|
Forensic Statistics
Forensic statistics is the application of probability models and statistical techniques to scientific evidence, such as DNA evidence, and the law. In contrast to "everyday" statistics, to not engender bias or unduly draw conclusions, forensic statisticians report likelihoods as likelihood ratios (LR). This ratio of probabilities is then used by juries or judges to draw inferences or conclusions and decide legal matters. Jurors and judges rely on the strength of a DNA match, given by statistics, to make conclusions and determine guilt or innocence in legal matters. In forensic science, the DNA evidence received for DNA profiling often contains a mixture of more than one person's DNA. DNA profiles are generated using a set procedure, however, the interpretation of a DNA profile becomes more complicated when the sample contains a mixture of DNA. Regardless of the number of contributors to the forensic sample, statistics and probabilities must be used to provide weight to the evide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Model
A statistical model is a mathematical model that embodies a set of statistical assumptions concerning the generation of Sample (statistics), sample data (and similar data from a larger Statistical population, population). A statistical model represents, often in considerably idealized form, the data-generating process. A statistical model is usually specified as a mathematical relationship between one or more random variables and other non-random variables. As such, a statistical model is "a formal representation of a theory" (Herman J. Adèr, Herman Adèr quoting Kenneth A. Bollen, Kenneth Bollen). All Statistical hypothesis testing, statistical hypothesis tests and all Estimator, statistical estimators are derived via statistical models. More generally, statistical models are part of the foundation of statistical inference. Introduction Informally, a statistical model can be thought of as a statistical assumption (or set of statistical assumptions) with a certain property: that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ''wikt:Statistik#German, Statistik'', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of statistical survey, surveys and experimental design, experiments.Dodge, Y. (2006) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', Oxford University Press. When census data cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey sample (statistics), samples. Representative sampling as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Profiling
DNA profiling (also called DNA fingerprinting) is the process of determining an individual's DNA characteristics. DNA analysis intended to identify a species, rather than an individual, is called DNA barcoding. DNA profiling is a forensic technique in criminal investigations, comparing criminal suspects' profiles to DNA evidence so as to assess the likelihood of their involvement in the crime. It is also used in paternity testing, to establish immigration eligibility, and in genealogical and medical research. DNA profiling has also been used in the study of animal and plant populations in the fields of zoology, botany, and agriculture. Background Starting in the 1980s, scientific advances allowed the use of DNA as a material for the identification of an individual. The first patent covering the direct use of DNA variation for forensicsUS5593832A was filed by Jeffrey Glassberg in 1983, based upon work he had done while at Rockefeller University in the United States in 1981. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Likelihood Function
The likelihood function (often simply called the likelihood) represents the probability of random variable realizations conditional on particular values of the statistical parameters. Thus, when evaluated on a given sample, the likelihood function indicates which parameter values are more ''likely'' than others, in the sense that they would have made the observed data more probable. Consequently, the likelihood is often written as \mathcal(\theta\mid X) instead of P(X \mid \theta), to emphasize that it is to be understood as a function of the parameters \theta instead of the random variable X. In maximum likelihood estimation, the arg max of the likelihood function serves as a point estimate for \theta, while local curvature (approximated by the likelihood's Hessian matrix) indicates the estimate's precision. Meanwhile in Bayesian statistics, parameter estimates are derived from the converse of the likelihood, the so-called posterior probability, which is calculated via Bayes' r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jury
A jury is a sworn body of people (jurors) convened to hear evidence and render an impartiality, impartial verdict (a Question of fact, finding of fact on a question) officially submitted to them by a court, or to set a sentence (law), penalty or Judgment (law), judgment. Juries developed in England during the Middle Ages and are a hallmark of the English common law system. As such, they are used by the United Kingdom, the United States, Canada, Ireland, Australia, and other countries whose legal systems were derived from the British Empire. But most other countries use variations of the European Civil law (legal system), civil law or Islamic sharia, sharia law systems, in which juries are not generally used. Most trial juries are "petit juries", and usually consist of twelve people. Historically, a larger jury known as a grand jury was used to investigate potential crimes and render indictments against suspects. All common law countries except the United States and Liberia hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judge
A judge is a person who presides over court proceedings, either alone or as a part of a panel of judges. A judge hears all the witnesses and any other evidence presented by the barristers or solicitors of the case, assesses the credibility and arguments of the parties, and then issues a ruling in the case based on their interpretation of the law and their own personal judgment. A judge is expected to conduct the trial impartially and, typically, in an open court. The powers, functions, method of appointment, discipline, and training of judges vary widely across different jurisdictions. In some jurisdictions, the judge's powers may be shared with a jury. In inquisitorial systems of criminal investigation, a judge might also be an examining magistrate. The presiding judge ensures that all court proceedings are lawful and orderly. Powers and functions The ultimate task of a judge is to settle a legal dispute in a final and publicly lawful manner in agreement with substantial p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genotype Frequencies
Genetic variation in populations can be analyzed and quantified by the frequency of alleles. Two fundamental calculations are central to population genetics: allele frequencies and genotype frequencies. Genotype frequency in a population is the number of individuals with a given genotype divided by the total number of individuals in the population. In population genetics, the genotype frequency is the frequency or proportion (i.e., 0 < ''f'' < 1) of genotypes in a population. Although allele and genotype frequencies are related, it is important to clearly distinguish them. Genotype frequency may also be used in the future (for "genomic profiling") to predict someone's having a disease or even a birth defect. It can also be used to determine ethnic diversity. Genotype frequencies may be represented by a . Numerical ...
