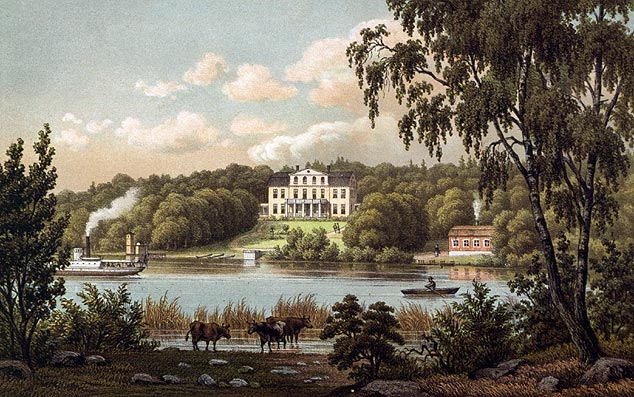|
Fornsigtuna
Signhildsberg (historically Fornsigtuna, where ''forn'' means ''ancient'', Old Sigtuna, ''Sithun'', ''Signesberg'') is a manor that formerly was a royal estate (Uppsala öd), located in the parish of Håtuna approximately west of the modern town of Sigtuna, by Lake Mälaren in Sweden. Although the location is nearly forgotten, it has a central role in Norse mythology, according to which it was founded by the Norse god Odin. Etymology The name ''Sigtuna'' is contested. According to one theory, it is a compound name where the second element is -''tuna'' and the first one is either of two closely related dialectal words, viz. ''sig'' meaning "seeping water" or "swamp" or ''sik'' meaning "swamp". As a basis for this intpretation, a brook south of Signhildsberg has been mentioned, or the fact that the estate was surrounded by marshy terrain.Entry ''Sigtuna'' in Svenskt ortnamnslexikon. Ed. Mats Wahlberg. Institutet för språk och folkminnen, Uppsala 2003. Another theory considers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signhildsberg
Signhildsberg (historically Fornsigtuna, where ''forn'' means ''ancient'', Old Sigtuna, ''Sithun'', ''Signesberg'') is a manor that formerly was a royal estate (Uppsala öd), located in the parish of Håtuna approximately west of the modern town of Sigtuna, by Lake Mälaren in Sweden. Although the location is nearly forgotten, it has a central role in Norse mythology, according to which it was founded by the Norse god Odin. Etymology The name ''Sigtuna'' is contested. According to one theory, it is a compound name where the second element is -''tuna'' and the first one is either of two closely related dialectal words, viz. ''sig'' meaning "seeping water" or "swamp" or ''sik'' meaning "swamp". As a basis for this intpretation, a brook south of Signhildsberg has been mentioned, or the fact that the estate was surrounded by marshy terrain.Entry ''Sigtuna'' in Svenskt ortnamnslexikon. Ed. Mats Wahlberg. Institutet för språk och folkminnen, Uppsala 2003. Another theory considers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigtuna
Sigtuna () is a locality situated in Sigtuna Municipality, Stockholm County, Sweden with 8,444 inhabitants in 2010. It is the namesake of the municipality even though the seat is in Märsta. Sigtuna is for historical reasons often still referred to as a ''stad''. Modern-day Sigtuna, a harbor town that was established around 980, developed approximately 4 kilometres east of Old Sigtuna (which, according to Norse mythology, was previously the home of Odin). Sigtuna has a medieval-style town centre with restaurants, cafes and small shops. The old church ruins, runic stones and the old main street (''Stora gatan'') are popular attractions for tourists, especially in the summertime. The small streets with low-built wooden houses lead up to several handicrafts shops and the old tiny town hall (''Sigtuna Rådhus''). There are restaurants and ''Sigtuna Stadshotell'', a hotel in the town centre. Geography Sigtuna is situated at the bay Skarven, stretching around Upplands-Bro and a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
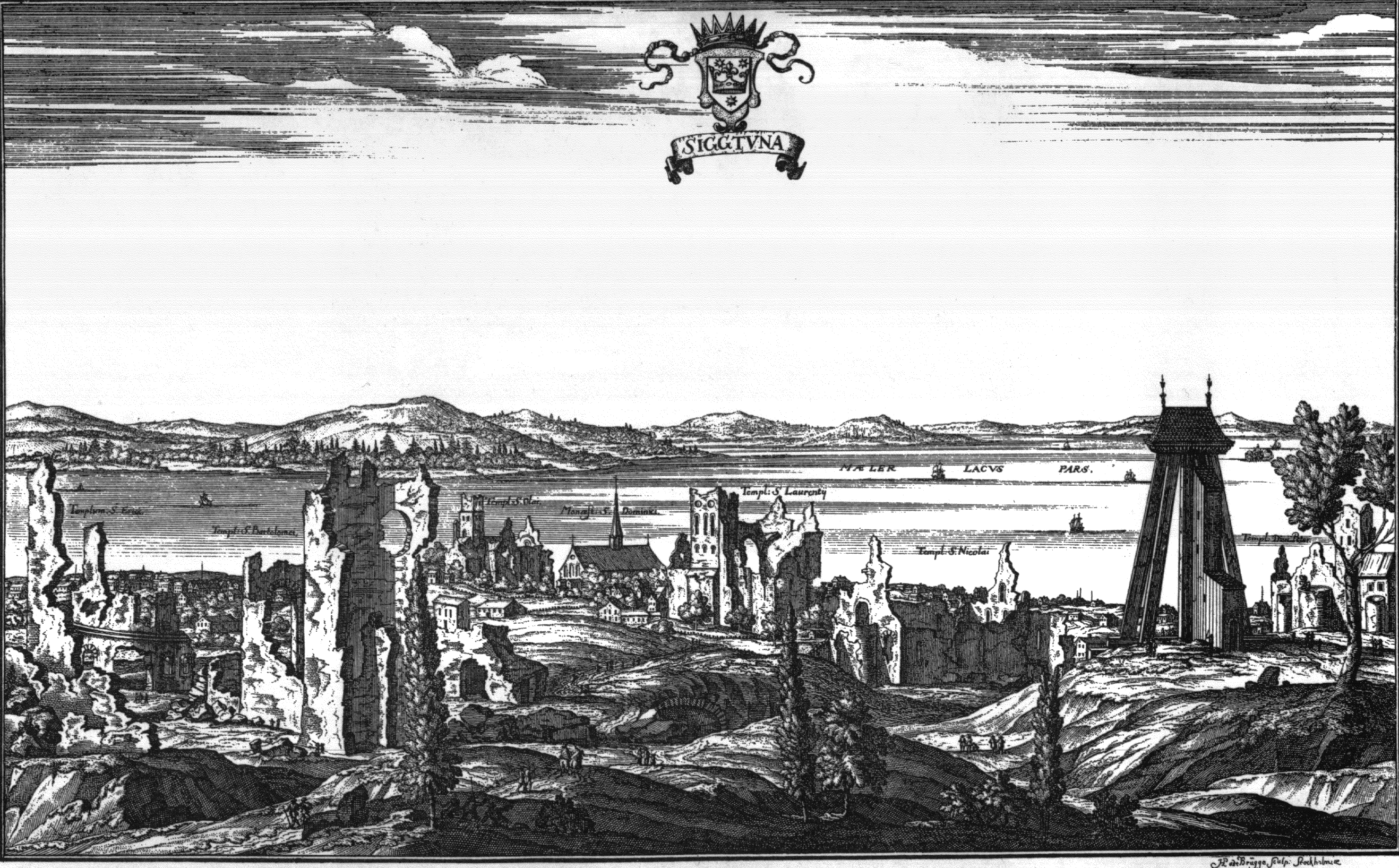
Signhildsberg 1881
Signhildsberg (historically Fornsigtuna, where ''forn'' means ''ancient'', Old Sigtuna, ''Sithun'', ''Signesberg'') is a manor that formerly was a royal estate (Uppsala öd), located in the parish of Håtuna approximately west of the modern town of Sigtuna, by Lake Mälaren in Sweden. Although the location is nearly forgotten, it has a central role in Norse mythology, according to which it was founded by the Norse god Odin. Etymology The name ''Sigtuna'' is contested. According to one theory, it is a compound name where the second element is -''tuna'' and the first one is either of two closely related dialectal words, viz. ''sig'' meaning "seeping water" or "swamp" or ''sik'' meaning "swamp". As a basis for this intpretation, a brook south of Signhildsberg has been mentioned, or the fact that the estate was surrounded by marshy terrain.Entry ''Sigtuna'' in Svenskt ortnamnslexikon. Ed. Mats Wahlberg. Institutet för språk och folkminnen, Uppsala 2003. Another theory considers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uppsala öd
Uppsala öd, Old Norse: ''Uppsala auðr'' or ''Uppsala øðr'' (''Uppsala domains'' or ''wealth of Uppsala'') was the name given to the collection of estates which was the property of the Swedish Crown in medieval Sweden.The article ''Uppsala öd'' in ''Nationalencyklopedin'' (1996). Its purpose was to finance the Swedish king, originally the "king of Uppsala",The article ''Uppsala öd'' in '''' (1920). and they supported the king and his retinue while he travelled through the country.Hadenius, Stig; Nilsson, Torbjörn & Åselius, Gunnar. (1996). ''Sveriges historia''. Centraltryckeriet, Borås. p. 83-84. There was one estate of this kind in most [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Segodunum
Segodūnum is an old Celtic place name derived from Proto-Celtic *'' sego''-'' dūno''-, meaning "strong fortress".The Place-Names of Roman Britain, pp. 452-3. A.L.F. Rivet & Colin Smith (1979). Princeton University Press. It can refer to the following locations: *Rodez, Aveyron, former town of the Ruteni in Aquitania *Segedunum, Wallsend, England. *Suin, Saône-et-Loire *Syon Haute-Savoie *Würzburg, Bavaria It may have Germanic counterparts in Swedish ''Fornsigtuna'' and ''Sigtuna'', from Proto-Germanic *''siga- tūna''-, Old Norse Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic languages, North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and t ... ''Sigtún''.Koch, John T. (2020)CELTO-GERMANIC Later Prehistory and Post-Proto-Indo-European vocabulary in the North and West p. 131Entry ''Sigtuna'' in Svenskt ortnamnslexikon. Ed. Mats Wahlberg. Ins ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freyr
Freyr (Old Norse: 'Lord'), sometimes anglicized as Frey, is a widely attested god in Norse mythology, associated with kingship, fertility, peace, and weather. Freyr, sometimes referred to as Yngvi-Freyr, was especially associated with Sweden and seen as an ancestor of the Swedish royal house. According to Adam of Bremen, Freyr was associated with peace and pleasure, and was represented with a phallic statue in the Temple at Uppsala. According to Snorri Sturluson, Freyr was "the most renowned of the æsir", and was venerated for good harvest and peace. In the mythological stories in the Icelandic books the ''Poetic Edda'' and the ''Prose Edda'', Freyr is presented as one of the Vanir, the son of the god Njörðr and his sister-wife, as well as the twin brother of the goddess Freyja. The gods gave him Álfheimr, the realm of the Elves, as a teething present. He rides the shining dwarf-made boar Gullinbursti and possesses the ship Skíðblaðnir which always has a favorable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nóatún (mythology)
In Norse mythology, Nóatún (Old Norse "ship-enclosure"Orchard (1997:119).) is the abode of the god Njörðr, described in the ''Prose Edda'' book ''Gylfaginning'' as located "in heaven".Faulkes (1995:23). Notes References *Faulkes, Anthony (Trans.) (1995). ''Edda''. Everyman The everyman is a stock character of fiction. An ordinary and humble character, the everyman is generally a protagonist whose benign conduct fosters the audience's identification with them. Origin The term ''everyman'' was used as early as .... *Orchard, Andy (1997). ''Dictionary of Norse Myth and Legend''. Cassell. Locations in Norse mythology Conceptions of heaven {{norse-myth-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Æsir
The Æsir (Old Norse: ) are the gods of the principal pantheon in Norse religion. They include Odin, Frigg, Höðr, Thor, and Baldr. The second Norse pantheon is the Vanir. In Norse mythology, the two pantheons wage war against each other, resulting in a unified pantheon. Unlike the Old English word ''god'' (and the Old Norse word '), Æsir was never converted over to Christian use. Etymology ''Æsir'' is the plural of '' áss'', ''ǫ́ss'' "god". In genitival compounds, it takes the form ', e.g. in ' ("Thor of the Æsir"), besides ' found in : '' ás-brú'' "gods' bridge" (the rainbow), : ' "gods' enclosure", : ' "gods' kin", : ' "gods' leader", : ' "gods' might" (especially of Thor), : ' "divine wrath" etc. : ' "national god" (') is a title of Thor, as is : ' "almighty god", while it is Odin who is "the" '. There is also Old East Norse dialectal : *''ās-ækia'' (OWN: *''áss-ekja''), i.e. "god ride" (Thor riding in his wagon), resulting in the modern Swedish word : '' ås ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th century, and the first Old English literature, Old English literary works date from the mid-7th century. After the Norman conquest of 1066, English was replaced, for a time, by Anglo-Norman language, Anglo-Norman (a langues d'oïl, relative of French) as the language of the upper classes. This is regarded as marking the end of the Old English era, since during this period the English language was heavily influenced by Anglo-Norman, developing into a phase known now as Middle English in England and Early Scots in Scotland. Old English developed from a set of Anglo-Frisian languages, Anglo-Frisian or Ingvaeonic dialects originally spoken by Germanic peoples, Germanic tribes traditionally known as the Angles, Sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heimskringla
''Heimskringla'' () is the best known of the Old Norse kings' sagas. It was written in Old Norse in Iceland by the poet and historian Snorre Sturlason (1178/79–1241) 1230. The name ''Heimskringla'' was first used in the 17th century, derived from the first two words of one of the manuscripts (''kringla heimsins'', "the circle of the world"). ''Heimskringla'' is a collection of sagas about Swedish and Norwegian kings, beginning with the saga of the legendary Swedish dynasty of the Ynglings, followed by accounts of historical Norwegian rulers from Harald Fairhair of the 9th century up to the death of the pretender Eystein Meyla in 1177. The exact sources of the Snorri's work are disputed, but they include earlier kings' sagas, such as Morkinskinna, Fagrskinna and the 12th-century Norwegian synoptic histories and oral traditions, notably many skaldic poems. He explicitly names the now lost work ''Hryggjarstykki'' as his source for the events of the mid-12th century. Although Sno ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ynglinga Saga
''Ynglinga saga'' ( ) is a Kings' saga, originally written in Old Norse by the Icelandic poet and historian Snorri Sturluson about 1225. It is the first section of his ''Heimskringla''. It was first translated into English and published in 1844 by Samuel Laing. Snorri Sturluson based his work on an earlier ''Ynglingatal'' which is attributed to the Norwegian 9th-century skald Þjóðólfr of Hvinir, and which also appears in ''Historia Norwegiae''. It tells the most ancient part of the story of the House of Ynglings (''Scylfings'' in ''Beowulf''). Snorri described the descent of the kings of Norway from this royal house of Sweden. ''Ynglinga saga'' is the first part of Snorri's history of the ancient Norse kings, the ''Heimskringla.'' Snorri's work covers the history of the Norwegian kings from the mythical prehistoric age until 1177, with the death of the pretender Eystein Meyla. Interwoven in this narrative are references to important historical events. The saga deals wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |