|
French Brig Observateur (1800)
The French brig ''Observateur'', which was launched in 1800 for the French Navy, was a ''Vigilant''-class 16-gun brig, one of six built to a design by Pierre-Alexandre-Laurent Forfait. The Royal Navy captured her in 1806 and took her into service as HMS ''Observateur''. She participated in two actions, one for the French Navy and one for the Royal Navy, and one campaign before she was laid up in 1810. The Navy did not succeed in selling her until 1814. French service The French Navy commissioned ''Observateur'' in 1802 and by 4 October 1802 she was under the command of ''lieutenant de vaisseau'' Bonamy, having sailed from Havre to Newfoundland protecting French fisherman, and then returning to Brest. Then between 8 April 1803 and 13 September, still under the command of Bonamy, by now a ''capitaine de frégate'', ''Observateur'' returned from Saint-Domingue to Brest, cruised to the region around Santa Maria Island, and then returned to Corogne, finishing at Ferrol. On 28 Januar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil And Naval Ensign Of France
Civil may refer to: *Civic virtue, or civility *Civil action, or lawsuit *Civil affairs *Civil and political rights *Civil disobedience *Civil engineering *Civil (journalism), a platform for independent journalism *Civilian, someone not a member of armed forces *Civil law (other), multiple meanings *Civil liberties *Civil religion *Civil service *Civil society *Civil war *Civil (surname) {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Cruz De Tenerife
Santa Cruz de Tenerife, commonly abbreviated as Santa Cruz (), is a city, the capital of the island of Tenerife, Province of Santa Cruz de Tenerife, and capital of the Canary Islands. Santa Cruz has a population of 206,593 (2013) within its administrative limits.Instituto Canario de Estadística , population The urban zone of Santa Cruz extends beyond the city limits with a population of 507,306 and 538,000 within urban area. It is the second largest city in the Canary Islands and the main city on the island of , with n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexander Cochrane
Admiral of the Blue Sir Alexander Inglis Cochrane (born Alexander Forrester Cochrane; 23 April 1758 – 26 January 1832) was a senior Royal Navy commander during the Napoleonic Wars and achieved the rank of admiral. He had previously captained HMS ''Ajax'' in Alexandria, Egypt during the Egyptian operation of 1801. Cochrane was knighted into the Order of the Bath for his services in 1806. In 1814 he became vice admiral and commander-in-chief of the North American Station, led the naval forces during the attacks on Washington and New Orleans, and was promoted to admiral in 1819 and became commander-in-chief of the Plymouth naval base. Naval career Alexander Inglis Cochrane was a younger son of the Scottish peer Thomas Cochrane, the eighth Earl of Dundonald, and his second wife, Jane Stuart. He joined the Royal Navy as a boy and served with British naval forces in North America. He served during the American War of Independence. Cochrane also participated in the Egyptian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
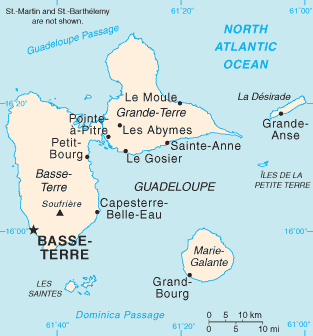
Marie Galante
Marie-Galante ( gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Mawigalant) is one of the islands that form Guadeloupe, an overseas department of France. Marie-Galante has a land area of . It had 11,528 inhabitants at the start of 2013, but by the start of 2018 the total was officially estimated to be 10,655, with a population density of . Administration Marie-Galante is divided into three communes (with populations at 1 January 2013): * Grand-Bourg (5,564 residents), * Capesterre-de-Marie-Galante (3,389) and * Saint-Louis (2,575). These three communes formed an intercommunal entity in 1994: the Community of Communes of Marie-Galante (french: communauté de communes de Marie-Galante). This is the oldest intercommunal structure of the overseas regions of France. History The Huecoids are the oldest known civilizations to have occupied Marie-Galante, followed by Arawaks, and then by the Island Caribs circa 850. The island was called ''Aichi'' by the Caribs and ''Touloukaera'' by the Arawaks. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
False Flag
A false flag operation is an act committed with the intent of disguising the actual source of responsibility and pinning blame on another party. The term "false flag" originated in the 16th century as an expression meaning an intentional misrepresentation of someone's allegiance. The term was famously used to describe a ruse in naval warfare whereby a vessel flew the flag of a neutral or enemy country in order to hide its true identity. The tactic was originally used by pirates and privateers to deceive other ships into allowing them to move closer before attacking them. It later was deemed an acceptable practice during naval warfare according to international maritime laws, provided the attacking vessel displayed its true flag once an attack had begun. The term today extends to include countries that organize attacks on themselves and make the attacks appear to be by enemy nations or terrorists, thus giving the nation that was supposedly attacked a pretext for domestic repr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roquebert's Expedition To The Caribbean
Roquebert's expedition to the Caribbean, was an unsuccessful operation by a French naval squadron to transport supplies to Guadeloupe in December 1809 at the height of the Napoleonic Wars. Over the previous year, British Royal Navy squadrons had isolated and defeated the French Caribbean colonies one by one, until by the autumn Guadeloupe was the only colony remaining in French hands. Cut off from the rest of the world by British blockade squadrons that intercepted all ships coming to or from the island, Guadeloupe was in a desperate situation, facing economic collapse, food shortages and social upheaval, as well as the impending threat of British invasion. In an effort to reinforce and resupply the colony, the French government sent four vessels to the West Indies in November 1809 under Commodore François Roquebert. Two of the ships were 20-gun flûtes carrying supplies and troops. The two others were 40-gun frigates, ordered to protect the storeships on their journey from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loire-class Flûte
The ''Loire''-class flûte was a French Navy class of two 20-gun flûtes that Louis, Antoine, and Marhurin Crucy, Basse Indre, built to a design by François-Louis Etesse, and under a contract dated 5 November 1802. Both were at anchor at Anse à la Barque, Guadeloupe Guadeloupe (; ; gcf, label=Antillean Creole, Gwadloup, ) is an archipelago and overseas department and region of France in the Caribbean. It consists of six inhabited islands—Basse-Terre, Grande-Terre, Marie-Galante, La Désirade, and the ... when their crews burned them on 18 December 1809 to avoid their falling into British hands during an attack by a British squadron comprising His Majesty's Ships , ''Blonde'', , , , , , and . British accounts of the battle generally refer to "the two ''armées en flute'' and late 40-gun frigates Loire and Seine".James and Chamier (1837), Vol. 5, pp.186-87. However, this description is a little misleading. The class were not designed as frigates, and then modified; t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMS Java (1811)
HMS ''Java'' was a British Royal Navy 38-gun fifth-rate frigate. She was originally laid down in 1805 as ''Renommée'', described as a 40-gun French Navy frigate, but the vessel actually carried 46 guns. The British captured her in 1811 in a noteworthy action during the Battle of Tamatave, but she is most famous for her defeat on 29 December 1812 in a three-hour single-ship action against . ''Java'' had a complement of about 277, but during her engagement with ''Constitution'' she allegedly had 426 aboard, in comparison with her opponent's 475. French service In May 1811, she was part of a three-sail squadron under François Roquebert, comprising ''Renommée'', and '' Néréide'', and ferrying troops to Mauritius. On 20 May, the French encountered a British squadron comprising , , , and . In the ensuing Battle of Tamatave, ''Renommée'' struck after her mainsail was set on fire. The British captured ''Néréide'' five days later at Tamatave, Madagascar. ''Clorinde'', commande ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Frigate Clorinde (1808)
''Clorinde'' was a 40-gun of the French Navy, designed by Sané. The British Royal Navy captured her in 1814 and renamed her HMS ''Aurora''. After 19 years as a coal hulk she was broken up in 1851. French frigate From June 1809, she was stationed with the 16-gun and the 38-gun . In September, she sailed with ''Renommée'', ''Loire'', and '' Seine'' to Guadeloupe. On 13 December, she and ''Renommée'' captured . On 15 December 1809, ''Clorinde'' ran aground, and freed herself by dropping guns and ammunition overboard. She took part in the action of 20 May 1811, fought off Madagascar, and returned to Brest. Captain Jacques Saint-Cricq was found guilty of failing to properly support his commodore. Saint-Cricq was demoted of rank, expelled from the Legion of Honour, and sentenced to three years in prison. On 6 December 1813, ''Clorinde'' captured the British merchant vessel in the Atlantic Ocean (). ''Lusitania'', Johnston, master, had been sailing from London to Suriname. ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Frigate Junon (1806)
The ''Junon'' was a ''Gloire'' class 40-gun frigate of the French Navy. Launched in 1806, she saw service during the Napoleonic Wars, escorting merchant convoys to France's besieged Caribbean colonies. In February 1809 she was captured at sea after a fierce engagement with four Royal Navy vessels. Recommissioned as HMS ''Junon'', she served as part of the British blockade of French ports in the Caribbean. French frigates recaptured her in December 1809 off the French colony of Guadeloupe. The engagement so damaged ''Junon'' that her captors scuttled her. Capture by Britain On 10 November 1808, under ''capitaine de frégate'' Rousseau, ''Junon'' departed for Martinique, along with ''Vénus'', ''Amphitrite'', ''Cygne'' and ''Papillon''. The squadron broke apart the next day, and she found herself isolated. On 10 February 1809 she ran across a British squadron composed of the frigates and , the brig , and the schooner ; ''Junon'' surrendered after a lengthy resistance that left ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Barthélemy
Saint Barthélemy (french: Saint-Barthélemy, ), officially the Collectivité territoriale de Saint-Barthélemy, is an overseas collectivity of France in the Caribbean. It is often abbreviated to St. Barth in French, and St. Barts in English. The island lies about south of the Caribbean island Saint Martin (island), Saint Martin, and is northeast of the Dutch islands of Saba (island), Saba, Sint Eustatius, and the independent country of Saint Kitts and Nevis. Saint Barthélemy was for many years a French commune forming part of Guadeloupe, which is an overseas region and department of France. In 2003 the island voted in favour of secession from Guadeloupe in order to form a separate overseas collectivity (''collectivité d'outre-mer'', abbreviated to ''COM'') of France. The collectivity is one of four territories among the Leeward Islands in the northeastern Caribbean that make up the French West Indies, along with Collectivity of Saint Martin, Saint Martin, Guadeloupe ( sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cap-Haïtien
Cap-Haïtien (; ht, Kap Ayisyen; "Haitian Cape"), typically spelled Cape Haitien in English and often locally referred to as or , is a commune of about 190,000 people on the north coast of Haiti and capital of the department of Nord. Previously named ''Cap‑Français'' ( ht, Kap-Fransè; initially ''Cap-François'' ht, Kap-Franswa) and ''Cap‑Henri'' ( ht, Kap-Enri) during the rule of Henri I, it was historically nicknamed the ''Paris of the Antilles'', because of its wealth and sophistication, expressed through its architecture and artistic life. It was an important city during the colonial period, serving as the capital of the French Colony of Saint-Domingue from the city's formal foundation in 1711 until 1770 when the capital was moved to Port-au-Prince. After the Haitian Revolution, it became the capital of the Kingdom of Haiti under King Henri I until 1820. Cap-Haïtien's long history of independent thought was formed in part by its relative distance from Port-au-Pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)