|
Fort Dunvegan
Dunvegan Provincial Park and Historic Dunvegan ( ) are a provincial park and a provincial historic site of Alberta located together on one site. They are located in Dunvegan, at the crossing of Peace River and Highway 2, between Rycroft and Fairview. The site was the location of one of Alberta's earliest fur trade posts and missionary centres. The location of the original Fort Dunvegan is also a National Historic Site of Canada. It was built in 1805 by Archibald Norman McLeod and named for his family's ancestral home, Dunvegan Castle. The historic site consists of a visitor centre and four historic buildings manned seasonally by historic interpreters. The campground consists of 67 sites with electrical hook ups, a day use area and playground. Dunvegan Provincial Park is jointly managed by the ministries of Alberta Parks (the campground) and Alberta Culture (the historic site). Dunvegan West Wildland Provincial Park follows the south bank of the Peace River west from thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Territories (NWT) to the north, and the U.S. state of Montana to the south. It is one of the only two landlocked provinces in Canada (Saskatchewan being the other). The eastern part of the province is occupied by the Great Plains, while the western part borders the Rocky Mountains. The province has a predominantly continental climate but experiences quick temperature changes due to air aridity. Seasonal temperature swings are less pronounced in western Alberta due to occasional Chinook winds. Alberta is the fourth largest province by area at , and the fourth most populous, being home to 4,262,635 people. Alberta's capital is Edmonton, while Calgary is its largest city. The two are Alberta's largest census metropolitan areas. More tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta Parks
Alberta Parks is an agency of the Government of Alberta which is responsible for managing Alberta's provincial parks and protected areas. History Alberta's system of provincial parks began with the striking of a committee on parks by then Premier J. E. Brownlee in 1929. This led to the passage of the ''Provincial Parks and Protected Areas Act'' in 1930 and the formation of the Provincial Board of Management to oversee the system. The first provincial parks were Aspen Beach Provincial Park, established in 1932, followed by Gooseberry Lake, Park Lake, Sylvan Lake and Saskatoon Island later that same year. However further development of the system was halted during the Great Depression and during the Second World War. Major changes began in 1950 with the passage of a new ''Parks Act'', the transferring of responsibilities for parks to the Department of Lands and Forests, and the creation of a new three-person Parks Board. A major budget increase in 1952-53 saw the hiring of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ămile Grouard
Ămile Jean-Baptiste Marie Grouard O.M.I., "one of the most influential clerics in northern Alberta," was Apostolic Vicar of Athabasca. A gifted linguist, Grouard learned a number of languages of the indigenous peoples. Life Grouard was born at Brulon, in Brittany, France February 1, 1840, the son of AndrĂ© and Anne MĂ©nard Grouard; his father was a gendarme. Vital-Justin Grandin O.M.I. was his cousin. He began seminary training at Le Mans, before emigrating in 1860 to Canada, where he completed his theological studies at the SĂ©minaire de QuĂ©bec. In May 1862, he was ordained by Alexandre-Antonin TachĂ©, Bishop of the Diocese of Saint Boniface in Manitoba. First journey North In June 1862, newly ordained Father Grouard then 22 years old, was in Fort Garry with Father Ămile Petitot, both having travelled there from Montreal with Bishop TachĂ©, and fellow Oblates, Constantine Scollen and John Duffy.The two then travelled north with the Portage La Loche Brigade. He described ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oblate
In Christianity (especially in the Roman Catholic, Orthodox, Anglican and Methodist traditions), an oblate is a person who is specifically dedicated to God or to God's service. Oblates are individuals, either laypersons or clergy, normally living in general society, who, while not professed monks or nuns, have individually affiliated themselves with a monastic community of their choice. They make a formal, private promise (annually renewable or for life, depending on the monastery with which they are affiliated) to follow the Rule of the Order in their private lives as closely as their individual circumstances and prior commitments permit. Such oblates are considered an extended part of the monastic community; for example, Benedictine oblates also often include the post-nominal letters 'OblSB' or 'ObSB' after their names on documents. They are comparable to the tertiaries associated with the various mendicant orders. The term "oblate" is also used in the official name of some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Flu
The 1918â1920 influenza pandemic, commonly known by the misnomer Spanish flu or as the Great Influenza epidemic, was an exceptionally deadly global influenza pandemic caused by the H1N1 influenza A virus. The earliest documented case was March 1918 in Kansas, United States, with further cases recorded in France, Germany and the United Kingdom in April. Two years later, nearly a third of the global population, or an estimated 500 million people, had been infected in four successive waves. Estimates of deaths range from 17 million to 50 million, and possibly as high as 100 million, making it one of the deadliest pandemics in history. The pandemic broke out near the end of World War I, when wartime censors suppressed bad news in the belligerent countries to maintain morale, but newspapers freely reported the outbreak in neutral Spain, creating a false impression of Spain as the epicenter and leading to the "Spanish flu" misnomer. Limited historical epidemiological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hudson's Hope
Hudson's Hope is a district municipality in northeastern British Columbia, Canada, in the Peace River Regional District. Having been first settled along the Peace River in 1805, it is the third-oldest European-Canadian community in the province, although it was not incorporated until 1965. Most jobs in the economy are associated with the nearby W. A. C. Bennett Dam and Peace Canyon Dam, and timber logging. There is debate about the origin of Hudson's Hope's name. One theory derives the word "Hudson's" from the Hudson's Bay Company and "Hope" from the Scottish word "hope" meaning a "small enclosed valley". Another theory has the name derived from a prospector named Hudson who came to the area searching for gold.Peace Liard Employment Development Association. (October 1985). ''Peace Liard Economic Profile''. page 53. The District of Hudson's Hope slogan is the "Playground of the Peace". History Nomadic aboriginal Dene zaa tribes originally occupied the area. Alexander Mackenzie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athapaskan
Athabaskan (also spelled ''Athabascan'', ''Athapaskan'' or ''Athapascan'', and also known as Dene) is a large family of indigenous languages of North America, located in western North America in three areal language groups: Northern, Pacific Coast and Southern (or Apachean). Kari and Potter (2010:10) place the total territory of the 53 Athabaskan languages at . Chipewyan is spoken over the largest area of any North American native language, while Navajo is spoken by the largest number of people of any native language north of Mexico. ''Athebaskan '' is a version of a Cree name for Lake Athabasca ( crm, ÄĂ°apÄskÄw, script=Latn 'herethere are reeds one after another'), in Canada. Cree is one of the Algonquian languages and therefore not itself an Athabaskan language. The name was assigned by Albert Gallatin in his 1836 (written 1826) classification of the languages of North America. He acknowledged that it was his choice to use that name for the language family and its asso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunne-za
The Dane-zaa (ááá, also spelled Dunne-za, or Tsattine) are an Athabaskan-speaking group of First Nations people. Their traditional territory is around the Peace River in Alberta and British Columbia, Canada. Today, about 1,600 Dane-zaa reside in British Columbia and an estimated half of them speak the Dane-zaa language. Approximately 2,000 Dane-zaa live in Alberta. Europeans historically referred to that Dane-zaa are the Beaver tribe. Name The name ''Dunne-za'' has been translated to "Those who live among the beaver." The spelling ''Dane-zaa'' is typically used for "the Real People." That spelling is used by the Dane-zaa Language Authority. Different tribes and First Nations use different spellings. For example, the Doig River First Nation (DRFN) and Halfway River First Nation (HRFN) use ''Dane-Zaa''. Prophet River First Nation (PRFN) uses ''Dunne Tsaa''; and the West Moberly First Nations (WMFNs) use ''Dunne-za'' or ''Dunne Za''. Where other spellings are used in citatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Fork
Fort Fork a North West Company (NWC) trading post on the Peace River, established in 1792. From 1 November 1792 to 9 May 1793, Alexander Mackenzie wintered there prior to his expedition to the Pacific Ocean. The fort was used until the NWC merged with the XY Company in 1805, after which it was replaced by Fort Dunvegan, further upstream. The fort was located southwest of the present-day town of Peace River, Alberta. No known physical remains of the fort have survived, but there is an archaeological site there marked by a semi-circular depression and a cairn. The site was declared a National Historic Site of Canada National Historic Sites of Canada (french: Lieux historiques nationaux du Canada) are places that have been designated by the federal Minister of the Environment on the advice of the Historic Sites and Monuments Board of Canada (HSMBC), as being ... in 1928. References North West Company forts Forts or trading posts on the National Historic Sites of Canad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voyageurs
The voyageurs (; ) were 18th and 19th century French Canadians who engaged in the transporting of furs via canoe during the peak of the North American fur trade. The emblematic meaning of the term applies to places (New France, including the ''Pays d'en Haut'' and the ''Illinois Country, Pays des Illinois'') and times where transportation of materials was mainly over long distances. The voyageurs were regarded as legendary. They were heroes celebrated in folklore and music. For reasons of promised celebrity status and wealth, this position was coveted. Despite the fame surrounding the voyageur, their life was one of toil and not nearly as glorious as folk tales make it out to be. For example, they had to be able to carry two bundles of fur over portages. Some carried up to four or five, and there is a report of a voyageur carrying seven bundles for half of a mile.Mike Hillman, "La Bonga: The Greatest Voyageur" Boundary Waters Journal Magazine, Summer 2010 Issue, pp 20â25 Her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
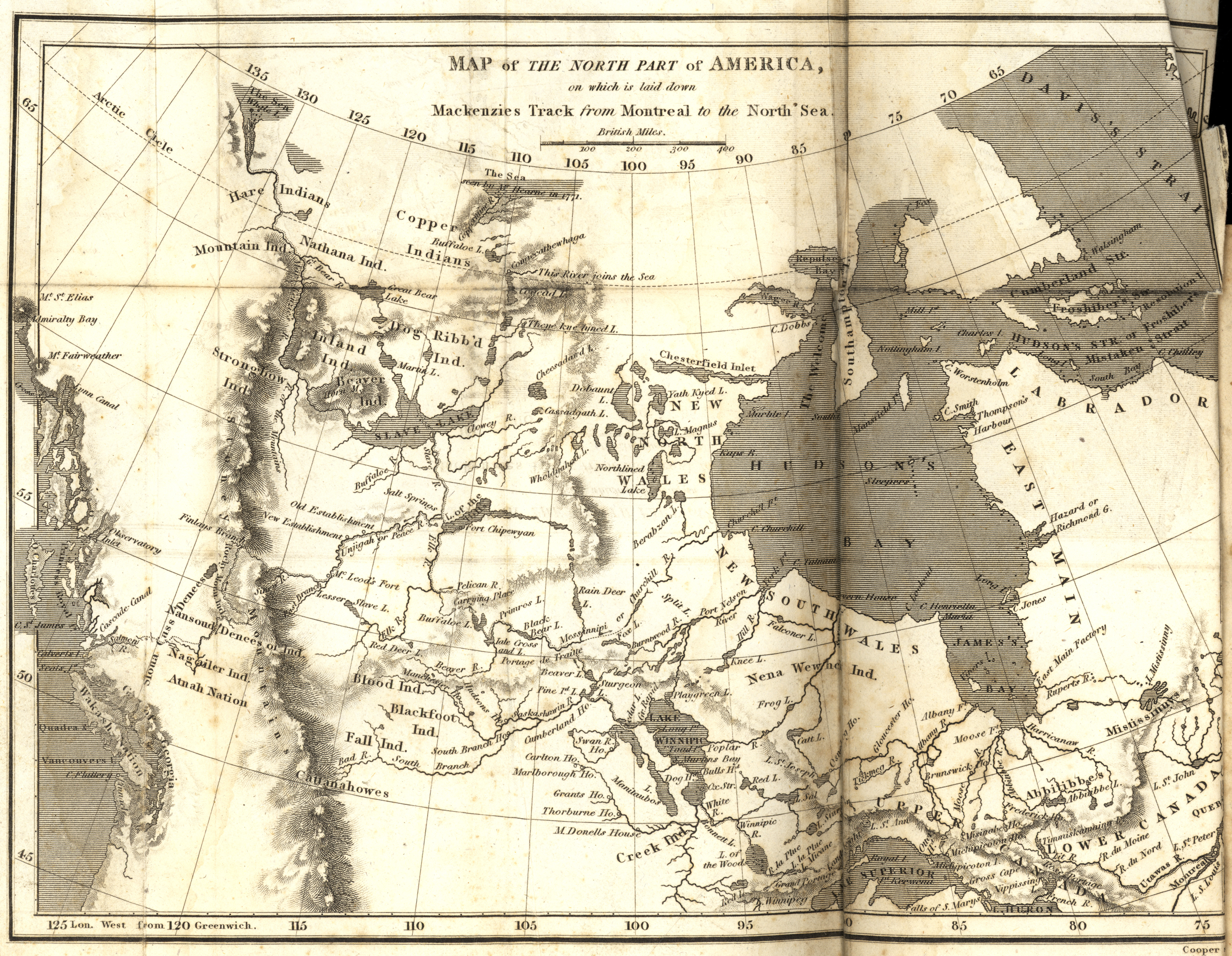
Sir Alexander Mackenzie
Sir Alexander Mackenzie (or MacKenzie, gd, Alasdair MacCoinnich; â 12 March 1820) was a Scottish explorer known for accomplishing the first crossing of America north of Mexico in 1793. The Mackenzie River is named after him. Early life Mackenzie was born in House in Stornoway in Lewis. He was the third of the four children born to Kenneth 'Corc' Mackenzie (1731â1780) and his wife Isabella MacIver, from another prominent mercantile family in Stornoway. When only 14 years old, Mackenzie's father served as an ensign to protect Stornoway during the Jacobite rising of 1745. He later became a merchant and held the tack of Melbost; his grandfather being a younger brother of Murdoch Mackenzie, 6th Laird of Fairburn. Educated at the same school as Colin Mackenzie, the army officer and first Surveyor General of India, he sailed to New York City with his father to join an uncle, John Mackenzie, in 1774, after his mother died in Scotland. In 1776, during the American War of Indepe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Dunvegan On The Peace River
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large stone walls had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae (famous for the huge stone blocks of its 'cyclopean' walls). A Greek ''Towns of ancient Greece#Military settlements, phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the ancient Roman, Roman castellum or English language, English fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |