 and 1824 he lived in London ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commodore (rank)
Commodore is a senior naval rank used in many navies which is equivalent to brigadier and air commodore. It is superior to a navy captain, but below a rear admiral. It is either regarded as the most junior of the flag officers rank or may not hold the jurisdiction of a flag officer at all depending on the officer's appointment. Non-English-speaking nations commonly use the rank of flotilla admiral, counter admiral, or senior captain as an equivalent, although counter admiral may also correspond to ''rear admiral lower half'' abbreviated as RDML. Traditionally, "commodore" is the title for any officer assigned to command more than one ship, even temporarily, much as "captain" is the traditional title for the commanding officer of a single ship even if the officer's official title in the service is a lower rank. As an official rank, a commodore typically commands a flotilla or squadron of ships as part of a larger task force or naval fleet commanded by an admiral. A commodo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charente (river)
The Charente (; oc, Charanta ) is a long river in southwestern France. Its source is in the Haute-Vienne ''département'' at Chéronnac, a small village near Rochechouart. It flows through the departments of Haute-Vienne, Charente, Vienne and Charente-Maritime. The river flows into the Atlantic Ocean near Rochefort. Navigation The Charente was described by the French king François I as 'the most beautiful river in the kingdom', and was navigable in its natural state until mills were erected at many locations in the 14th century. Some locks were built but through navigation remained impossible for centuries. Improvements to the navigation were projected under Louis XVI in 1772, but work was interrupted by the Revolution. The project was revived under the Restoration and canalisation completed in 1835. The waterway was abandoned in 1957. The ''départements'' took over operation in 1963, and recreational vessels have now taken possession of the waterway throughout the 164 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oléron
The Isle of Oléron or Oléron Island (french: île d'Oléron, ; Saintongese: ''ilâte d'Olerun''; oc, illa d'Olairon or ; la, Uliarus insula, ) is an island off the Atlantic coast of France (due west of Rochefort), on the southern side of the Pertuis d'Antioche strait. It is the second largest island of Metropolitan France, after Corsica, with a length of 30 km and a width of 8 km. It has an area of 174 km and more than 21,000 permanent inhabitants. History In the 7th and 8th century, the island, along with Ré, formed the ''Vacetae Insulae'' or Vacetian Islands, according to the '' Cosmographia''. Vaceti being another name for the Vascones, the reference is evidence to Basque (Gascon) settlement or control of the islands by that date. It was at Oléron in about 1152 to 1160 that Eleanor of Aquitaine introduced the first 'maritime' or 'admiralty' laws in that part of the world: the Rolls of Oleron. In 1306, Edward I of England granted the island to his son, E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schooner
A schooner () is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: fore-and-aft rigged on all of two or more masts and, in the case of a two-masted schooner, the foremast generally being shorter than the mainmast. A common variant, the topsail schooner also has a square topsail on the foremast, to which may be added a topgallant. Differing definitions leave uncertain whether the addition of a fore course would make such a vessel a brigantine. Many schooners are gaff-rigged, but other examples include Bermuda rig and the staysail schooner. The origins of schooner rigged vessels is obscure, but there is good evidence of them from the early 17th century in paintings by Dutch marine artists. The name "schooner" first appeared in eastern North America in the early 1700s. The name may be related to a Scots word meaning to skip over water, or to skip stones. The schooner rig was used in vessels with a wide range of purposes. On a fast hull, good ability to windward was useful for priv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brig
A brig is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: two masts which are both square rig, square-rigged. Brigs originated in the second half of the 18th century and were a common type of smaller merchant vessel or warship from then until the latter part of the 19th century. In commercial use, they were gradually replaced by fore-and-aft rigged vessels such as schooners, as owners sought to reduce crew costs by having rigs that could be handled by fewer men. In Royal Navy use, brigs were retained for training use when the battle fleets consisted almost entirely of iron-hulled steamships. Brigs were prominent in the coasting coal trade of British waters. 4,395 voyages to London with coal were recorded in 1795. With an average of eight or nine trips per year for one vessel, that is a fleet of over 500 colliers trading to London alone. Other ports and coastal communities were also be served by colliers trading to Britain's coal ports. In the first half of the 19th century, the va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Rochelle
La Rochelle (, , ; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''La Rochéle''; oc, La Rochèla ) is a city on the west coast of France and a seaport on the Bay of Biscay, a part of the Atlantic Ocean. It is the capital of the Charente-Maritime department. With 75,735 inhabitants in 2017, La Rochelle is the most populated commune in the department and ranks fifth in the New Aquitaine region after Bordeaux, the regional capital, Limoges, Poitiers and Pau. Its inhabitants are called "les Rochelaises" and "les Rochelais". Situated on the edge of the Atlantic Ocean the city is connected to the Île de Ré by a bridge completed on 19 May 1988. Since the Middle-Ages the harbour has opened onto a protected strait, the Pertuis d'Antioche and is regarded as a "Door océane" or gateway to the ocean because of the presence of its three ports (fishing, trade and yachting). The city has a strong commercial tradition, having an active port from very early on in its history. La Rochelle underwent sustained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basque Roads
Basque Roads, sometimes referred to as ''Aix Roads'', is a roadstead (a sheltered bay) on the Biscay shore of the Charente-Maritime département of France, bounded by the Île d'Oléron to the west and the Île de Ré to the north. The port of La Rochelle stands at the northeast corner of the roads, and the town of Rochefort is near the mouth of the river Charente to the south. It was the location of a failed British attack on Rochefort in 1757 during the Seven Years' War, of an attack by HMS ''Unicorn'' and HMS ''St Fiorenzo'' on a Spanish squadron on 2 July 1799, and of the final surrender of Napoleon Bonaparte on HMS ''Bellerophon'' on 15 July 1815. It was also the site of the British naval victory over a French fleet at the 1809 Battle of Basque Roads. A further engagement took place on 13 February 1810, when Lieutenant Gardiner Henry Guion was put in command of eight boats from HMS ''Christian VII'' under Sir Joseph Sydney Yorke, HMS ''Armide'' under Captain Lucius Fer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Sydney Yorke
Admiral Sir Joseph Sydney Yorke KCB (6 June 1768 – 5 May 1831) was an officer of the Royal Navy. As a junior officer he saw action at the Battle of the Saintes in April 1782 during the American Revolutionary War. He commanded at the defeat of the Dutch fleet in August 1795 during the French Revolutionary Wars and went on to be First Naval Lord during the closing stages of the Napoleonic Wars. Family and early life Yorke was born in Great Berkhampstead, Hertfordshire, on 6 June 1768, the second son, by his second marriage, of the politician Charles Yorke. He joined the navy at the age of 11, becoming a midshipman aboard , then under the command of Sir Charles Douglas, on 15 February 1780. He followed Douglas to his next command, , which flew the flag of Admiral George Rodney. Yorke was then present at Rodney's victory over François Joseph Paul de Grasse at the Battle of the Saintes from 9 to 12 April 1782. The end of the American Revolutionary War led to the ''Formidable'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
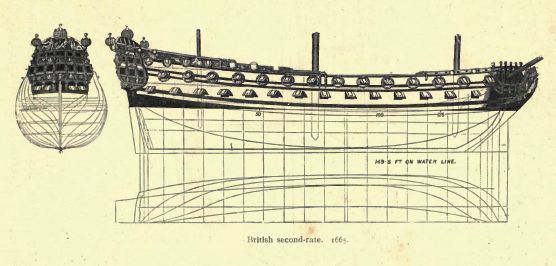
Second Rate
In the rating system of the Royal Navy used to categorise sailing warships, a second-rate was a ship of the line which by the start of the 18th century mounted 90 to 98 guns on three gun decks; earlier 17th-century second rates had fewer guns and were originally two-deckers or had only partially armed third gun decks. A "second rate" was the second largest class of warships in a hierarchical system of six "ratings" based on size and firepower. They were essentially smaller and hence cheaper versions of the three-decker first rates. Like the first rates, they fought in the line of battle, but unlike the first rates, which were considered too valuable to risk in distant stations, the second rates often served also in major overseas stations as flagships. They had a reputation for poor handling and slow sailing. They were popular as flagships of admirals commanding the Windward and/or Leeward Islands station, which was usually a Rear-admiral of the red. Rating Typically measuri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |