|
Fort McKinley (Maine)
Fort McKinley is a former United States Army coastal defense fort on Great Diamond Island, Maine in Casco Bay, which operated from 1873 to 1947. It was named for President William McKinley. It included a sub-post, Fort Lyon, on Cow Island, just north of Great Diamond Island. Fort Lyon was named for Nathaniel Lyon. Both forts were part of the Coast Defenses of Portland, renamed the Harbor Defenses of Portland in 1925, a command which protected Portland's port and naval anchorage 1895-1950. In 1946 Fort Lyon was closed and turned over to the City of Portland. After Fort McKinley's closure it was transferred to the United States Navy, which sold the site (via the General Services Administration) to private interests in 1961. The Fort McKinley Historic District was listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1985. History Construction and armament The Board of Fortifications, often called the Endicott Board, recommended a comprehensive program of new fortifications in 1885 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12-inch-M1897-Firing
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12-inch Mortars At Battery Meigs, Fort Washington, MD
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Dashiell Bayard
George Dashiell Bayard (December 18, 1835 – December 14, 1862) was a career soldier in the United States Army and a general in the Union Army in the American Civil War. He was wounded in the Battle of Fredericksburg and died the next day. Early life He was born in Seneca Falls, New York, on December 18, 1835, to Jane Ann Dashiell and Samuel John Bayard, the son of Samuel Bayard (1766–1840) and the grandson of John Bayard (1738–1807). His family moved as homesteaders to the Iowa Territory. He attended the United States Military Academy at West Point, graduating in 1856 as a second lieutenant in the U.S. cavalry. He graduated 11th in a class of 49. Bayard fought in the Indian Wars in Kansas and Colorado from 1856 to 1861. Bayard was shot in the face with a Kiowa arrow on July 11, 1860, and suffered considerable pain for months. Civil War On August 27, 1861, Bayard was promoted to colonel in the 1st Pennsylvania Cavalry, based in Tenallytown (now Tenleytown, Washington ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6-inch Gun M1900
The 6-inch gun M1897 (152 mm) and its variants the M1900, M1903, M1905, M1908, and M1 (a.k.a. T2) were coastal artillery pieces installed to defend major American seaports between 1897 and 1945. For most of their history they were operated by the United States Army Coast Artillery Corps. They were installed on disappearing carriages or pedestal (a.k.a. barbette) mountings, and during World War II many were remounted on shielded barbette carriages. Most of the weapons not in the Philippines were scrapped within a few years after World War II. History In 1885, William C. Endicott, President Grover Cleveland's Secretary of War, was tasked with creating the Board of Fortifications to review seacoast defenses. The findings of the board illustrated a grim picture of existing defenses in its 1886 report and recommended a massive $127 million construction program of breech-loading cannons, mortars, floating batteries, and submarine mines for some 29 locations on the US coastline. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Weymouth
George Weymouth (Waymouth) () was an English explorer of the area now occupied by the state of Maine. Voyages George Weymouth was a native of Cockington, Devon, who spent his youth studying shipbuilding and mathematics. In 1602 Weymouth was hired to seek a northwest passage to India by the recently formed East India Company. He sailed the ship ''Discovery'' 300 miles into Hudson Strait but turned back on July 26, as the year was far spent and many men were ill. Weymouth reached Dartmouth on September 5, 1602. 1605 expedition In March 1605 Thomas Arundell, 1st Baron Arundell of Wardour and Henry Wriothesley, 3rd Earl of Southampton sent Captain Weymouth to found a colony in Virginia under the ruse of searching again for a northwest passage. Weymouth sailed from England on March 31, 1605 on the ship ''Archangel''Drake, Samuel Adams. ''The Pine-tree Coast'', (Estes & Lauriat, 1890), 218. and landed near Monhegan off the coast of Maine on May 17, 1605. A report of the voyage, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
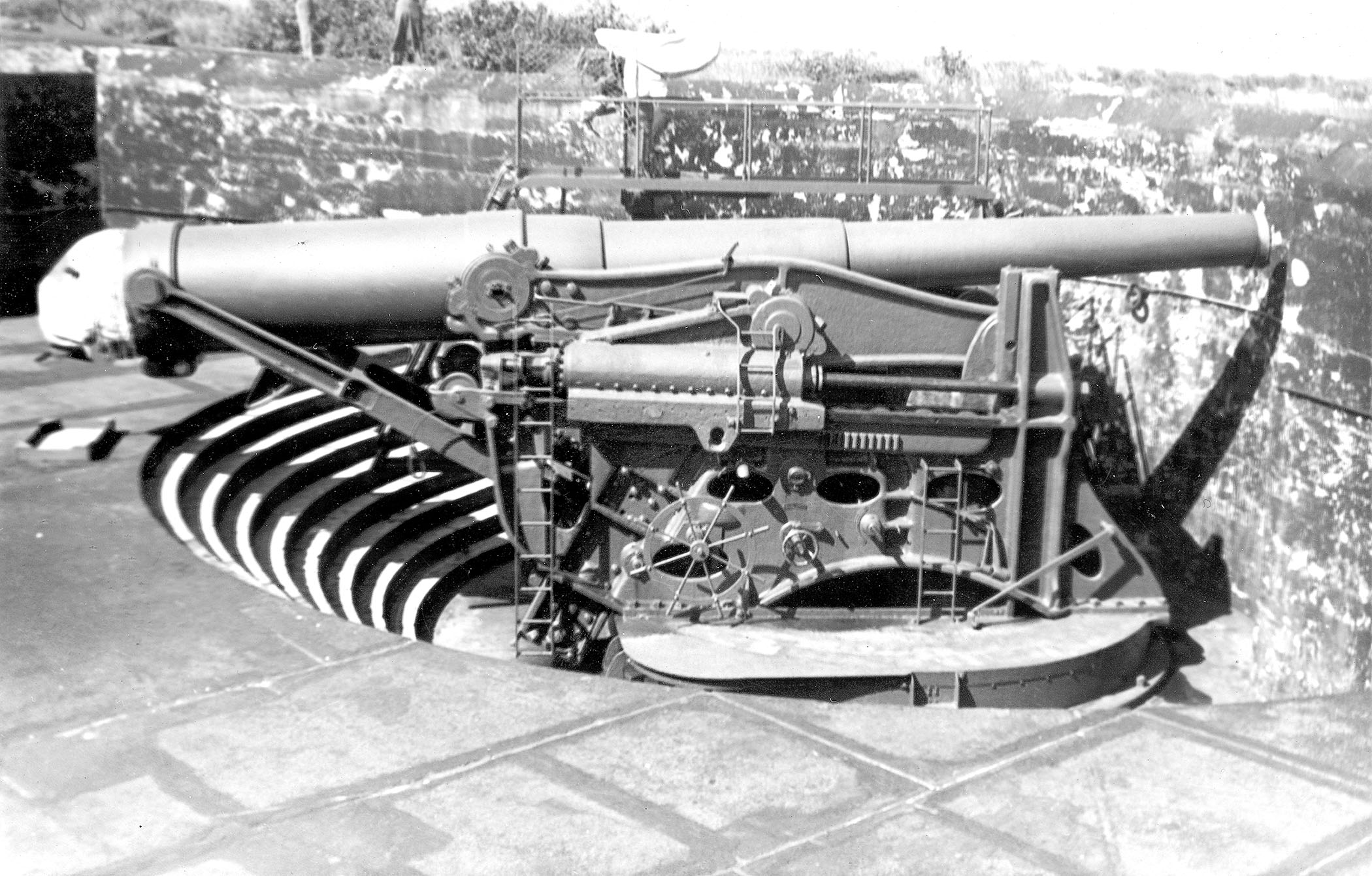
Masking Parapet
A disappearing gun, a gun mounted on a ''disappearing carriage'', is an obsolete type of artillery which enabled a gun to hide from direct fire and observation. The overwhelming majority of carriage designs enabled the gun to rotate backwards and down behind a parapet, or into a pit protected by a wall, after it was fired; a small number were simply barbette mounts on a retractable platform. Either way, retraction lowered the gun from view and direct fire by the enemy while it was being reloaded. It also made reloading easier, since it lowered the breech to a level just above the loading platform, and shells could be rolled right up to the open breech for loading and ramming. Other benefits over non-disappearing types were a higher rate of repetitive fire and less fatigue for the gun crew. Some disappearing carriages were complicated mechanisms, protection from aircraft observation and attack was difficult, and almost all restricted the elevation of the gun. With a few ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-inch Gun M1898
The 3-inch gun M1903 and its predecessors the M1898 and M1902 were rapid fire breech-loading artillery guns with a 360-degree traverse. In some references they are called "15-pounders" due to their projectile weight. They were originally emplaced from 1899 to 1917 and served until shortly after World War II. These 3-inch guns were placed to provide fire to protect underwater mines and nets against minesweepers, and also to protect against motor torpedo boats. In some documentation they are called "mine defense guns". The 3-inch guns were mounted on pedestal mounts (or a retractable "masking parapet" mount for the M1898) that bolted into a concrete emplacement that provided cover and safety for the gun's crew. History The 3-inch mine defense guns were part of a comprehensive plan of new fortifications specified by the Board of Fortifications of 1885. The new forts initially included guns up to 12-inch (305 mm) on disappearing carriages, to conceal the fort from obser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6-inch Gun M1897
The 6-inch gun M1897 (152 mm) and its variants the M1900, M1903, M1905, M1908, and M1 (a.k.a. T2) were coastal artillery pieces installed to defend major American seaports between 1897 and 1945. For most of their history they were operated by the United States Army Coast Artillery Corps. They were installed on disappearing carriages or pedestal (a.k.a. barbette) mountings, and during World War II many were remounted on shielded barbette carriages. Most of the weapons not in the Philippines were scrapped within a few years after World War II. History In 1885, William C. Endicott, President Grover Cleveland's Secretary of War, was tasked with creating the Board of Fortifications to review seacoast defenses. The findings of the board illustrated a grim picture of existing defenses in its 1886 report and recommended a massive $127 million construction program of breech-loading cannons, mortars, floating batteries, and submarine mines for some 29 locations on the US coastline. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8-inch Gun M1888
The 8-inch gun M1888 (203 mm) was a U.S. Army Coast Artillery Corps gun, initially deployed 1898–1908 in about 75 fixed emplacements, usually on a disappearing carriage. During World War I, 37 or 47 of these weapons (references vary) were removed from fixed emplacements or from storage to create a railway gun version, the 8-inch Gun M1888MIA1 Barbette carriage M1918 on railway car M1918MI, converted from the fixed coast defense mountings and used during World War I and World War II. History The M1888 gun was a coastal artillery gun initially deployed as part of the Endicott system of fortifications. The first nine were deployed on the M1892 barbette carriage in 1898, but the improved M1894 and M1896 disappearing carriages soon became available, and approximately 64 additional weapons were deployed on these carriages by 1908. An "emergency" converted Rodman carriage was also used during the Spanish–American War in 1898 to quickly arm 21 emplacements with the modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brigadier Samuel Thompson
Thompson's War was an early American Revolutionary War confrontation between Samuel Thompson's patriot militia and loyalists supported by HMS ''Canceaux''. The confrontation ended without fatalities, but provoked the retaliatory Burning of Falmouth five months later. Falmouth is now known as Portland, Maine, but Maine was part of Massachusetts at the time. Background Brunswick, Maine tavern owner Samuel Thompson had been elected to the Brunswick Board of selectmen in 1768, 1770, and 1771. He was elected commander of the Brunswick militia in 1774 and headed the local enforcement committee for the Continental Association created by the First Continental Congress to boycott all goods from Great Britain. The Continental Association attempted to enforce the boycott on 2 March 1775 against a shipload of sail, rope, and rigging for loyalist shipbuilder Captain Samuel Coulson of Portland by demanding the delivery ship leave port. Coulson requested delay while the English sloop comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
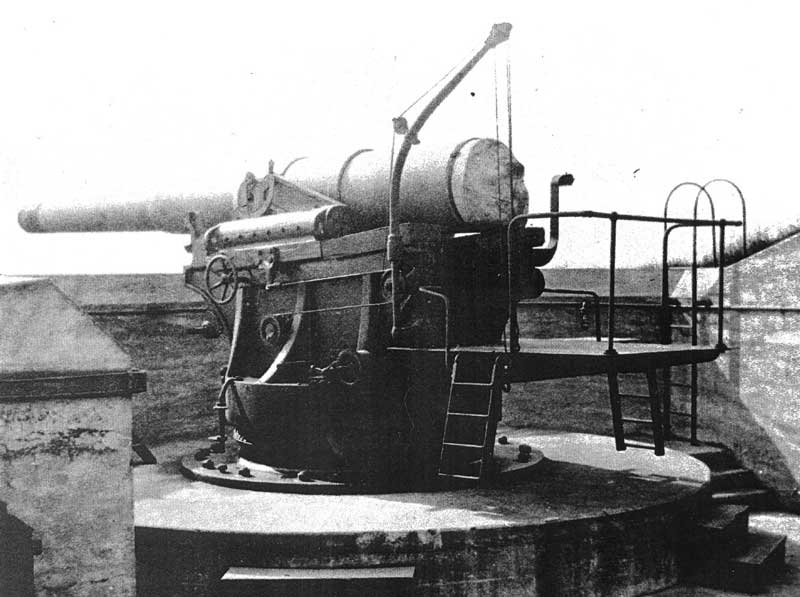
12-inch Gun M1888
The 12-inch coastal defense gun M1895 (305 mm) and its variants the M1888 and M1900 were large coastal artillery pieces installed to defend major American seaports between 1895 and 1945. For most of their history they were operated by the United States Army Coast Artillery Corps. Most were installed on disappearing carriages, with early installations on low-angle barbette mountings. From 1919, 19 long-range two-gun batteries were built using the M1895 on an M1917 long-range barbette carriage. Almost all of the weapons not in the Philippines were scrapped during and after World War II. History In 1885, William C. Endicott, President Grover Cleveland's secretary of war, was tasked with creating the Board of Fortifications to review seacoast defenses. The findings of the board illustrated a grim picture of existing defenses, and in its 1886 report recommended a massive $127 million construction program of breech-loading cannons, mortars, floating batteries, and submarine mines f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hiram Gregory Berry
Hiram Gregory Berry (August 27, 1824 – May 3, 1863) was an American politician and general in the Army of the Potomac during the American Civil War. Birth and early years Hiram Gregory Berry was born on August 27, 1824 on his parents' farm in the Meadows of Thomaston (now the City of Rockland), Maine. He was the fourth child of Frances Gregory Berry and Jeremiah Berry. He had 3 brothers and one sister. Hiram G. Berry was born in Rockland, Maine, where he worked as a carpenter and a navigator. He served several terms in the State Legislature and subsequently became the mayor of Rockland. He also originated and commanded the "Rockland Guard," a volunteer militia company, which held a reputation for drill and discipline. On April 21, 1852, Hiram co-founded the Rockland Steam Manufacturing Company along with I. K. Kimball, A. H. Kimball, and Joseph C. Libby. The company created doors, sashes, and blinds. Its buildings, however, caught fire in 1855 and were destroyed. After bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_Gun_on_Moncrieff_disappearing_mount%2C_at_Scaur_Hill_Fort%2C_Bermuda.jpg)