|
Frank J. Becker
Frank John Becker (August 27, 1899 – September 4, 1981) was an American business executive and politician. A member of the Republican Party, he served five terms in the New York State Assembly and six terms in the United States House of Representatives from New York. Early life Becker was born in Brooklyn son of Maximilian and Eva (Sperling) Becker. He moved with his parents to Lynbrook, Nassau County, Long Island, in November 1905. He attended the public schools of Lynbrook and Brown's Business College, Jamaica, Long Island. During World War I, Becker enlisted in the United States Army on July 22, 1918, and served until September 22, 1919. He founded a real estate and insurance business in Lynbrook, New York, and was also chairman emeritus of the board of directors of the Suburbia Federal Savings and Loan Association in Garden City. Political career Becker was elected to the New York State Assembly in 1944, representing the 1st district in Nassau County and won four more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New York (state)
New York, officially the State of New York, is a state in the Northeastern United States. It is often called New York State to distinguish it from its largest city, New York City. With a total area of , New York is the 27th-largest U.S. state by area. With 20.2 million people, it is the fourth-most-populous state in the United States as of 2021, with approximately 44% living in New York City, including 25% of the state's population within Brooklyn and Queens, and another 15% on the remainder of Long Island, the most populous island in the United States. The state is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and Connecticut, Massachusetts, and Vermont to the east; it has a maritime border with Rhode Island, east of Long Island, as well as an international border with the Canadian provinces of Quebec to the north and Ontario to the northwest. New York City (NYC) is the most populous city in the United States, and around two-thirds of the state's popul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
166th New York State Legislature
The 166th New York State Legislature, consisting of the New York State Senate and the New York State Assembly, met from January 8, 1947, to March 13, 1948, during the fifth and sixth years of Thomas E. Dewey's governorship, in Albany. Background Under the provisions of the New York Constitution of 1938, re-apportioned in 1943, 56 Senators and 150 assemblymen were elected in single-seat districts for two-year terms. The senatorial districts consisted either of one or more entire counties; or a contiguous area within a single county. The counties which were divided into more than one senatorial district were Kings (nine districts), New York (six), Bronx (five), Queens (four), Erie (three), Westchester (three), Monroe (two) and Nassau (two). The Assembly districts consisted either of a single entire county (except Hamilton Co.), or of contiguous area within one county. At this time there were two major political parties: the Republican Party and the Democratic Party. The American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1956 Republican National Convention
The 1956 Republican National Convention was held by the Republican Party of the United States at the Cow Palace in San Francisco, California, from August 20 to August 23, 1956. U.S. Senator William F. Knowland was temporary chairman and former speaker of the House Joseph W. Martin Jr. served as permanent chairman. It renominated President Dwight D. Eisenhower and Vice President Richard M. Nixon as the party's candidates for the 1956 presidential election. On August 23, 1956, singer Nat King Cole spoke at the Republican Convention. The 1956 Republican convention was held after that year's Democratic National Convention. This was unusual, as since 1864, in every election but 1888, Democrats had held their convention second. It has become an informal tradition that the party holding the White House (which, accordingly, in 1956 had been the Republican Party) hosts their convention second, but it is unclear when this tradition began (Democrats had held the White House and held ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1952 Republican National Convention
The 1952 Republican National Convention was held at the International Amphitheatre in Chicago, Illinois from July 7 to 11, 1952, and nominated the popular general and war hero Dwight D. Eisenhower of New York, nicknamed "Ike," for president and the anti-communist crusading Senator from California, Richard M. Nixon, for vice president. The Republican platform pledged to end the unpopular war in Korea, supported the development of nuclear weapons as a deterrence strategy, to fire all "the loafers, incompetents and unnecessary employees" at the State Department, condemned the Roosevelt and Truman administrations' economic policies, supported retention of the Taft–Hartley Act, opposed " discrimination against race, religion or national origin", supported "Federal action toward the elimination of lynching", and pledged to bring an end to communist subversion in the United States. Presidential candidates Withdrew before the convention * Businessman Riley A. Bender of Il ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
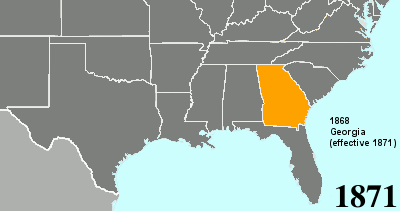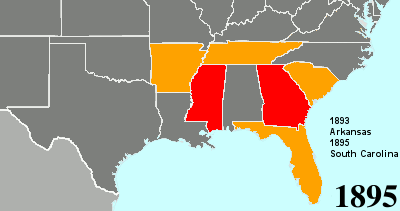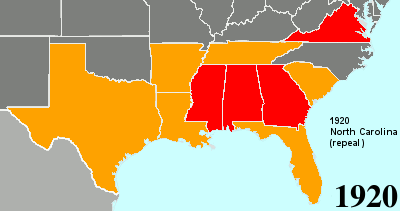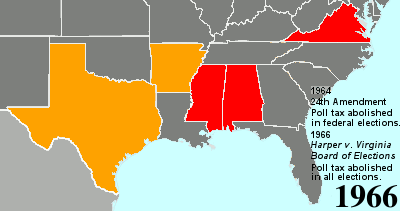
Twenty-fourth Amendment To The United States Constitution
The Twenty-fourth Amendment (Amendment XXIV) of the United States Constitution prohibits both Congress and the states from conditioning the right to vote in federal elections on payment of a poll tax or other types of tax. The amendment was proposed by Congress to the states on August 27, 1962, and was ratified by the states on January 23, 1964. Southern states of the former Confederate States of America adopted poll taxes in laws of the late 19th century and new constitutions from 1890 to 1908, after the Democratic Party had generally regained control of state legislatures decades after the end of Reconstruction, as a measure to prevent African Americans and often poor whites (and following passage of the Nineteenth Amendment, women) from voting. Use of the poll taxes by states was held to be constitutional by the Supreme Court of the United States in the 1937 decision ''Breedlove v. Suttles''. When the 24th Amendment was ratified in 1964, five states still retained a po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Rights Act Of 1964
The Civil Rights Act of 1964 () is a landmark civil rights and United States labor law, labor law in the United States that outlaws discrimination based on Race (human categorization), race, Person of color, color, religion, sex, and national origin. It prohibits unequal application of voter registration requirements, racial segregation in schools and public accommodations, and employment discrimination. The act "remains one of the most significant legislative achievements in American history". Initially, powers given to enforce the act were weak, but these were supplemented during later years. Congress asserted its authority to legislate under several different parts of the United States Constitution, principally its power to regulate interstate commerce under Article One of the United States Constitution, Article One (section 8), its duty to guarantee all citizens Equal Protection Clause, equal protection of the laws under the Fourteenth Amendment to the U.S. Constitution, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Rights Act Of 1960
The Civil Rights Act of 1960 () is a United States federal law that established federal inspection of local voter registration polls and introduced penalties for anyone who obstructed someone's attempt to register to vote. It dealt primarily with discriminatory laws and practices in the segregated South, by which African Americans and Mexican-American Texans had been effectively disenfranchised since the late 19th and start of the 20th century. This was the fifth Civil Rights Act to be enacted in United States history. Over an 85-year period, it was preceded only by the Civil Rights Act of 1957, whose shortcomings largely influenced its creation. This law served to more effectively enforce what was set forth in the 1957 act through eliminating certain loopholes in it, and to establish additional provisions. Aside from addressing voting rights, the Civil Rights Act of 1960 also imposed criminal penalties for obstruction of court orders to limit resistance to the Supreme Court ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Rights Act Of 1957
The Civil Rights Act of 1957 was the first federal civil rights legislation passed by the United States Congress since the Civil Rights Act of 1875. The bill was passed by the 85th United States Congress and signed into law by President Dwight D. Eisenhower on September 9, 1957. The Supreme Court of the United States, Supreme Court's 1954 ruling in the case of ''Brown v. Board of Education'' brought the issue of school desegregation to the fore of public attention, as Southern Democratic leaders began a campaign of "massive resistance" against desegregation. In the midst of this campaign, President Eisenhower proposed a civil rights bill designed to provide federal protection for African Americans, African American voting rights; most African Americans in the Southern United States had been Disenfranchisement after the Reconstruction Era, disenfranchised by state and local laws. Though the civil rights bill passed Congress, opponents of the act were able to remove or weaken se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abington School District V
Abington may refer to: People *Abington (surname) Places Ireland *Abington, County Limerick, part of a civil parish in Ireland which straddles two counties, Limerick and Tipperary **Abington (townland), a townland in the above civil parish in County Limerick *Abington, County Tipperary, part of a civil parish in Ireland which straddles two counties, Limerick and Tipperary United Kingdom * Abington, Cambridgeshire, England *Abington, Northamptonshire, England, a former village merged into Northampton *Abington (ward), an electoral ward of Northampton, England *Abington, South Lanarkshire, Scotland United States *Abington, Connecticut *Abington, Indiana *Abington, Massachusetts *Abington Township, Mercer County, Illinois *Abington Township, Wayne County, Indiana *Waverly Township, Lackawanna County, Pennsylvania (formerly Abington Township) *Abington Township, Montgomery County, Pennsylvania Other uses *Pinta Island, also known as Abington Island, located in the Galápagos Island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engel V
Engel means "angel" in some Germanic languages. Engel or Die Engel may refer to: People * Engel (surname) * Engel Beltré (born 1989), Dominican baseball player Music * Engel (band), a Swedish industrial/melodic death metal band * "Engel" (song), by Rammstein * "Engel", a 2014 song by Admiral P featuring Nico D * "Engel", a 2012 song from the album ''Raise Your Fist'' by Doro Others uses * ''Engel'' (role-playing game), a 2002 role-playing game * Frau Engel, a character in the Wolfenstein video game series * Marian Engle Award, a Canadian literary award presented annually from 1986 to 2007 * Engel Stadium, a baseball stadium in Chattanooga, Tennessee, United States * De Engel (Lisse), a community in the municipality of Lisse, South Holland, the Netherlands * De Engel (restaurant), Rotterdam, the Netherlands See also * * Engle (other) * Engels (other) * ''Engel v. Vitale ''Engel v. Vitale'', 370 U.S. 421 (1962), was a landmark United States Supreme Court ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point of federal law. It also has original jurisdiction over a narrow range of cases, specifically "all Cases affecting Ambassadors, other public Ministers and Consuls, and those in which a State shall be Party." The court holds the power of judicial review, the ability to invalidate a statute for violating a provision of the Constitution. It is also able to strike down presidential directives for violating either the Constitution or statutory law. However, it may act only within the context of a case in an area of law over which it has jurisdiction. The court may decide cases having political overtones, but has ruled that it does not have power to decide non-justiciable political questions. Established by Article Three of the United States C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
School Prayer
School prayer, in the context of religious liberty, is state-sanctioned or mandatory prayer by students in public schools. Depending on the country and the type of school, state-sponsored prayer may be required, permitted, or prohibited. Countries which prohibit or limit school prayer often differ in their reasons for doing so. In the United States, school prayer cannot be required of students in accordance with the Establishment Clause of the First Amendment to the United States Constitution. This is generally rigorously applied in public schools; the Establishment Clause does not prevent prayer in private schools that have no public funding. In Canada, school-sponsored prayer is disallowed under the concept of freedom of conscience as outlined in the Canadian Charter on Rights & Fundamental Freedoms. School-sponsored prayer is disallowed in France as a byproduct of its status as a secular (religiously neutral) nation. Countries that allow or require school and other state-sponsore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |