|
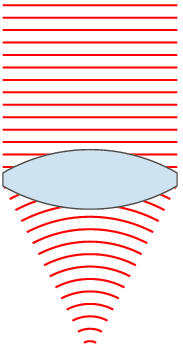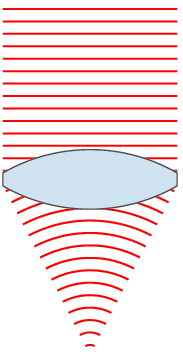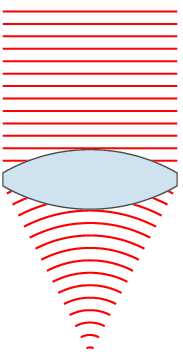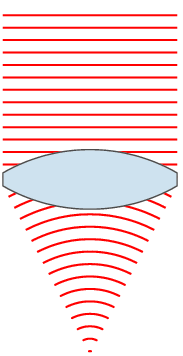
Focal Length
The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system converges light, while a negative focal length indicates that the system diverges light. A system with a shorter focal length bends the rays more sharply, bringing them to a focus in a shorter distance or diverging them more quickly. For the special case of a thin lens in air, a positive focal length is the distance over which initially collimated (parallel) rays are brought to a focus, or alternatively a negative focal length indicates how far in front of the lens a point source must be located to form a collimated beam. For more general optical systems, the focal length has no intuitive meaning; it is simply the inverse of the system's optical power. In most photography and all telescopy, where the subject is essentially infinitely far away, longer focal length (lower ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
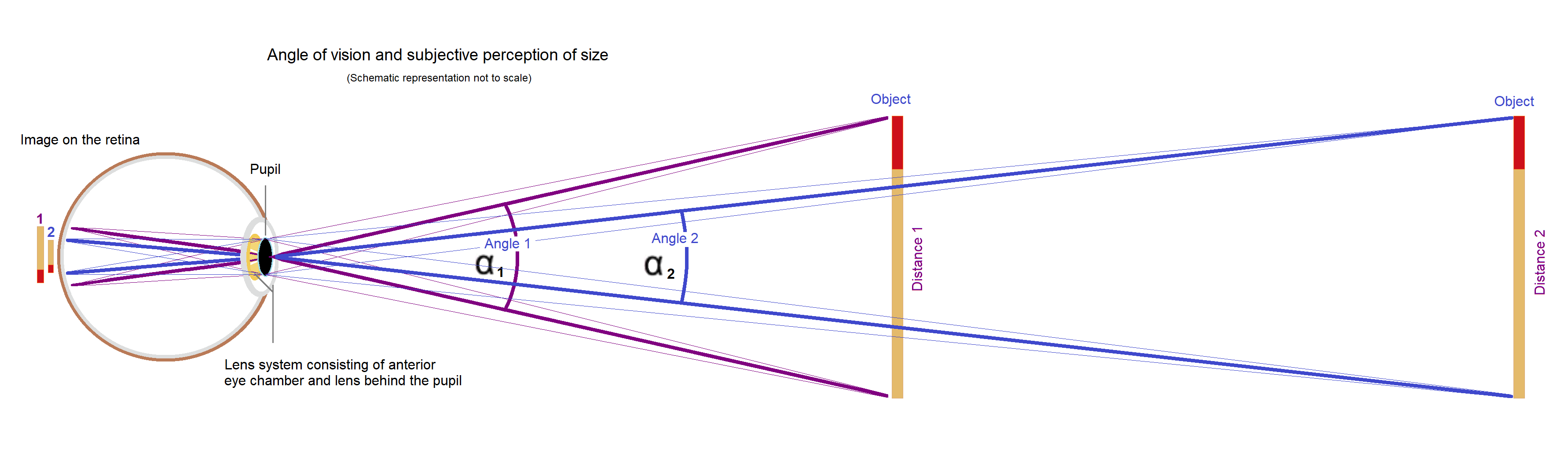
Angle Of View
The angle of view is the decisive variable for the visual perception of the size or projection of the size of an object. Angle of view and perception of size The perceived size of an object depends on the size of the image projected onto the retina. The size of the image depends on the angle of vision. A near and a far object can appear the same size if their edges produce the same angle of vision. With an optical device such as glasses or binoculars, microscope and telescope the angle of vision can be widened so that the object appears larger, which is favourable for the resolving power of the eye (see visual angle). Angle of view in photography In photography, angle of view (AOV) describes the angular extent of a given scene that is imaged by a camera. It is used interchangeably with the more general term field of view. It is important to distinguish the angle of view from the angle of coverage, which describes the angle range that a lens can image. Typically the ima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished or molded to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses. Lenses are used in various imaging devices like telescopes, binoculars and cameras. They are also used as visual aids in glasses to correct defects of vision such as myopia and hypermetropia. History The word ''lens'' comes from '' lēns'', the Latin name of the lentil (a seed of a lent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sign Convention
In physics, a sign convention is a choice of the physical significance of signs (plus or minus) for a set of quantities, in a case where the choice of sign is arbitrary. "Arbitrary" here means that the same physical system can be correctly described using different choices for the signs, as long as one set of definitions is used consistently. The choices made may differ between authors. Disagreement about sign conventions is a frequent source of confusion, frustration, misunderstandings, and even outright errors in scientific work. In general, a sign convention is a special case of a choice of coordinate system for the case of one dimension. Sometimes, the term "sign convention" is used more broadly to include factors of '' i'' and 2 π, rather than just choices of sign. Relativity Metric signature In relativity, the metric signature can be either or . (Note that throughout this article we are displaying the signs of the eigenvalues of the metric in the order that presents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lensmaker's Equation
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic, and are ground and polished or molded to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses. Lenses are used in various imaging devices like telescopes, binoculars and cameras. They are also used as visual aids in glasses to correct defects of vision such as myopia and hypermetropia. History The word ''lens'' comes from '' lēns'', the Latin name of the lentil (a seed of a lentil plant) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radius Of Curvature (optics)
Radius of curvature (ROC) has specific meaning and sign convention in optical design. A spherical lens or mirror surface has a center of curvature located either along or decentered from the system local optical axis. The vertex of the lens surface is located on the local optical axis. The distance from the vertex to the center of curvature is the radius of curvature of the surface. The sign convention for the optical radius of curvature is as follows: * If the vertex lies to the left of the center of curvature, the radius of curvature is positive. * If the vertex lies to the right of the center of curvature, the radius of curvature is negative. Thus when viewing a biconvex lens from the side, the left surface radius of curvature is positive, and the right radius of curvature is negative. Note however that ''in areas of optics other than design'', other sign conventions are sometimes used. In particular, many undergraduate physics textbooks use the Gaussian sign conve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensional picture, that resembles a subject. In the context of signal processing, an image is a distributed amplitude of color(s). In optics, the term “image” may refer specifically to a 2D image. An image does not have to use the entire visual system to be a visual representation. A popular example of this is of a greyscale image, which uses the visual system's sensitivity to brightness across all wavelengths, without taking into account different colors. A black and white visual representation of something is still an image, even though it does not make full use of the visual system's capabilities. Images are typically still, but in some cases can be moving or animated. Characteristics Images may be two or three-dimensional, such as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SPIE
SPIE (formerly the Society of Photographic Instrumentation Engineers, later the Society of Photo-Optical Instrumentation Engineers) is an international not-for-profit professional society for optics and photonics technology, founded in 1955. It organizes technical conferences, trade exhibitions, and continuing education programs for researchers and developers in the light-based fields of physics, including: optics, photonics, and imaging engineering. The society publishes peer-reviewed scientific journals, conference proceedings, monographs, tutorial texts, field guides, and reference volumes in print and online. SPIE is especially well-known for Photonics West, one of the laser and photonics industry's largest combined conferences and tradeshows which is held annually in San Francisco. SPIE also participates as partners in leading educational initiatives, and in 2020, for example, provided more than $5.8 million in support of optics education and outreach programs around the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Refractive Index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is a dimensionless number that gives the indication of the light bending ability of that medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, , where ''θ''1 and ''θ''2 are the angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices ''n''1 and ''n''2. The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity ( Fresnel's equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is , and similarly the wavelength in that medium is , where ''� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principal Plane
In Gaussian optics, the cardinal points consist of three pairs of points located on the optical axis of a rotationally symmetric, focal, optical system. These are the '' focal points'', the principal points, and the nodal points. For ''ideal'' systems, the basic imaging properties such as image size, location, and orientation are completely determined by the locations of the cardinal points; in fact only four points are necessary: the focal points and either the principal or nodal points. The only ideal system that has been achieved in practice is the plane mirror, however the cardinal points are widely used to ''approximate'' the behavior of real optical systems. Cardinal points provide a way to analytically simplify a system with many components, allowing the imaging characteristics of the system to be approximately determined with simple calculations. Explanation The cardinal points lie on the optical axis of the optical system. Each point is defined by the effect the optica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addison Wesley
Addison-Wesley is an American publisher of textbooks and computer literature. It is an imprint of Pearson PLC, a global publishing and education company. In addition to publishing books, Addison-Wesley also distributes its technical titles through the O'Reilly Online Learning e-reference service. Addison-Wesley's majority of sales derive from the United States (55%) and Europe (22%). The Addison-Wesley Professional Imprint produces content including books, eBooks, and video for the professional IT worker including developers, programmers, managers, system administrators. Classic titles include ''The Art of Computer Programming'', ''The C++ Programming Language'', ''The Mythical Man-Month'', and ''Design Patterns''. History Lew Addison Cummings and Melbourne Wesley Cummings founded Addison-Wesley in 1942, with the first book published by Addison-Wesley being Massachusetts Institute of Technology professor Francis Weston Sears' ''Mechanics''. Its first computer book was ''Progra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Vertex
In Gaussian optics, the cardinal points consist of three pairs of points located on the optical axis of a rotationally symmetric, focal, optical system. These are the '' focal points'', the principal points, and the nodal points. For ''ideal'' systems, the basic imaging properties such as image size, location, and orientation are completely determined by the locations of the cardinal points; in fact only four points are necessary: the focal points and either the principal or nodal points. The only ideal system that has been achieved in practice is the plane mirror, however the cardinal points are widely used to ''approximate'' the behavior of real optical systems. Cardinal points provide a way to analytically simplify a system with many components, allowing the imaging characteristics of the system to be approximately determined with simple calculations. Explanation The cardinal points lie on the optical axis of the optical system. Each point is defined by the effect the optica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |