|
Fort Andrews
Fort Andrews was created in 1897 as part of the Coast (later Harbor) Defenses of Boston, Massachusetts. Construction began in 1898 and the fort was substantially complete by 1904. The fort was named after Major General George Leonard Andrews, an engineer and Civil War commander, who assisted in the construction of nearby Fort Warren in Boston Harbor. It occupies the entire northeast end of Peddocks Island in Boston Harbor, and was originally called the Peddocks Island Military Reservation. Once an active Coast Artillery post, it was manned by hundreds of soldiers and bristled with mortars and guns that controlled the southern approaches to Boston and Quincy Bay. The fort also served as a prisoner-of-war camp for Italian prisoners during World War II, who were employed as laborers following the Italian surrender to the Allies in 1943. Today, the fort is abandoned, and is managed by the Massachusetts Department of Conservation and Recreation, as part of the Boston Harbor I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harbor Defenses Of Boston
The Harbor Defenses of Boston was a United States Army Coast Artillery Corps harbor defense command. It coordinated the coast defenses of Boston, Massachusetts from 1895 to 1950, beginning with the Endicott program. These included both coast artillery forts and underwater minefields. The command originated circa 1895 as the Boston Artillery District, was renamed Coast Defenses of Boston in 1913, and again renamed Harbor Defenses of Boston in 1925.Stanton, pp. 455-481Rinaldi, pp. 165-166Berhow, p. 430-434 History Early Boston forts Colonial period Boston Harbor's principal coastal fort of the colonial era was Castle William, whose site was first fortified in 1634 and called "the Castle" until 1692, when it was renamed for William III, the King of England at the time. It is one of the oldest continuously fortified sites in the northeastern United States; however, the site of Fort William and Mary near Portsmouth, New Hampshire was fortified at least two years previously. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coast Defenses Of Boston
The Harbor Defenses of Boston was a United States Army Coast Artillery Corps harbor defense command. It coordinated the coast defenses of Boston, Massachusetts from 1895 to 1950, beginning with the Endicott program. These included both coast artillery forts and underwater minefields. The command originated circa 1895 as the Boston Artillery District, was renamed Coast Defenses of Boston in 1913, and again renamed Harbor Defenses of Boston in 1925.Stanton, pp. 455-481Rinaldi, pp. 165-166Berhow, p. 430-434 History Early Boston forts Colonial period Boston Harbor's principal coastal fort of the colonial era was Castle William, whose site was first fortified in 1634 and called "the Castle" until 1692, when it was renamed for William III, the King of England at the time. It is one of the oldest continuously fortified sites in the northeastern United States; however, the site of Fort William and Mary near Portsmouth, New Hampshire was fortified at least two years previously. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Andrew
Fort Andrew is a former fort built as Gurnet Fort in 1776 for the American Revolutionary War on Gurnet Point in Plymouth, Massachusetts. It became a federal fort and was rebuilt in 1808, and again in 1863 during the Civil War when it received its current name. It is named for John A. Andrew, governor of Massachusetts 1861–1866.Roberts, p. 393 In 1863 Fort Standish was built nearby on Saquish Head. After the war, the federal government declared Fort Andrew an inactive military reservation in 1869. The reservation was sold in 1926 and mostly became private property, except for the US Coast Guard light station. A World War II fire control tower was built on the parapet of the old fort. Plymouth (Gurnet Point) lighthouse is also on Gurnet Point, and was moved inside the fort's earthworks to protect it from beach erosion in 1997–1998. History Gurnet Fort was built in 1776 for the American Revolutionary War, via a resolution of the Massachusetts General Court of June 3, 1776. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Board Of Fortifications
Several boards have been appointed by US presidents or Congress to evaluate the US defensive fortifications, primarily coastal defenses near strategically important harbors on the US shores, its territories, and its protectorates. Endicott Board In 1885 US President Grover Cleveland appointed a joint Army, Navy and civilian board, headed by Secretary of War William Crowninshield Endicott, known as the Board of Fortifications (now usually referred to simply as the Endicott Board). The findings of the Board in its 1886 report illustrated a grim picture of neglect of America's coast defenses and recommended a massive $127 million construction program for a series of new forts with breech-loading cannons, mortars, floating batteries, and submarine mines for some 29 locations on the US coast. Coast Artillery fortifications built between 1885 and 1905 are often referred to as Endicott Period fortifications. Prior efforts at harbor defense construction had ceased in the 1870s. Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Banks (Massachusetts)
Fort Banks was a U.S. Coast Artillery fort located in Winthrop, Massachusetts. It served to defend Boston Harbor from enemy attack from the sea and was built in the 1809 during what is known as the Endicott period, a time in which the coast defenses of the United States were seriously expanded and upgraded with new technology. Today, the fort's mortar battery is on the National Register of Historic Places. The fort was active during World War II as the site of the Harbor Defense Command Post (HDCP) for the Harbor Defenses of Boston, and was greatly expanded with numerous temporary structures (see 1938 map at top left). Because of its campus-like appearance and the fact that it was located on land, close of Boston, the fort was known as "The Country Club" by Coast Artillery soldiers pleased to be posted there. Fort Banks was named for Nathaniel P. Banks, a Civil War general, the 24th Governor of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts and a former Speaker of the U.S. House of Represe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3-inch M1902 Seacoast Gun
The 3-inch gun M1903 and its predecessors the M1898 and M1902 were rapid fire breech-loading artillery guns with a 360-degree traverse. In some references they are called "15-pounders" due to their projectile weight. They were originally emplaced from 1899 to 1917 and served until shortly after World War II. These 3-inch guns were placed to provide fire to protect underwater mines and nets against minesweepers, and also to protect against motor torpedo boats. In some documentation they are called "mine defense guns". The 3-inch guns were mounted on pedestal mounts (or a retractable "masking parapet" mount for the M1898) that bolted into a concrete emplacement that provided cover and safety for the gun's crew. History The 3-inch mine defense guns were part of a comprehensive plan of new fortifications specified by the Board of Fortifications of 1885. The new forts initially included guns up to 12-inch (305 mm) on disappearing carriages, to conceal the fort from observ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-inch Gun M1900
The 5-inch gun M1897 (127 mm) and its variant the M1900 were coastal artillery pieces installed to defend major American seaports between 1897 and 1920. For most of their history they were operated by the United States Army Coast Artillery Corps. They were installed on balanced pillar (a form of disappearing carriage) or pedestal (aka barbette) mountings; generally the M1897 was on the balanced pillar mounting and the M1900 was on the pedestal mounting. All of these weapons were scrapped within a few years after World War I. History In 1885, William C. Endicott, President Grover Cleveland's Secretary of War, was tasked with creating the Board of Fortifications to review seacoast defenses. The findings of the board illustrated a grim picture of existing defenses in its 1886 report and recommended a massive $127 million construction program of breech-loading cannons, mortars, floating batteries, and submarine mines for some 29 locations on the US coastline. Most of the Board' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Clay Rice
James Clay Rice (December 27, 1828 – May 10, 1864) was a lawyer from Massachusetts, who became a brigadier general of volunteers in the Union Army during the American Civil War. Early life Rice was born in Worthington, Massachusetts on December 27, 1828 to William Rice and Welthea (Cottrell) Rice. He was self-educated for most of his early life and eventually graduated from Yale University. He became a teacher in Natchez, Mississippi, and worked for a newspaper. During this time he began studying law and was admitted to the bar in New York City where he began his practice. Civil War When the Civil War began Rice enlisted on 28 May 1861 in the 39th New York Infantry Regiment quickly becoming a captain of Company B and engaging at the First Battle of Bull Run. Rice was mustered out of the 39th New York Volunteer Infantry Regiment on 12 Sep 1861. The next day Rice became lieutenant colonel of the newly formed 44th New York Volunteer Infantry Regiment (also known as People's Ellsw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6-inch Gun M1900
The 6-inch gun M1897 (152 mm) and its variants the M1900, M1903, M1905, M1908, and M1 (a.k.a. T2) were coastal artillery pieces installed to defend major American seaports between 1897 and 1945. For most of their history they were operated by the United States Army Coast Artillery Corps. They were installed on disappearing carriages or pedestal (a.k.a. barbette) mountings, and during World War II many were remounted on shielded barbette carriages. Most of the weapons not in the Philippines were scrapped within a few years after World War II. History In 1885, William C. Endicott, President Grover Cleveland's Secretary of War, was tasked with creating the Board of Fortifications to review seacoast defenses. The findings of the board illustrated a grim picture of existing defenses in its 1886 report and recommended a massive $127 million construction program of breech-loading cannons, mortars, floating batteries, and submarine mines for some 29 locations on the US coastline. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daniel McCook
Daniel McCook (June 20, 1798 – July 21, 1863) was an attorney and an officer in the Union army during the American Civil War. He was one of two Ohio brothers who, along with 13 of their sons, became widely known as the “Fighting McCooks” for their contributions to the war effort. Biography McCook was born in Canonsburg, Pennsylvania, the son of an Irish revolutionary, George McCook, who had fled to the United States about 1780. He graduated from Jefferson College. On August 28, 1817, he married Martha Latimer; they would have twelve children (nine boys and three girls). In 1826 the family moved to New Lisbon, Ohio, then to Carrollton, where McCook practiced law. He became an elder in the Presbyterian church and was a pioneer in the regional Sunday School movement. He was an elder at John McMillan's church. With the outbreak of the Civil War, McCook, although 63 years old, volunteered his services to the Union. He was commissioned as a major and paymaster. When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbette
Barbettes are several types of gun emplacement in terrestrial fortifications or on naval ships. In recent naval usage, a barbette is a protective circular armour support for a heavy gun turret. This evolved from earlier forms of gun protection that eventually led to the pre-dreadnought. The name ''barbette'' ultimately comes from fortification - it originally meant a raised platform or mound, as in the French phrase ''en barbette'', which refers to the practice of firing a cannon over a parapet rather than through an embrasure in a fortification's casemate. The former gives better angles of fire but less protection than the latter. The disappearing gun was a variation on the barbette gun; it consisted of a heavy gun on a carriage that would retract behind a parapet or into a gunpit for reloading. Barbettes were primarily used in coastal defences, but saw some use in a handful of warships, and some inland fortifications. The term is also used for certain aircraft gun mounts. Sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
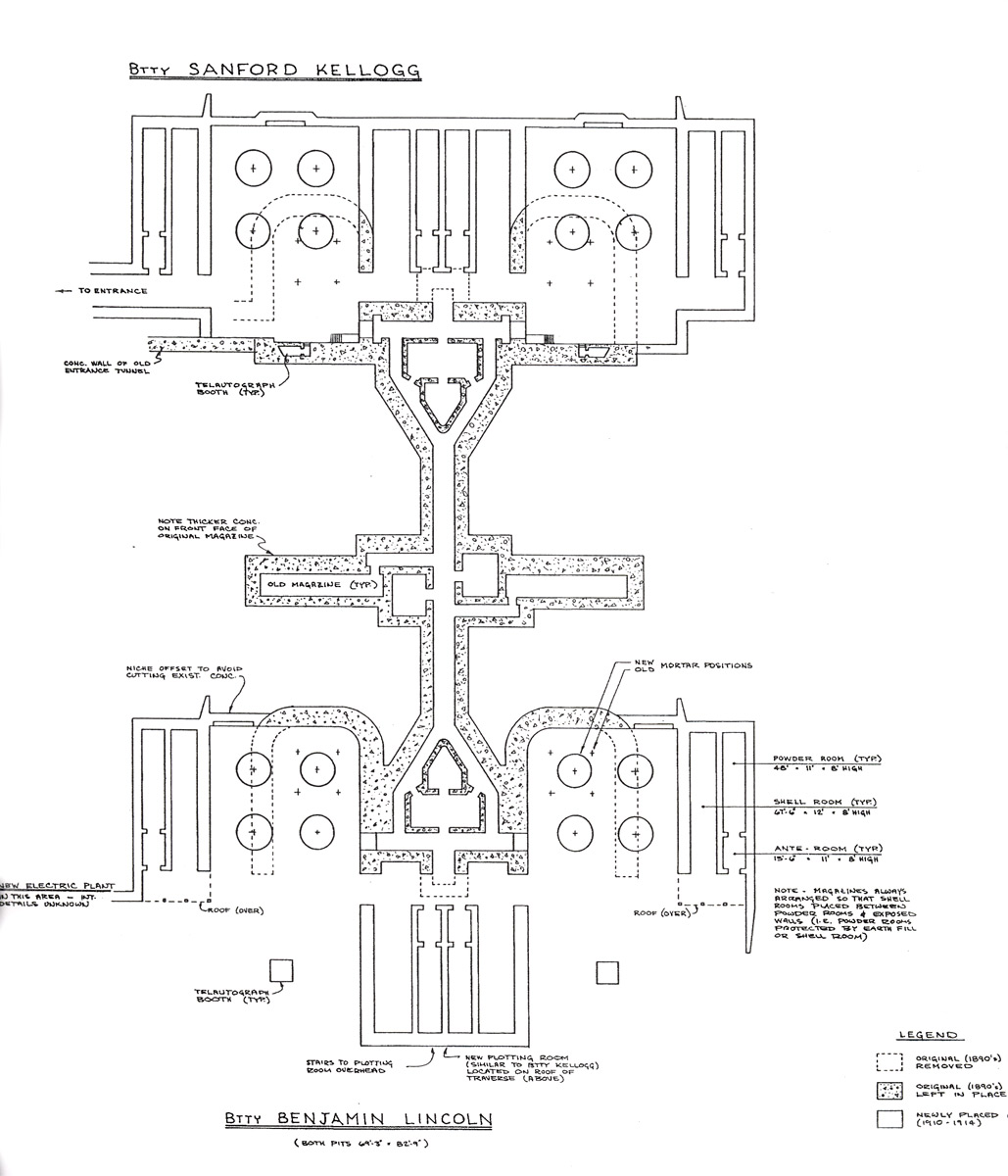
12-inch Coast Defense Mortar
The 12-inch coast defense mortar was a weapon of caliber emplaced during the 1890s and early 20th century to defend US harbors from seaborne attack. In 1886, when the Endicott Board set forth its initial plan for upgrading the coast defenses of the United States, it relied primarily on mortars, not guns, to defend American harbors. "Sea-Coast Mortar Fire", Report of a Board, in ''Journal of the United States Artillery'', Vol. 7, No. 3, 1897. Over the years, provision was made for fortifications that would mount some 476 of these weapons, although not all of these tubes were installed. Ninety-one of these weapons were remounted as railway artillery in 1918-1919, but this was too late to see action in World War I. The railway mortars were only deployed in small quantities, and none overseas. The fixed mortars in the Philippines saw action in the Japanese invasion in World War II. All of the fixed mortars (except four) in the United States were scrapped by 1944, as new weapons replac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





_(14595131440).jpg)



