|
Fok1
The restriction endonuclease ''Fok''1, naturally found in ''Flavobacterium okeanokoites'', is a bacterial type IIS restriction endonuclease consisting of an N-terminal DNA-binding domain and a non-specific DNA cleavage domain at the C-terminal. Once the protein is bound to duplex DNA via its DNA-binding domain at the 5'-GGATG-3' recognition site, the DNA cleavage domain is activated and cleaves, without further sequence specificity, the first strand 9 nucleotides downstream and the second strand 13 nucleotides upstream of the nearest nucleotide of the recognition site. Its molecular mass is 65.4 kDa, being composed of 587 amino acids. DNA-binding domain The recognition domain contains three subdomains (D1, D2 and D3) that are evolutionarily related to the DNA-binding domain of the catabolite gene activator protein which contains a helix-turn-helix. DNA-cleavage domain DNA cleavage is mediated through the non-specific cleavage domain which also includes the dimerisation su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Data Bank
The Protein Data Bank (PDB) is a database for the three-dimensional structural data of large biological molecules, such as proteins and nucleic acids. The data, typically obtained by X-ray crystallography, NMR spectroscopy, or, increasingly, cryo-electron microscopy, and submitted by biologists and biochemists from around the world, are freely accessible on the Internet via the websites of its member organisations (PDBe, PDBj, RCSB, and BMRB). The PDB is overseen by an organization called the Worldwide Protein Data Bank, wwPDB. The PDB is a key in areas of structural biology, such as structural genomics. Most major scientific journals and some funding agencies now require scientists to submit their structure data to the PDB. Many other databases use protein structures deposited in the PDB. For example, SCOP and CATH classify protein structures, while PDBsum provides a graphic overview of PDB entries using information from other sources, such as Gene ontology. History Two force ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Finger
A zinc finger is a small protein structural motif that is characterized by the coordination of one or more zinc ions (Zn2+) in order to stabilize the fold. It was originally coined to describe the finger-like appearance of a hypothesized structure from the African clawed frog (''Xenopus laevis'') transcription factor IIIA. However, it has been found to encompass a wide variety of differing protein structures in eukaryotic cells. ''Xenopus laevis'' TFIIIA was originally demonstrated to contain zinc and require the metal for function in 1983, the first such reported zinc requirement for a gene regulatory protein followed soon thereafter by the Krüppel factor in ''Drosophila''. It often appears as a metal-binding domain in multi-domain proteins. Proteins that contain zinc fingers (zinc finger proteins) are classified into several different structural families. Unlike many other clearly defined supersecondary structures such as Greek keys or β hairpins, there are a number of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Finger Nuclease
Zinc-finger nucleases (ZFNs) are artificial restriction enzymes generated by fusing a zinc finger DNA-binding domain to a DNA-cleavage domain. Zinc finger domains can be engineered to target specific desired DNA sequences and this enables zinc-finger nucleases to target unique sequences within complex genomes. By taking advantage of endogenous DNA repair machinery, these reagents can be used to precisely alter the genomes of higher organisms. Alongside CRISPR/Cas9 and TALEN, ZFN is a prominent tool in the field of genome editing. Domains DNA-binding domain The DNA-binding domains of individual ZFNs typically contain between three and six individual zinc finger repeats and can each recognize between 9 and 18 basepairs. If the zinc finger domains perfectly recognize a 3 basepair DNA sequence, they can generate a 3-finger array that can recognize a 9 basepair target site. Other procedures can utilize either 1-finger or 2-finger modules to generate zinc-finger arrays with six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA is obtained by either isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using recombinant DNA methods or by artificially synthesising the DNA. A construct is usually created and used to insert this DNA into the host organism. The first recombinant DNA molecule was made by Paul Berg in 1972 by combining DNA from the monkey virus SV40 with the lambda virus. As well as inserting genes, the process can be used to remove, or "knock out", genes. The new DNA can be inserted randomly, or targeted to a specific part of the genome. An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be genetically modified (GM) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Engineering
Protein engineering is the process of developing useful or valuable proteins. It is a young discipline, with much research taking place into the understanding of protein folding and recognition for protein design principles. It has been used to improve the function of many enzymes for industrial catalysis. It is also a product and services market, with an estimated value of $168 billion by 2017. There are two general strategies for protein engineering: rational protein design and directed evolution. These methods are not mutually exclusive; researchers will often apply both. In the future, more detailed knowledge of protein structure and function, and advances in high-throughput screening, may greatly expand the abilities of protein engineering. Eventually, even unnatural amino acids may be included, via newer methods, such as expanded genetic code, that allow encoding novel amino acids in genetic code. Approaches Rational design In rational protein design, a scientist uses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Nucleotide Polymorphism
In genetics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population (e.g. 1% or more), many publications do not apply such a frequency threshold. For example, at a specific base position in the human genome, the G nucleotide may appear in most individuals, but in a minority of individuals, the position is occupied by an A. This means that there is a SNP at this specific position, and the two possible nucleotide variations – G or A – are said to be the alleles for this specific position. SNPs pinpoint differences in our susceptibility to a wide range of diseases, for example age-related macular degeneration (a common SNP in the CFH gene is associated with increased risk of the disease) or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (a SNP in the PNPLA3 gene is associated with incr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcitriol Receptor
The vitamin D receptor (VDR also known as the calcitriol receptor) is a member of the nuclear receptor family of transcription factors. Calcitriol (the active form of vitamin D, 1,25-(OH)2vitamin D3) binds to VDR, which then forms a heterodimer with the retinoid-X receptor. The VDR heterodimer then enters the nucleus and binds to Vitamin D responsive elements (VDRE) in genomic DNA. VDR binding results in expression or transrepression of many specific gene products. VDR is also involved in microRNA-directed post transcriptional mechanisms. In humans, the vitamin D receptor is encoded by the ''VDR'' gene located on chromosome 12q13.11. VDR is expressed in most tissues of the body, and regulates transcription of genes involved in intestinal and renal transport of calcium and other minerals. Glucocorticoids decrease VDR expression. Many types of immune cells also express VDR. Function The VDR gene encodes the nuclear hormone receptor for vitamin D. The most potent natural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cas9
Cas9 (CRISPR associated protein 9, formerly called Cas5, Csn1, or Csx12) is a 160 kilodalton protein which plays a vital role in the immunological defense of certain bacteria against DNA viruses and plasmids, and is heavily utilized in genetic engineering applications. Its main function is to cut DNA and thereby alter a cell's genome. The CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing technique was a significant contributor to the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 2020 being awarded to Emmanuelle Charpentier and Jennifer Doudna. More technically, Cas9 is a dual RNA-guided DNA endonuclease enzyme associated with the Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats ( CRISPR) adaptive immune system in ''Streptococcus pyogenes''. ''S. pyogenes'' utilizes CRISPR to memorize and Cas9 to later interrogate and cleave foreign DNA, such as invading bacteriophage DNA or plasmid DNA. Cas9 performs this interrogation by unwinding foreign DNA and checking for sites complementary to the 20 nucleotide spacer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Finger Nuclease
Zinc-finger nucleases (ZFNs) are artificial restriction enzymes generated by fusing a zinc finger DNA-binding domain to a DNA-cleavage domain. Zinc finger domains can be engineered to target specific desired DNA sequences and this enables zinc-finger nucleases to target unique sequences within complex genomes. By taking advantage of endogenous DNA repair machinery, these reagents can be used to precisely alter the genomes of higher organisms. Alongside CRISPR/Cas9 and TALEN, ZFN is a prominent tool in the field of genome editing. Domains DNA-binding domain The DNA-binding domains of individual ZFNs typically contain between three and six individual zinc finger repeats and can each recognize between 9 and 18 basepairs. If the zinc finger domains perfectly recognize a 3 basepair DNA sequence, they can generate a 3-finger array that can recognize a 9 basepair target site. Other procedures can utilize either 1-finger or 2-finger modules to generate zinc-finger arrays with six ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
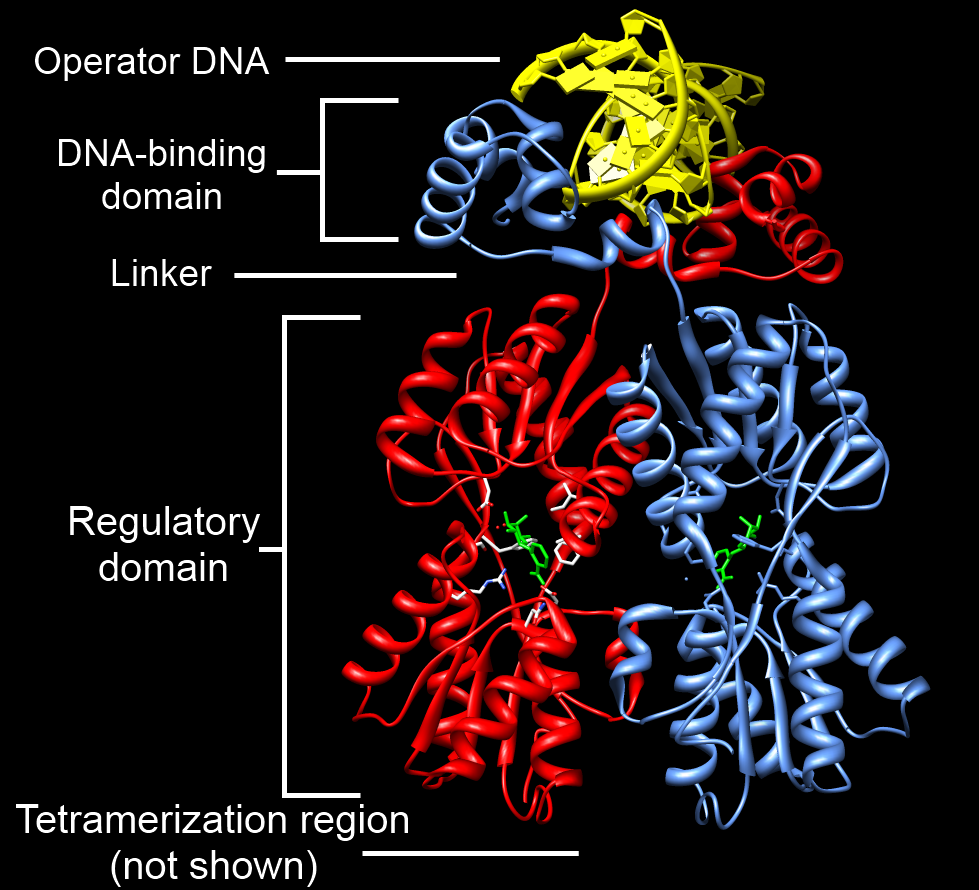
DNA-binding Domains
A DNA-binding domain (DBD) is an independently folded protein domain that contains at least one structural motif that recognizes double- or single-stranded DNA. A DBD can recognize a specific DNA sequence (a recognition sequence) or have a general affinity to DNA. Some DNA-binding domains may also include nucleic acids in their folded structure. Function One or more DNA-binding domains are often part of a larger protein consisting of further protein domains with differing function. The extra domains often regulate the activity of the DNA-binding domain. The function of DNA binding is either structural or involves transcription regulation, with the two roles sometimes overlapping. DNA-binding domains with functions involving DNA structure have biological roles in DNA replication, repair, storage, and modification, such as methylation. Many proteins involved in the regulation of gene expression contain DNA-binding domains. For example, proteins that regulate transcription by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |