|
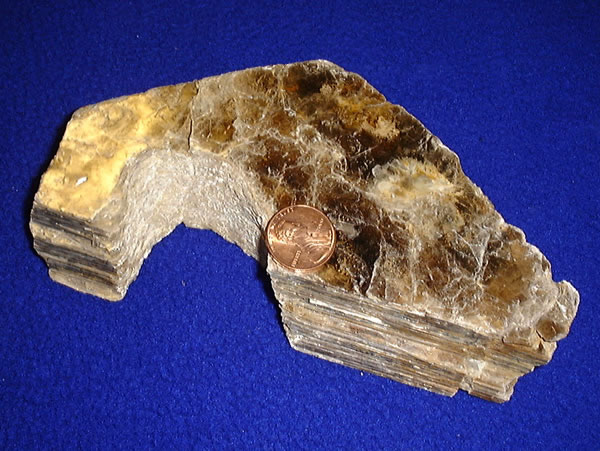
Forbach Granite
Forbach Granite (german: Forbachgranit), also called Raumünzach Granite (''Raumünzach-Granit''), is a type of granite rock that occurs in the Northern Black Forest. It is part of the Northern Black Forest's granitic massif, to which Bühlertal granite and Wildbad granite also belong. Forbach granite predominantly outcrops in the counties of Calw and Rastatt. The most important quarrying area for Forbach granite used to be the middle Murg valley near Forbach. Today it is only quarried near Raumünzach. Forbach Granite is about 305 million years old. The stone is coarse-grained - this points to a slowly cooling of the lava / magma (at the time the formation of the stone). Forbach Granite is a bright mica, coloured from gray to pink. Forbach Granite includes the following minerals. * Alkali feldspars (up to 44 percent) have a size of up to 5 centimetre and leads to a red colour. * Quartz (26 percent). * Plagioclase (20 percent) * Muscovite (5 percent) * Biotite (5 percent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bundesarchiv Koblenz
, type = Archive , seal = , seal_size = , seal_caption = , seal_alt = , logo = Bundesarchiv-Logo.svg , logo_size = , logo_caption = , logo_alt = , image = Bundesarchiv Koblenz.jpg , image_caption = The Federal Archives in Koblenz , image_alt = , formed = , preceding1 = , preceding2 = , dissolved = , superseding1 = , superseding2 = , agency_type = , jurisdiction = , status = Active , headquarters = PotsdamerStraße156075Koblenz , coordinates = , motto = , employees = , budget = million () , chief1_name = Michael Hollmann , chief1_position = President of the Federal Archives , chief2_name = Dr. Andrea Hänger , chief2_position ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) feldspars and the ''alkali'' (potassium-sodium) feldspars. Feldspars make up about 60% of the Earth's crust, and 41% of the Earth's continental crust by weight. Feldspars crystalize from magma as both intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks and are also present in many types of metamorphic rock. Rock formed almost entirely of calcic plagioclase feldspar is known as anorthosite. Feldspars are also found in many types of sedimentary rocks. Compositions The feldspar group of minerals consists of tectosilicates, silicate minerals in which silicon ions are linked by shared oxygen ions to form a three-dimensional network. Compositions of major elements in common feldspars can be expressed in terms of three endmembers: * potassium feldspar (K-spar) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rastatt (district)
Rastatt is a ''Landkreis'' (district) in the west of Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Neighbouring districts are (from north clockwise) Karlsruhe, Calw, Freudenstadt and the Ortenaukreis. To the west it borders the French ''département'' Bas-Rhin. Rastatt completely surrounds the district-free city Baden-Baden. History The district was created in 1939 as the successor of the ''Oberamt Rastatt'' and later the ''Großkreis Baden''. In 1973 it was merged with the majority of the neighboring district Bühl, and some small parts of the district Kehl. Geography The district is located in the Rhine valley. The south-east part, however, is part of the Northern Black Forest. The highest elevation is the Hoher Ochsenkopf. The county has three small exclaves within the borough of Baden-Baden. The largest of these is home to the Waldenecksee, the smallest, the old abbey of Fremersberg. Partnerships Since 1968 the district has partnership with the Finnish city Vantaa. The partnership with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies underground. It is common in the continental crust of Earth, where it is found in igneous intrusions. These range in size from dikes only a few centimeters across to batholiths exposed over hundreds of square kilometers. Granite is typical of a larger family of ''granitic rocks'', or ''granitoids'', that are composed mostly of coarse-grained quartz and feldspars in varying proportions. These rocks are classified by the relative percentages of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase (the QAPF classification), with true granite representing granitic rocks rich in quartz and alkali feldspar. Most granitic rocks also contain mica or amphibole minerals, though a few (known as leucogranites) contain almost no dark minerals. Granite is nearly alway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South German Scarplands
The South German Scarplands is a geological and geomorphological natural region or landscape in Switzerland and the south German states of Bavaria and Baden-Württemberg. The landscape is characterised by escarpments. It is variously referred to in the German literature as the: * ' (Southwest German Scarplands) * ' (Southwest German Scarp Landscape) * ' (Swabian-Franconian Scarpland(scape)) * ' (South German Scarpland(scape)) Location and short description The South German Scarplands run (from north(-northeast) to south(-southwest)) more or less between the southern Rhön, the Spessart, the Odenwald and the Black Forest in the west, the Franconian Jura in the east, the Swabian Jura to the southeast and the northeastern foothills of the Jura to the south. The wooded west and northwest-facing scarps drop sharply towards the Rhine Rift Valley and the Rhine-Main Plain, whilst the dip slopes fall comparatively gradually towards the (north-)east into the depressions beyond which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xenotime
Xenotime is a rare-earth phosphate mineral, the major component of which is yttrium orthophosphate ( Y P O4). It forms a solid solution series with chernovite-(Y) ( Y As O4) and therefore may contain trace impurities of arsenic, as well as silicon dioxide and calcium. The rare-earth elements dysprosium, erbium, terbium and ytterbium, as well as metal elements such as thorium and uranium (all replacing yttrium) are the expressive secondary components of xenotime. Due to uranium and thorium impurities, some xenotime specimens may be weakly to strongly radioactive. Lithiophyllite, monazite and purpurite are sometimes grouped with xenotime in the informal "anhydrous phosphates" group. Xenotime is used chiefly as a source of yttrium and heavy lanthanide metals (dysprosium, ytterbium, erbium and gadolinium). Occasionally, gemstones are also cut from the finest xenotime crystals. Etymology The name ''xenotime'' is from the Greek words κενός ''vain'' and τιμή ''honor'', ak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monazite
Monazite is a primarily reddish-brown phosphate mineral that contains rare-earth elements. Due to variability in composition, monazite is considered a group of minerals. The most common species of the group is monazite-(Ce), that is, the cerium-dominant member of the group. It occurs usually in small isolated crystals. It has a hardness of 5.0 to 5.5 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness and is relatively dense, about 4.6 to 5.7 g/cm3. There are five different most common species of monazite, depending on the relative amounts of the rare earth elements in the mineral: * monazite-(Ce), ( Ce, La, Nd, Th) PO4 (the most common member), * monazite-(La), (La,Ce,Nd)PO4, * monazite-(Nd), (Nd,La,Ce)PO4, * monazite-(Sm), ( Sm, Gd,Ce,Th)PO4, * monazite-(Pr), ( Pr,Ce,Nd,Th)PO4. The elements in parentheses are listed in the order of their relative proportion within the mineral: lanthanum is the most common rare-earth element in monazite-(La), and so forth. Silica (SiO2) is present in trace a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apatite
Apatite is a group of phosphate minerals, usually hydroxyapatite, fluorapatite and chlorapatite, with high concentrations of OH−, F− and Cl− ions, respectively, in the crystal. The formula of the admixture of the three most common endmembers is written as Ca10( PO4)6(OH,F,Cl)2, and the crystal unit cell formulae of the individual minerals are written as Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2, Ca10(PO4)6F2 and Ca10(PO4)6Cl2. The mineral was named apatite by the German geologist Abraham Gottlob Werner in 1786, although the specific mineral he had described was reclassified as fluorapatite in 1860 by the German mineralogist Karl Friedrich August Rammelsberg. Apatite is often mistaken for other minerals. This tendency is reflected in the mineral's name, which is derived from the Greek word ἀπατάω (apatáō), which means ''to deceive''. Geology Apatite is very common as an accessory mineral in igneous and metamorphic rocks, where it is the most common phosphate mineral. However, occu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotite
Biotite is a common group of phyllosilicate minerals within the mica group, with the approximate chemical formula . It is primarily a solid-solution series between the iron-endmember annite, and the magnesium-endmember phlogopite; more aluminous end-members include siderophyllite and eastonite. Biotite was regarded as a mineral ''species'' by the International Mineralogical Association until 1998, when its status was changed to a mineral ''group''. The term ''biotite'' is still used to describe unanalysed dark micas in the field. Biotite was named by J.F.L. Hausmann in 1847 in honor of the French physicist Jean-Baptiste Biot, who performed early research into the many optical properties of mica. Members of the biotite group are sheet silicates. Iron, magnesium, aluminium, silicon, oxygen, and hydrogen form sheets that are weakly bound together by potassium ions. The term "iron mica" is sometimes used for iron-rich biotite, but the term also refers to a flaky micaceous form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscovite
Muscovite (also known as common mica, isinglass, or potash mica) is a hydrated phyllosilicate mineral of aluminium and potassium with formula K Al2(Al Si3 O10)( F,O H)2, or ( KF)2( Al2O3)3( SiO2)6( H2O). It has a highly perfect basal cleavage yielding remarkably thin laminae (sheets) which are often highly elastic. Sheets of muscovite 5 meters × 3 meters (16.5 feet × 10 feet) have been found in Nellore, India. Muscovite has a Mohs hardness of 2–2.25 parallel to the 01face, 4 perpendicular to the 01and a specific gravity of 2.76–3. It can be colorless or tinted through grays, browns, greens, yellows, or (rarely) violet or red, and can be transparent or translucent. It is anisotropic and has high birefringence. Its crystal system is monoclinic. The green, chromium-rich variety is called fuchsite; mariposite is also a chromium-rich type of muscovite. Muscovite is the most common mica, found in granites, pegmatites, gneisses, and schists, and as a contact metamorphic ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical formula of SiO2. Quartz is the second most abundant mineral in Earth's continental crust, behind feldspar. Quartz exists in two forms, the normal α-quartz and the high-temperature β-quartz, both of which are chiral. The transformation from α-quartz to β-quartz takes place abruptly at . Since the transformation is accompanied by a significant change in volume, it can easily induce microfracturing of ceramics or rocks passing through this temperature threshold. There are many different varieties of quartz, several of which are classified as gemstones. Since antiquity, varieties of quartz have been the most commonly used minerals in the making of jewelry and hardstone carvings, especially in Eurasia. Quartz is the mineral defining the val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mica
Micas ( ) are a group of silicate minerals whose outstanding physical characteristic is that individual mica crystals can easily be split into extremely thin elastic plates. This characteristic is described as perfect basal cleavage. Mica is common in igneous and metamorphic rock and is occasionally found as small flakes in sedimentary rock. It is particularly prominent in many granites, pegmatites, and schists, and "books" (large individual crystals) of mica several feet across have been found in some pegmatites. Micas are used in products such as drywalls, paints, fillers, especially in parts for automobiles, roofing and shingles, as well as in electronics. The mineral is used in cosmetics and food to add "shimmer" or "frost." Properties and structure The mica group is composed of 37 phyllosilicate minerals. All crystallize in the monoclinic system, with a tendency towards pseudohexagonal crystals, and are similar in structure but vary in chemical composition. Micas are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |