|
Fort Stark
Fort Stark is a former military fortification in New Castle, New Hampshire, United States. Located at Jerry's Point (also called Jaffrey's Point) on the southeastern tip of New Castle Island, most of the surviving fort was developed in the early 20th century, following the Spanish–American War, although there were several earlier fortifications on the site, portions of which survive. The fort was named for John Stark, a New Hampshire officer who distinguished himself at the Battle of Bennington in the American Revolution. The purpose of Fort Stark was to defend the harbor of nearby Portsmouth and the Portsmouth Naval Shipyard. The fort remained in active use through the Second World War, after which it was used for reserve training by the US Navy. The property was partially turned over to the state of New Hampshire in 1979, which established Fort Stark Historic Site, and the remainder of the property was turned over in 1983. The grounds are open to the public during daylight ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Castle, New Hampshire
New Castle is a New England town, town in Rockingham County, New Hampshire, Rockingham County, New Hampshire, United States. The population was 1,000 at the 2020 census. It is the smallest and easternmost town in New Hampshire, and the only one located entirely on islands. It is home to Fort William and Mary#Fort Constitution, Fort Constitution Historic Site, Fort Stark Historic Site, and the New Castle Common, a recreation area on the Atlantic Ocean. New Castle is also home to a United States Coast Guard station, as well as the historic Wentworth by the Sea hotel. History The main island on which the town sits is the largest of several at the mouth of the Piscataqua River and was originally called "Great Island". Settled in 1623, an earthwork defense was built on Fort Point which would evolve into Fort William and Mary (rebuilt in 1808 as Fort Constitution). Chartered in 1679 as a parish of Portsmouth, New Hampshire, Portsmouth, it was incorporated on May 30, 1693, and was name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
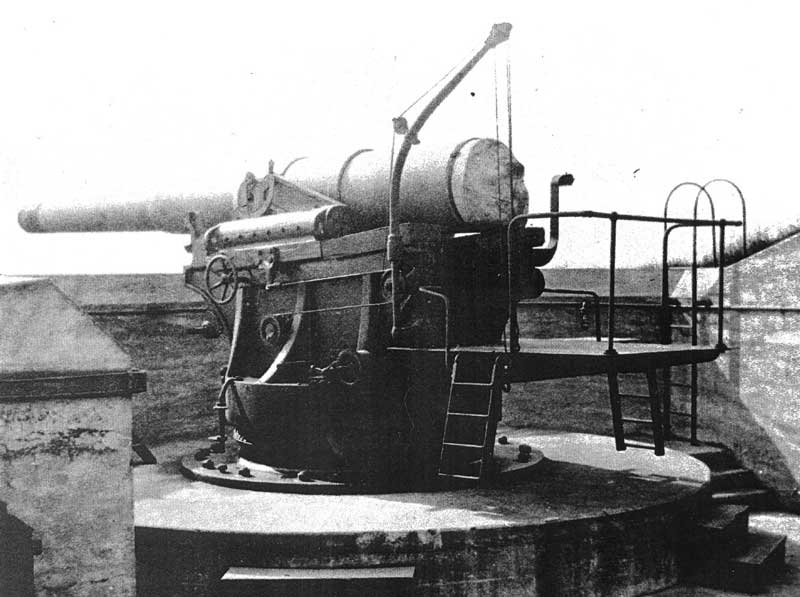
8-inch Gun M1888
The 8-inch gun M1888 (203 mm) was a U.S. Army Coast Artillery Corps gun, initially deployed 1898–1908 in about 75 fixed emplacements, usually on a disappearing carriage. During World War I, 37 or 47 of these weapons (references vary) were removed from fixed emplacements or from storage to create a railway gun version, the 8-inch Gun M1888MIA1 Barbette carriage M1918 on railway car M1918MI, converted from the fixed coast defense mountings and used during World War I and World War II. History The M1888 gun was a coastal artillery gun initially deployed as part of the Endicott system of fortifications. The first nine were deployed on the M1892 barbette carriage in 1898, but the improved M1894 and M1896 disappearing carriages soon became available, and approximately 64 additional weapons were deployed on these carriages by 1908. An "emergency" converted Rodman carriage was also used during the Spanish–American War in 1898 to quickly arm 21 emplacements with the modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Navy
The Spanish Navy or officially, the Armada, is the maritime branch of the Spanish Armed Forces and one of the oldest active naval forces in the world. The Spanish Navy was responsible for a number of major historic achievements in navigation, the most famous being the discovery of America and the first global circumnavigation by Elcano. For several centuries, it played a crucial logistical role in the expansion and consolidation of the Spanish Empire, and defended a vast trade network across the Atlantic Ocean between the Americas and Europe, and the Manila Galleon across the Pacific Ocean between the Philippines and the Americas. The Spanish Navy was the most powerful maritime force in the world from the late 15th century to the early 18th century. In the early 19th century, with the loss of most of its empire, Spain transitioned to a smaller fleet but maintained a major shipbuilding industry which produced important technical innovations. The Spanish Navy built and oper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Of Fortifications
Several boards have been appointed by US presidents or Congress to evaluate the US defensive fortifications, primarily coastal defenses near strategically important harbors on the US shores, its territories, and its protectorates. Endicott Board In 1885 US President Grover Cleveland appointed a joint Army, Navy and civilian board, headed by Secretary of War William Crowninshield Endicott, known as the Board of Fortifications (now usually referred to simply as the Endicott Board). The findings of the Board in its 1886 report illustrated a grim picture of neglect of America's coast defenses and recommended a massive $127 million construction program for a series of new forts with breech-loading cannons, mortars, floating batteries, and submarine mines for some 29 locations on the US coast. Coast Artillery fortifications built between 1885 and 1905 are often referred to as Endicott Period fortifications. Prior efforts at harbor defense construction had ceased in the 1870s. Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Foster (Kittery, Maine)
Fort Foster, now part of Fort Foster Park, is a historic fort active 1901-1946 on the southwest tip of Gerrish Island in the Kittery Point area of Kittery, Maine. The park includes beaches and trails. Battery Bohlen and Battery Chapin were the major parts of the fort. History The land was acquired by the U.S. federal government in 1872 and the fort was built from 1898 to 1901 as part of the large-scale Endicott Program. Other forts of this era in the Coast Defenses of Portsmouth included Fort Constitution and Fort Stark.Berhow, p. 205 The site was a sub-post of Fort Constitution and was named for American Civil War-era Brevet Major General John G. Foster of New Hampshire. Fort Foster originally had two gun batteries: Battery Bohlen with three 10-inch (254 mm) M1895 disappearing guns and Battery Chapin with two 3-inch (76 mm) M1902 guns on pedestal mounts. Battery Bohlen was built in 1898-1901 and Battery Chapin was completed in 1904. Battery Bohlen was named for Brigadier ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodman Gun
Drawing comparing Model 1844 8-inch columbiad and Model 1861 10-inch "Rodman" columbiad. The powder chamber on the older columbiad is highlighted by the red box. The Rodman gun is any of a series of American Civil War–era columbiads designed by Union artilleryman Thomas Jackson Rodman (1815–1871). The guns were designed to fire both shot and shell. These heavy guns were intended to be mounted in seacoast fortifications. They were built in 8-inch, 10-inch, 13-inch, 15-inch, and 20-inch bore. Other than size, the guns were all nearly identical in design, with a curving bottle shape, large flat cascabels with ratchets or sockets for the elevating mechanism. Rodman guns were true guns that did not have a howitzer-like powder chamber, as did many earlier columbiads. Rodman guns differed from all previous artillery because they were hollow cast, a new technology that Rodman developed that resulted in cast-iron guns that were much stronger than their predecessors. Casting file:R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states that had seceded. The central cause of the war was the dispute over whether slavery would be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prevented from doing so, which was widely believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Decades of political controversy over slavery were brought to a head by the victory in the 1860 U.S. presidential election of Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion into the west. An initial seven southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding from the United States and, in 1861, forming the Confederacy. The Confederacy seized U.S. forts and other federal assets within their borders. Led by Confederate President Jefferson Davis, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
War Of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It began when the United States declared war on 18 June 1812 and, although peace terms were agreed upon in the December 1814 Treaty of Ghent, did not officially end until the peace treaty was ratified by Congress on 17 February 1815. Tensions originated in long-standing differences over territorial expansion in North America and British support for Native American tribes who opposed US colonial settlement in the Northwest Territory. These escalated in 1807 after the Royal Navy began enforcing tighter restrictions on American trade with France and press-ganged men they claimed as British subjects, even those with American citizenship certificates. Opinion in the US was split on how to respond, and although majorities in both the House and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Redoubt
A redoubt (historically redout) is a fort or fort system usually consisting of an enclosed defensive emplacement outside a larger fort, usually relying on earthworks, although some are constructed of stone or brick. It is meant to protect soldiers outside the main defensive line and can be a permanent structure or a hastily constructed temporary fortification. The word means "a place of retreat". Redoubts were a component of the military strategies of most European empires during the colonial era, especially in the outer works of Vauban-style fortresses made popular during the 17th century, although the concept of redoubts has existed since medieval times. A redoubt differs from a redan in that the redan is open in the rear, whereas the redoubt was considered an enclosed work. The advent of mobile warfare in the 20th century diminished the importance of stationary defence positions and siege warfare. Historically important redoubts English Civil War During the English Civ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seacoast Defense In The United States
Seacoast defense was a major concern for the United States from its independence until World War II. Before Military aviation, airplanes, many of America's enemies could only reach it from the sea, making coastal forts an economical alternative to Standing army, standing armies or a large navy. After the 1940s, it was recognized that fixed fortifications were obsolete and ineffective against aircraft and missiles. However, in prior eras foreign fleets were a realistic threat, and substantial fortifications were built at key locations, especially protecting major harbors. The defenses heavily depended on fortifications but also included Submarine mines in United States harbor defense, submarine minefields, nets and boom (navigational barrier), booms, ships, and airplanes. Therefore, all of the armed forces participated in seacoast defense, but the United States Army Corps of Engineers, U.S. Army Corps of Engineers played the central role in constructing fixed defenses. Designs evo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort William And Mary
Fort William and Mary was a colonial fortification in Britain's worldwide system of defenses, defended by soldiers of the Province of New Hampshire who reported directly to the royal governor. The fort, originally known as "The Castle," was situated on the island of New Castle, New Hampshire, at the mouth of the Piscataqua River estuary. It was renamed Fort William and Mary circa 1692, after the accession of the monarchs William III and Mary II to the British throne.Roberts, pp. 498-499 It was captured by Patriot forces, recaptured, and later abandoned by the British in the Revolutionary War. The fort was renamed Fort Constitution in 1808 following rebuilding. The fort was further rebuilt and expanded through 1899 and served actively through World War II. Colonial period First fortified by the British prior to 1632, the fort guarded access to the harbor at Portsmouth and served as the colony's main munitions depot. The fort also served to protect Kittery, Maine, on the oppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.png)