|
Product Rule
In calculus, the product rule (or Leibniz rule or Leibniz product rule) is a formula used to find the derivatives of products of two or more functions. For two functions, it may be stated in Lagrange's notation as (u \cdot v)' = u ' \cdot v + u \cdot v' or in Leibniz's notation as \frac (u\cdot v) = \frac \cdot v + u \cdot \frac. The rule may be extended or generalized to products of three or more functions, to a rule for higher-order derivatives of a product, and to other contexts. Discovery Discovery of this rule is credited to Gottfried Leibniz, who demonstrated it using differentials. (However, J. M. Child, a translator of Leibniz's papers, argues that it is due to Isaac Barrow.) Here is Leibniz's argument: Let ''u''(''x'') and ''v''(''x'') be two differentiable functions of ''x''. Then the differential of ''uv'' is : \begin d(u\cdot v) & = (u + du)\cdot (v + dv) - u\cdot v \\ & = u\cdot dv + v\cdot du + du\cdot dv. \end Since the term ''du''·''dv'' is "negligi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
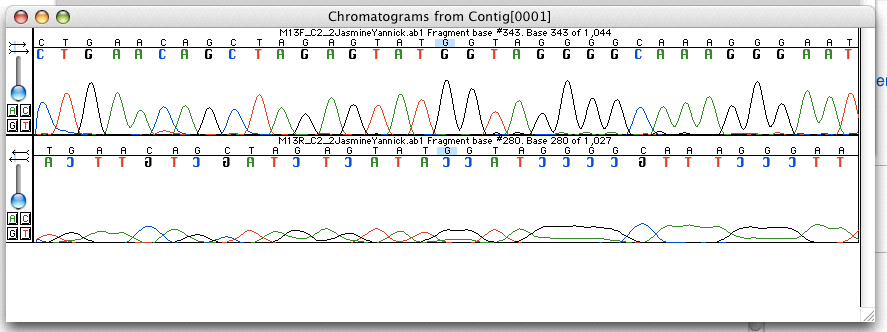
Electropherogram
An electropherogram, or electrophoregram, can also be referred to as an EPG or e-gram. It is a record or chart produced when electrophoresis is used in an analytical technique, primarily in the fields of forensic biology, molecular biology and biochemistry. The method utilizes data points that correspond with a specific time and fluorescence intensity at various wavelengths of light to represent a DNA profile. In the field of genetics, an electropherogram is a plot of DNA fragment sizes, typically used for genotyping such as DNA sequencing. The data is plotted with time, shown via base pairs (bps), on the x-axis and fluorescence intensity on the y-axis. Such plots are often achieved using an instrument such as an automated DNA sequencer paired with capillary electrophoresis (CE). Such electropherograms may be used to determine DNA sequence genotypes, or genotypes that are based on the length of specific DNA fragments or number of short tandem repeats (STR) at a specific locus b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Forensic Statistics
Forensic statistics is the application of probability models and statistical techniques to scientific evidence, such as DNA evidence, and the law. In contrast to "everyday" statistics, to not engender bias or unduly draw conclusions, forensic statisticians report likelihoods as likelihood ratios (LR). This ratio of probabilities is then used by juries or judges to draw inferences or conclusions and decide legal matters. Jurors and judges rely on the strength of a DNA match, given by statistics, to make conclusions and determine guilt or innocence in legal matters. In forensic science, the DNA evidence received for DNA profiling often contains a mixture of more than one person's DNA. DNA profiles are generated using a set procedure, however, the interpretation of a DNA profile becomes more complicated when the sample contains a mixture of DNA. Regardless of the number of contributors to the forensic sample, statistics and probabilities must be used to provide weight to the evide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Applied Statistics
Statistics (from German language, German: ''wikt:Statistik#German, Statistik'', "description of a State (polity), state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of statistical survey, surveys and experimental design, experiments.Dodge, Y. (2006) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', Oxford University Press. When census data cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey sample (statistics), samples. Representative sampling as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |