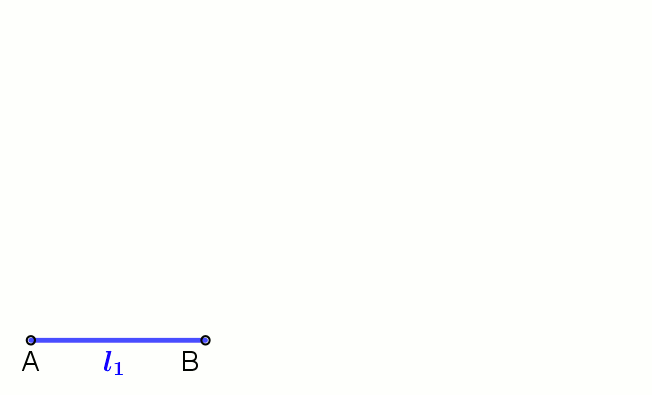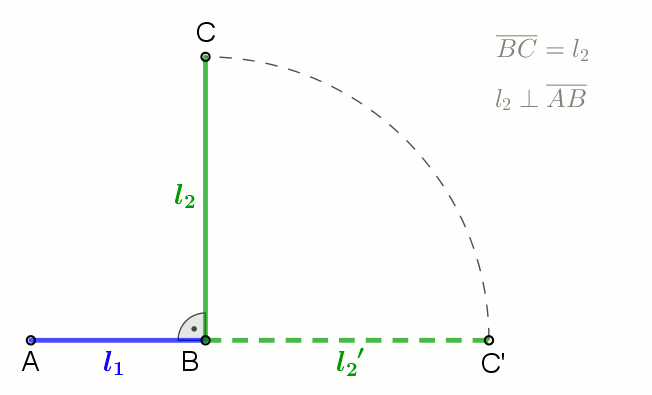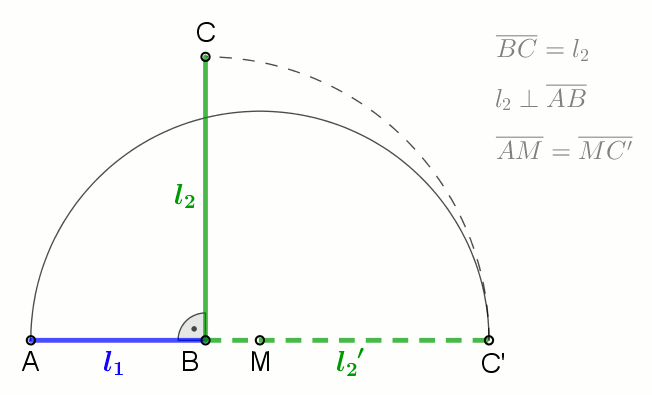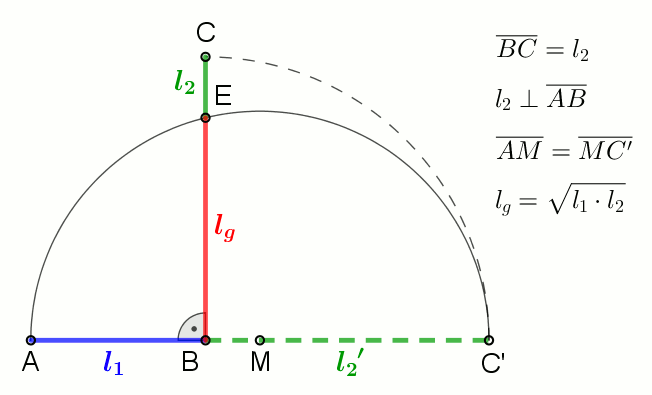|
Fowlkes–Mallows Index
The Fowlkes–Mallows index is an external evaluation method that is used to determine the similarity between two clusterings (clusters obtained after a clustering algorithm), and also a metric to measure confusion matrices. This measure of similarity could be either between two hierarchical clusterings or a clustering and a benchmark classification. A higher value for the Fowlkes–Mallows index indicates a greater similarity between the clusters and the benchmark classifications. It was invented by Bell Labs statisticians Edward Fowlkes and Collin Mallows in 1983. Preliminaries The Fowlkes–Mallows index, when results of two clustering algorithms are used to evaluate the results, is defined as : FM = \sqrt= \sqrt where TP is the number of true positives, FP is the number of false positives, and FN is the number of false negatives. TPR is the ''true positive rate'', also called '' sensitivity'' or ''recall'', and PPV is the ''positive predictive rate'', also known as ''prec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cluster Analysis
Cluster analysis or clustering is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster) are more similar (in some sense) to each other than to those in other groups (clusters). It is a main task of exploratory data analysis, and a common technique for statistics, statistical data analysis, used in many fields, including pattern recognition, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphics and machine learning. Cluster analysis itself is not one specific algorithm, but the general task to be solved. It can be achieved by various algorithms that differ significantly in their understanding of what constitutes a cluster and how to efficiently find them. Popular notions of clusters include groups with small Distance function, distances between cluster members, dense areas of the data space, intervals or particular statistical distributions. Clustering can therefore be formulated as a multi-object ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precision And Recall
In pattern recognition, information retrieval, object detection and classification (machine learning), precision and recall are performance metrics that apply to data retrieved from a collection, corpus or sample space. Precision (also called positive predictive value) is the fraction of relevant instances among the retrieved instances, while recall (also known as sensitivity) is the fraction of relevant instances that were retrieved. Both precision and recall are therefore based on relevance. Consider a computer program for recognizing dogs (the relevant element) in a digital photograph. Upon processing a picture which contains ten cats and twelve dogs, the program identifies eight dogs. Of the eight elements identified as dogs, only five actually are dogs (true positives), while the other three are cats (false positives). Seven dogs were missed (false negatives), and seven cats were correctly excluded (true negatives). The program's precision is then 5/8 (true positives / se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R (programming Language)
R is a programming language for statistical computing and graphics supported by the R Core Team and the R Foundation for Statistical Computing. Created by statisticians Ross Ihaka and Robert Gentleman, R is used among data miners, bioinformaticians and statisticians for data analysis and developing statistical software. Users have created packages to augment the functions of the R language. According to user surveys and studies of scholarly literature databases, R is one of the most commonly used programming languages used in data mining. R ranks 12th in the TIOBE index, a measure of programming language popularity, in which the language peaked in 8th place in August 2020. The official R software environment is an open-source free software environment within the GNU package, available under the GNU General Public License. It is written primarily in C, Fortran, and R itself (partially self-hosting). Precompiled executables are provided for various operating systems. R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confusion Matrix
In the field of machine learning and specifically the problem of statistical classification, a confusion matrix, also known as an error matrix, is a specific table layout that allows visualization of the performance of an algorithm, typically a supervised learning one (in unsupervised learning it is usually called a matching matrix). Each row of the matrix represents the instances in an actual class while each column represents the instances in a predicted class, or vice versa – both variants are found in the literature. The name stems from the fact that it makes it easy to see whether the system is confusing two classes (i.e. commonly mislabeling one as another). It is a special kind of contingency table, with two dimensions ("actual" and "predicted"), and identical sets of "classes" in both dimensions (each combination of dimension and class is a variable in the contingency table). __TOC__ Example Given a sample of 12 individuals, 8 that have been diagnosed with cancer an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matthews Correlation Coefficient
In statistics, the phi coefficient (or mean square contingency coefficient and denoted by φ or rφ) is a measure of association for two binary variables. In machine learning, it is known as the Matthews correlation coefficient (MCC) and used as a measure of the quality of binary (two-class) Binary classification, classifications, introduced by biochemist Brian Matthews (biochemist), Brian W. Matthews in 1975. Introduced by Karl Pearson, and also known as the ''Yule phi coefficient'' from its introduction by Udny Yule in 1912 this measure is similar to the Pearson correlation coefficient in its interpretation. In fact, a Pearson correlation coefficient estimated for two binary variables will return the phi coefficient. Two binary variables are considered positively associated if most of the data falls along the diagonal cells. In contrast, two binary variables are considered negatively associated if most of the data falls off the diagonal. If we have a 2×2 table for two random varia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F1 Score
In statistical analysis of binary classification, the F-score or F-measure is a measure of a test's accuracy. It is calculated from the precision and recall of the test, where the precision is the number of true positive results divided by the number of all positive results, including those not identified correctly, and the recall is the number of true positive results divided by the number of all samples that should have been identified as positive. Precision is also known as positive predictive value, and recall is also known as sensitivity in diagnostic binary classification. The F1 score is the harmonic mean of the precision and recall. The more generic F_\beta score applies additional weights, valuing one of precision or recall more than the other. The highest possible value of an F-score is 1.0, indicating perfect precision and recall, and the lowest possible value is 0, if either precision or recall are zero. Etymology The name F-measure is believed to be named after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rand Index
The RAND Corporation (from the phrase "research and development") is an American nonprofit global policy think tank created in 1948 by Douglas Aircraft Company to offer research and analysis to the United States Armed Forces. It is financed by the U.S. government and private endowment, corporations, universities and private individuals. The company assists other governments, international organizations, private companies and foundations with a host of defense and non-defense issues, including healthcare. RAND aims for interdisciplinary and quantitative problem solving by translating theoretical concepts from formal economics and the physical sciences into novel applications in other areas, using applied science and operations research. Overview RAND has approximately 1,850 employees. Its American locations include: Santa Monica, California (headquarters); Arlington, Virginia; Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania; and Boston, Massachusetts. The RAND Gulf States Policy Institute has an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Precision And Recall
In pattern recognition, information retrieval, object detection and classification (machine learning), precision and recall are performance metrics that apply to data retrieved from a collection, corpus or sample space. Precision (also called positive predictive value) is the fraction of relevant instances among the retrieved instances, while recall (also known as sensitivity) is the fraction of relevant instances that were retrieved. Both precision and recall are therefore based on relevance. Consider a computer program for recognizing dogs (the relevant element) in a digital photograph. Upon processing a picture which contains ten cats and twelve dogs, the program identifies eight dogs. Of the eight elements identified as dogs, only five actually are dogs (true positives), while the other three are cats (false positives). Seven dogs were missed (false negatives), and seven cats were correctly excluded (true negatives). The program's precision is then 5/8 (true positives / se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Mean
In mathematics, the geometric mean is a mean or average which indicates a central tendency of a set of numbers by using the product of their values (as opposed to the arithmetic mean which uses their sum). The geometric mean is defined as the th root of the product of numbers, i.e., for a set of numbers , the geometric mean is defined as :\left(\prod_^n a_i\right)^\frac = \sqrt /math> or, equivalently, as the arithmetic mean in logscale: :\exp For instance, the geometric mean of two numbers, say 2 and 8, is just the square root of their product, that is, \sqrt = 4. As another example, the geometric mean of the three numbers 4, 1, and 1/32 is the cube root of their product (1/8), which is 1/2, that is, \sqrt = 1/2. The geometric mean applies only to positive numbers. The geometric mean is often used for a set of numbers whose values are meant to be multiplied together or are exponential in nature, such as a set of growth figures: values of the human population or inter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Retrieval
Information retrieval (IR) in computing and information science is the process of obtaining information system resources that are relevant to an information need from a collection of those resources. Searches can be based on full-text or other content-based indexing. Information retrieval is the science of searching for information in a document, searching for documents themselves, and also searching for the metadata that describes data, and for databases of texts, images or sounds. Automated information retrieval systems are used to reduce what has been called information overload. An IR system is a software system that provides access to books, journals and other documents; stores and manages those documents. Web search engines are the most visible IR applications. Overview An information retrieval process begins when a user or searcher enters a query into the system. Queries are formal statements of information needs, for example search strings in web search engines. In inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensitivity (test)
''Sensitivity'' and ''specificity'' mathematically describe the accuracy of a test which reports the presence or absence of a condition. Individuals for which the condition is satisfied are considered "positive" and those for which it is not are considered "negative". *Sensitivity (true positive rate) refers to the probability of a positive test, conditioned on truly being positive. *Specificity (true negative rate) refers to the probability of a negative test, conditioned on truly being negative. If the true condition can not be known, a " gold standard test" is assumed to be correct. In a diagnostic test, sensitivity is a measure of how well a test can identify true positives and specificity is a measure of how well a test can identify true negatives. For all testing, both diagnostic and screening, there is usually a trade-off between sensitivity and specificity, such that higher sensitivities will mean lower specificities and vice versa. If the goal is to return the ratio at w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clustering Algorithm
Cluster analysis or clustering is the task of grouping a set of objects in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster) are more similar (in some sense) to each other than to those in other groups (clusters). It is a main task of exploratory data analysis, and a common technique for statistical data analysis, used in many fields, including pattern recognition, image analysis, information retrieval, bioinformatics, data compression, computer graphics and machine learning. Cluster analysis itself is not one specific algorithm, but the general task to be solved. It can be achieved by various algorithms that differ significantly in their understanding of what constitutes a cluster and how to efficiently find them. Popular notions of clusters include groups with small distances between cluster members, dense areas of the data space, intervals or particular statistical distributions. Clustering can therefore be formulated as a multi-objective optimization problem. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |