|
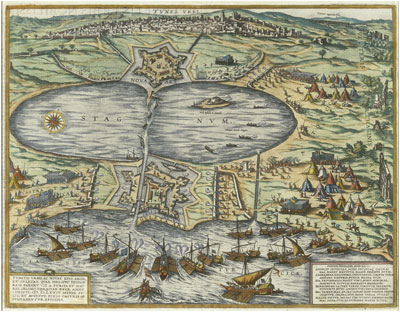
France–Morocco Relations
France–Morocco relations are bilateral relations between Morocco and France. They are part of the France–Africa relations. First exchanges (8th century) Following the invasion of Spain from the coast of Morocco by the Umayyad Commander Tariq ibn Ziyad in 711, during the 8th century the Arab caliphate armies invaded Southern France, as far as Poitiers and the Rhône valley as far as Avignon, Lyon, Autun, until the turning point of the Battle of Tours in 732. France would again become threatened by the proximity of the expanding Almoravid Empire in the 11th and 12th centuries. Consuls and physicians (1577–1600) In 1402, the French adventurer Jean de Béthencourt left La Rochelle and sailed along the coast of Morocco to conquer the Canary islands. In the 16th century, the sealing of a Franco-Ottoman alliance between Francis I and Suleiman the Magnificent permitted numerous contacts between French traders and countries under Ottoman influence. In 1533, Francis I sent colon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bilateral Relations
Bilateralism is the conduct of political, economic, or cultural relations between two sovereign states. It is in contrast to unilateralism or multilateralism, which is activity by a single state or jointly by multiple states, respectively. When states recognize one another as sovereign states and agree to diplomatic relations, they create a bilateral relationship. States with bilateral ties will exchange diplomatic agents such as ambassadors to facilitate dialogues and cooperations. Economic agreements, such as free trade agreements (FTA) or foreign direct investment (FDI), signed by two states, are a common example of bilateralism. Since most economic agreements are signed according to the specific characteristics of the contracting countries to give preferential treatment to each other, not a generalized principle but a situational differentiation is needed. Thus through bilateralism, states can obtain more tailored agreements and obligations that only apply to particular cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean De Béthencourt
Jean de Béthencourt () (1362–1425) was a French explorer who in 1402 led an expedition to the Canary Islands, landing first on the north side of Lanzarote. From there he conquered for Castile the islands of Fuerteventura (1405) and El Hierro, ousting their local chieftains (''majos'' and ''bimbaches'', ancient peoples). Béthencourt received the title King of the Canary Islands but he recognized King Henry III of Castile, who had provided aid during the conquest, as his overlord. Background The Canary Islands were apparently known to the Carthaginians of Cadiz. The Roman writer Pliny the Elder called them "the Fortunate Islands". Genoese navigator Lancelotto Malocello is credited with the rediscovery of the Canary Islands in 1312. In 1339, Majorcan Angelino Dulcert drew the first map of the Canaries, labeling one of the islands "Lanzarote". Life Jean de Béthencourt, Baron of Saint-Martin-le-Gaillard, was born in Grainville-la-Teinturière, province of Normandy, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Istanbul
Neolithic artifacts, uncovered by archeologists at the beginning of the 21st century, indicate that Istanbul's historic peninsula was settled as far back as the 6th millennium BCE. That early settlement, important in the spread of the Neolithic Revolution from the Near East to Europe, lasted for almost a millennium before being inundated by rising water levels. The first human settlement on the Asian side, the Fikirtepe mound, is from the Copper Age period, with artifacts dating from 5500 to 3500 BCE. It's also worth noting that in the European side, near the point of the peninsula ( Sarayburnu) there was a settlement during the early 1st millennium BCE. Modern authors have linked it to the possible Thracian toponym ''Lygos'', mentioned by Pliny the Elder as an earlier name for the site of Byzantium. The history of the city proper begins around 660 BC when Greek settlers from Megara colonized the area and established Byzantium on the European side of the Bosphorus. It fell to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Marwan Abd Al-Malik I Saadi
Abu Marwan Abd al-Malik I ( ar, أبو مروان عبد الملك الغازي), often simply Abd al-Malik or Mulay Abdelmalek, (b. 1541 – d. 4 August 1578) was the Saadian Sultan of Morocco from 1576 until his death right after the Battle of al-Kasr al-Kabir against Portugal in 1578. Biography Saadian Prince (1541–1557) Abd al-Malik was one of the sons of the Saadian Sultan Mohammed al-Shaykh, who was assassinated by the Ottomans in 1557 by order of Hasan Pasha, son of Barbarossa, as he was preparing for an alliance with Spain against the Ottomans. One of his brothers Abdallah al-Ghalib (1557–1574) then took power and ascended to the throne. He planned to eliminate his other brothers in the process. Abd al-Malik had to escape from Morocco and stay abroad with his mother Sahâba al-Rehmânia, his elder brother Abd al-Mu'min al-Saadi and his younger brother Ahmad until 1576. Exile to the Ottoman Empire (1557–1576) Abd al-Malik spent 17 years among the Ottoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guillaume Bérard
Guillaume Bérard was a French Consul established in Fes, Fez, Morocco, in 1577 by Henry III of France. He was the first European to be named Consul in Morocco. His nomination followed the mission of Louis Cabrette, a French captain who had been used as an envoy to France by Sultan Abu Marwan Abd al-Malik I Saadi, Al-Malek in 1576. Guillaume Bérard was born in Saorge near Nice. Guillaume Bérard was a doctor by profession, who first went to live in Constantinople. In 1574, he saved the life of Moroccan prince Abu Marwan Abd al-Malik I Saadi, Abd al-Malik during an epidemic in Constantinople, where he was then in exile since the death of Abdallah al-Ghalib, Moulay Abdallah in January 1574. They later became friends due to this event. When Abd al-Malik became Sultan, he asked Henry III of France that Guillaume Bérard be appointed Consul of France. Berard, who was a subject of the Duke of Savoy, was then naturalized French, and on 10 June 1577 he was elevated to the position of Consul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry III Of France
Henry III (french: Henri III, né Alexandre Édouard; pl, Henryk Walezy; lt, Henrikas Valua; 19 September 1551 – 2 August 1589) was King of France from 1574 until his assassination in 1589, as well as King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1573 to 1575. As the fourth son of King Henry II of France, he was not expected to inherit the French throne and thus was a good candidate for the vacant throne of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, where he was elected List of Polish rulers#Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, 1569–1795, monarch in 1573. During his brief rule, he signed the Henrician Articles into law, recognizing the szlachta's right to Royal elections in Poland, freely elect their monarch. Aged 22, Henry abandoned Poland–Lithuania upon inheriting the French throne when his brother, Charles IX of France, Charles IX, died without issue. France was at the time plagued by the French Wars of Religion, Wars of Religion, and Henry's authority was undermi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry II Of France
Henry II (french: Henri II; 31 March 1519 – 10 July 1559) was King of France from 31 March 1547 until his death in 1559. The second son of Francis I and Duchess Claude of Brittany, he became Dauphin of France upon the death of his elder brother Francis in 1536. As a child, Henry and his elder brother spent over four years in captivity in Spain as hostages in exchange for their father. Henry pursued his father's policies in matters of art, war, and religion. He persevered in the Italian Wars against the Habsburgs and tried to suppress the Reformation, even as the Huguenot numbers were increasing drastically in France during his reign. Under the April 1559 Peace of Cateau-Cambrésis which ended the Italian Wars, France renounced its claims in Italy, but gained certain other territories, including the Pale of Calais and the Three Bishoprics. These acquisitions strengthened French borders while the abdication of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor in January 1556 and division of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Al-Abbas Ahmad Ibn Muhammad
Abu al-Abbas Ahmad ibn Muhammad (), also Sultan Ahmad, or Ahmed el Outassi, was a Sultan of the Moroccan Wattasid dynasty. He ruled from 1526 to 1545, and again between 1547 and 1549.C. E. Bosworth''The New Islamic Dynasties: A Chronological and Genealogical Manual'' Edinburgh University Press (2004), pp. 48–49 Life In 1532, Ahmad ibn Muhammad sent a letter to Francis I of France through trader Hémon de Molon, encouraging the French king to develop trade relations."THE EMBASSY OF PIERRE DE PITON: In the year 1533, the year of Montaigne's birth, a French merchant, from Bresse, Hemon de Molon, returned from Morocco, filled with such enthusiasm that Francis I decided to find out more" in ''Ecrits de Paris: revue de questions actuelles'' Centre d'études des questions actuelles, politiques, économiques et sociales (Paris, France) - 1953 (in English) In 1533, Francis I of France sent as ambassador to Ahmad ibn Muhammad, in the person of colonel Pierre de Piton. The embassy was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wattassid
The Wattasid dynasty ( ber, Iweṭṭasen; ar, الوطاسيون, ''al-waṭṭāsīyūn'') was a ruling dynasty of Morocco. Like the Marinid dynasty, its rulers were of Zenata Berber descent. The two families were related, and the Marinids recruited many viziers from the Wattasids. These viziers assumed the powers of the Sultans, seizing control of the Marinid dynasty's realm when the last Marinid, Abu Muhammad Abd al-Haqq, who had massacred many of the Wattasids in 1459, was murdered during a popular revolt in Fez in 1465. Abu Abd Allah al-Sheikh Muhammad ibn Yahya was the first Sultan of the Wattasid Dynasty. He controlled only the northern part of Morocco, the south being divided into several principalities. The Wattasids were finally supplanted in 1554, after the Battle of Tadla, by the Saadi dynasty princes of Tagmadert who had ruled all of southern Morocco since 1511. Overview Morocco endured a prolonged multifaceted crisis in the 15th and early 16th centuries brought ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre De Piton
Pierre de Piton was a French colonel of the 16th century, and an ambassador to the kingdom of Morocco. He was sent in 1533 by Francis I, initiating France-Morocco relations. Pierre de Piton sailed to Morocco to the harbour of Larache on the royal galleass ''Le Saint-Pierre'', equipped with 28 cannons, and captained by the Genoese Baptiste Auxyllia. Pierre de Piton was accompanied by 5 men, as well as French trader Hémon de Molon, who had brought enthusiastic reports from Morocco in a trip there in 1531–32, as well as a letter from the Sultan to Francis I. Following Pierre de Piton's embassy, in a letter to Francis I dated August 13, 1533, the Wattassid ruler of Fez, Ahmed ben Mohammed, welcomed French overtures and granted freedom of shipping and protection of French traders. France started to send ships to Morocco in 1555, under the rule of Henry II, son of Francis I. The Genoese captain later betrayed Pierre de Piton during the time he was in Fes, by going to the Portugu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suleiman The Magnificent
Suleiman I ( ota, سليمان اول, Süleyman-ı Evvel; tr, I. Süleyman; 6 November 14946 September 1566), commonly known as Suleiman the Magnificent in the West and Suleiman the Lawgiver ( ota, قانونى سلطان سليمان, Ḳānūnī Sulṭān Süleymān) in his realm, was the tenth and longest-reigning Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1520 until his death in 1566. Under his administration, the Ottoman Empire ruled over at least 25 million people. Suleiman succeeded his father, Selim I, as sultan on 30 September 1520 and began his reign with campaigns against the Christian powers in central Europe and the Mediterranean. Belgrade fell to him in 1521 and the island of Rhodes in 1522–23. At Mohács, in August 1526, Suleiman broke the military strength of Hungary. Suleiman became a prominent monarch of 16th-century Europe, presiding over the apex of the Ottoman Empire's economic, military and political power. Suleiman personally led Ottoman armies in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francis I Of France
Francis I (french: François Ier; frm, Francoys; 12 September 1494 – 31 March 1547) was King of France from 1515 until his death in 1547. He was the son of Charles, Count of Angoulême, and Louise of Savoy. He succeeded his first cousin once removed and father-in-law Louis XII, who died without a son. A prodigious patron of the arts, he promoted the emergent French Renaissance by attracting many Italian artists to work for him, including Leonardo da Vinci, who brought the ''Mona Lisa'' with him, which Francis had acquired. Francis' reign saw important cultural changes with the growth of central power in France, the spread of humanism and Protestantism, and the beginning of French exploration of the New World. Jacques Cartier and others claimed lands in the Americas for France and paved the way for the expansion of the first French colonial empire. For his role in the development and promotion of the French language, he became known as ''le Père et Restaurateur des Lettr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |