|
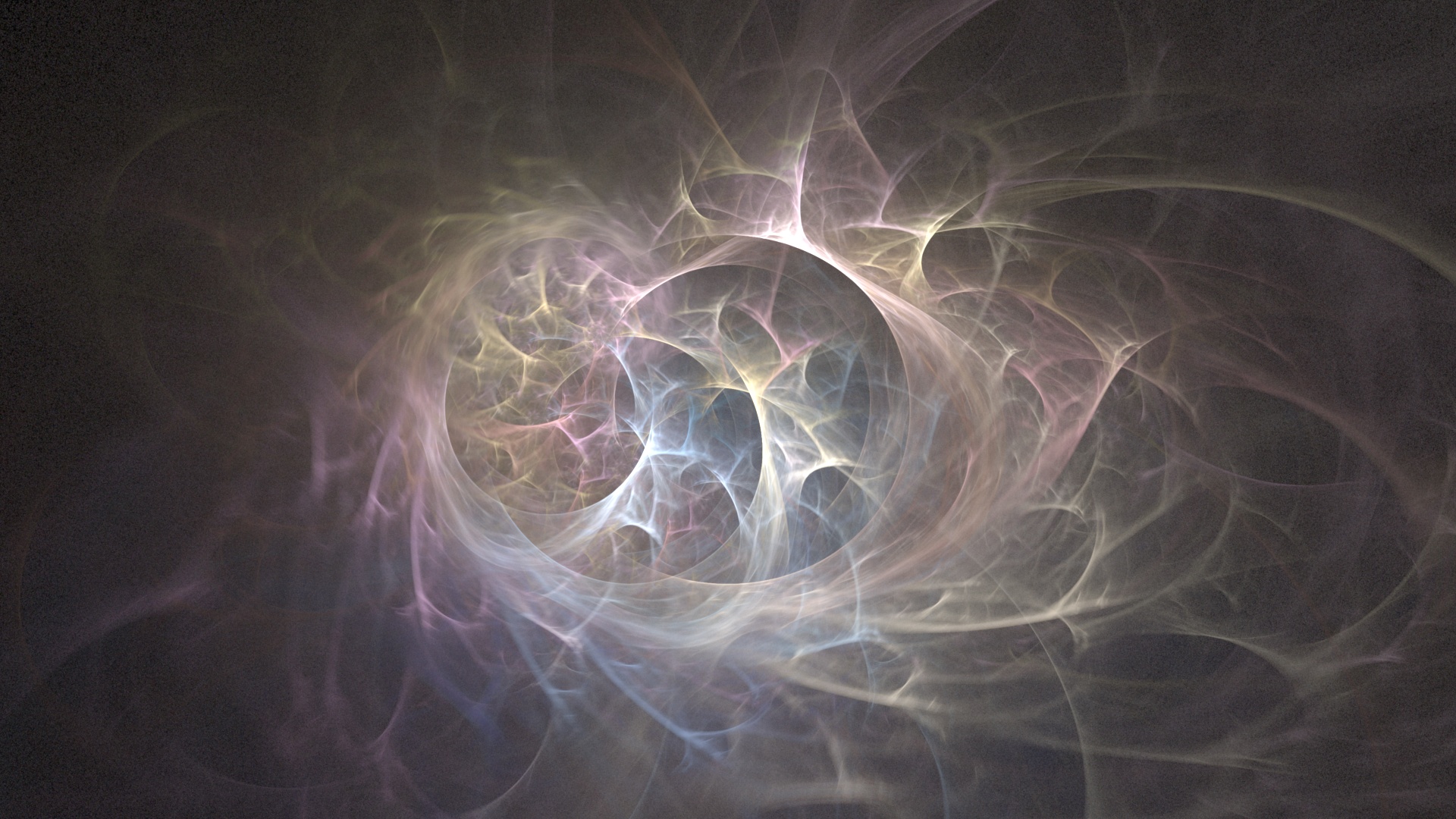
Fractal Flames
Fractal flames are a member of the iterated function system class of fractals created by Scott Draves in 1992. Draves' open-source code was later ported into Adobe After Effects graphics softwareChris Gehman and Steve Reinke (2005). ''The Sharpest Point: Animation at the End of Cinema''. YYZ Books. pp 269. and translated into the Apophysis fractal flame editor. Fractal flames differ from ordinary iterated function systems in three ways: * Nonlinear functions are iterated in addition to affine transforms. * Log-density display instead of linear or binary (a form of tone mapping) * Color by structure (i.e. by the recursive path taken) instead of monochrome or by density. The tone mapping and coloring are designed to display as much of the detail of the fractal as possible, which generally results in a more aesthetically pleasing image. Algorithm The algorithm consists of two steps: creating a histogram and then rendering the histogram. Creating the histogram First, one ite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apophysis (software)
Apophysis is an open source fractal flame editor and renderer for Microsoft Windows and Macintosh. Apophysis has many features for creating and editing fractal flames, including an editor that allows one to directly edit the transforms by manipulating triangles, a mutations window, which applies random edits to the triangles, an adjust window, which allows the adjustment of coloring and location of the image. It also provides a scripting language with direct access to most of the components of the fractal, which allows for effects such as the animations seen in Electric Sheep, which are also fractal flames. Users can export fractal flames to other fractal flame rendering programs, such as FLAM3. There is a separate version of Apophysis that supports 3D. There are numerous clones, ports, and forks of it. History Scott Draves invented Fractal Flames and published an open source implementation written in C in the early 90s. In 2001, Ronald Hordijk translated his code into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Software
Free software or libre software is computer software distributed under terms that allow users to run the software for any purpose as well as to study, change, and distribute it and any adapted versions. Free software is a matter of liberty, not price; all users are legally free to do what they want with their copies of a free software (including profiting from them) regardless of how much is paid to obtain the program.Selling Free Software (gnu.org) Computer programs are deemed "free" if they give end-users (not just the developer) ultimate control over the software and, subsequently, over their devices. The right to study and modify a computer program entails that |
GIMP
GIMP ( ; GNU Image Manipulation Program) is a free and open-source raster graphics editor used for image manipulation (retouching) and image editing, free-form drawing, transcoding between different image file formats, and more specialized tasks. It is not designed to be used for drawing, though some artists and creators have used it for such. GIMP is released under the GPL-3.0-or-later license and is available for Linux, macOS, and Microsoft Windows. History In 1995, Spencer Kimball and Peter Mattis began developing GIMP – originally named ''General Image Manipulation Program –'' as a semester-long project at the University of California, Berkeley for the eXperimental Computing Facility''.'' The acronym was coined first, with the letter ''G'' being added to ''-IMP'' as a reference to "the gimp" in the scene from the 1994 ''Pulp Fiction'' film. In 1996 was the initial public release of GIMP (0.54). The editor was quickly adopted and a community of contributors formed. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distributed Computing
A distributed system is a system whose components are located on different computer network, networked computers, which communicate and coordinate their actions by message passing, passing messages to one another from any system. Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems. The components of a distributed system interact with one another in order to achieve a common goal. Three significant challenges of distributed systems are: maintaining concurrency of components, overcoming the clock synchronization, lack of a global clock, and managing the independent failure of components. When a component of one system fails, the entire system does not fail. Examples of distributed systems vary from service-oriented architecture, SOA-based systems to massively multiplayer online games to peer-to-peer, peer-to-peer applications. A computer program that runs within a distributed system is called a distributed program, and ''distributed programming' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Sheep
Electric Sheep is a volunteer computing project for animating and evolving fractal flames, which are in turn distributed to the networked computers, which display them as a screensaver. Process The process is transparent to the casual user, who can simply install the software as a screensaver. Alternatively, the user may become more involved with the project, manually creating a fractal flame file for upload to the server where it is rendered into a video file of the animated fractal flame. As the screensaver entertains the user, their computer is also used for rendering commercial projects, sales of which keep the servers and developers running. There are about 500,000 active users (monthly uniques). According to Mitchell Whitelaw in his ''Metacreation: Art and Artificial Life'', "On the screen they are luminous, twisting, elastic shapes, abstract tangles and loops of glowing filaments." The name "Electric Sheep" is taken from the title of Philip K. Dick's novel ''Do And ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaotica (software)
Chaotica is a commercial fractal art Fractal art is a form of algorithmic art created by calculating fractal objects and representing the calculation results as still digital images, animations, and media. Fractal art developed from the mid-1980s onwards. It is a genre of compute ... editor and renderer extending flam3 and Apophysis's functionality. There is also a free version with limited render resolution and animation length. History Chaotica began as a personal project of Thomas E. Ludwig (lycium) in the deviantArt fractal community in 2010, but has since been handed over to Glare Technologies, the developers of Indigo Renderer. Features Chaotica implements a generalized iterated function system and features a modern rendering engine based on advanced algorithms not found in open-source IFS implementations. It has an animation editor, selective randomization of parameters, and imaging controls such as different anti-aliasing modes and RGB-channel response curves. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inversely Proportional
In mathematics, two sequences of numbers, often experimental data, are proportional or directly proportional if their corresponding elements have a constant ratio, which is called the coefficient of proportionality or proportionality constant. Two sequences are inversely proportional if corresponding elements have a constant product, also called the coefficient of proportionality. This definition is commonly extended to related varying quantities, which are often called ''variables''. This meaning of ''variable'' is not the common meaning of the term in mathematics (see variable (mathematics)); these two different concepts share the same name for historical reasons. Two functions f(x) and g(x) are ''proportional'' if their ratio \frac is a constant function. If several pairs of variables share the same direct proportionality constant, the equation expressing the equality of these ratios is called a proportion, e.g., (for details see Ratio). Proportionality is closely r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winter School Of Computer Graphics
Winter is the coldest season of the year in polar and temperate climates. It occurs after autumn and before spring. The tilt of Earth's axis causes seasons; winter occurs when a hemisphere is oriented away from the Sun. Different cultures define different dates as the start of winter, and some use a definition based on weather. When it is winter in the Northern Hemisphere, it is summer in the Southern Hemisphere, and vice versa. In many regions, winter brings snow and freezing temperatures. The moment of winter solstice is when the Sun's elevation with respect to the North or South Pole is at its most negative value; that is, the Sun is at its farthest below the horizon as measured from the pole. The day on which this occurs has the shortest day and the longest night, with day length increasing and night length decreasing as the season progresses after the solstice. The earliest sunset and latest sunrise dates outside the polar regions differ from the date of the wint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density Estimation
In statistics, probability density estimation or simply density estimation is the construction of an estimate, based on observed data, of an unobservable underlying probability density function. The unobservable density function is thought of as the density according to which a large population is distributed; the data are usually thought of as a random sample from that population. A variety of approaches to density estimation are used, including Parzen windows and a range of data clustering techniques, including vector quantization. The most basic form of density estimation is a rescaled histogram. Example We will consider records of the incidence of diabetes. The following is quoted verbatim from the data set description: :''A population of women who were at least 21 years old, of Pima Indian heritage and living near Phoenix, Arizona, was tested for diabetes mellitus according to World Health Organization criteria. The data were collected by the US National Inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaussian Blur
In image processing, a Gaussian blur (also known as Gaussian smoothing) is the result of blurring an image by a Gaussian function (named after mathematician and scientist Carl Friedrich Gauss). It is a widely used effect in graphics software, typically to reduce image noise and reduce detail. The visual effect of this blurring technique is a smooth blur resembling that of viewing the image through a translucent screen, distinctly different from the bokeh effect produced by an out-of-focus lens or the shadow of an object under usual illumination. Gaussian smoothing is also used as a pre-processing stage in computer vision algorithms in order to enhance image structures at different scales—see scale space representation and scale space implementation. Mathematics Mathematically, applying a Gaussian blur to an image is the same as convolving the image with a Gaussian function. This is also known as a two-dimensional Weierstrass transform. By contrast, convolving by a circle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |