|
Flatfish (shogi)
In shogi, Flatfish (olive flounder, 平目 ''hirame'') is a Central Rook (Ranging Rook) shogi opening, opening. It characteristically uses the Flatfish castle (shogi), castle (平目囲い or ヒラメ囲い ''hiramegakoi'') instead of the more usual Mino castle. See also * Central Rook * Central Rook Silver Horns * Cheerful Central Rook * Ranging Rook Bibliography {{Shogi openings Shogi openings Ranging Rook openings Central Rook openings ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi
, also known as Japanese chess, is a strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as Western chess, ''chaturanga, Xiangqi'', Indian chess, and '' janggi''. ''Shōgi'' means general's (''shō'' ) board game (''gi'' ). Western chess is sometimes called (''Seiyō Shōgi'' ) in Japan. Shogi was the earliest chess-related historical game to allow captured pieces to be returned to the board by the capturing player. This drop rule is speculated to have been invented in the 15th century and possibly connected to the practice of 15th century mercenaries switching loyalties when captured instead of being killed. The earliest predecessor of the game, chaturanga, originated in India in the sixth century, and the game was likely transmitted to Japan via China or Korea sometime after the Nara period."Shogi". ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2002. Shogi in its present form was played as early as the 16th century, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olive Flounder
The olive flounder (''Paralichthys olivaceus''), bastard halibut or Japanese halibut, is a temperate marine species of large-tooth flounder native to the North-western Pacific Ocean. It is often referred to as the Japanese flatfish or Korean flatfish (광어) when mentioned in the context of those countries. It is the highest valued finfish in the world, known to be excellent for aquaculture due to a rapid growth rate and popularity in Korea. It reaches a length of and a weight of . In 2017 its genome and transcriptome was sequenced as a model to study flatfish asymmetry. Habitat and diet The olive flounder is often found in soft and muddy offshore, coastal areas where the water level goes down to 100 m in depth. The temperature of water in these areas range from 21- 24 °C or 69 -75 °F. Some flounder have been found in the Mariana Trench. Olive flounder typically eat fish spawn, crustaceans, polychaetes, and small fish. Life cycle Olive flounder spawn any ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
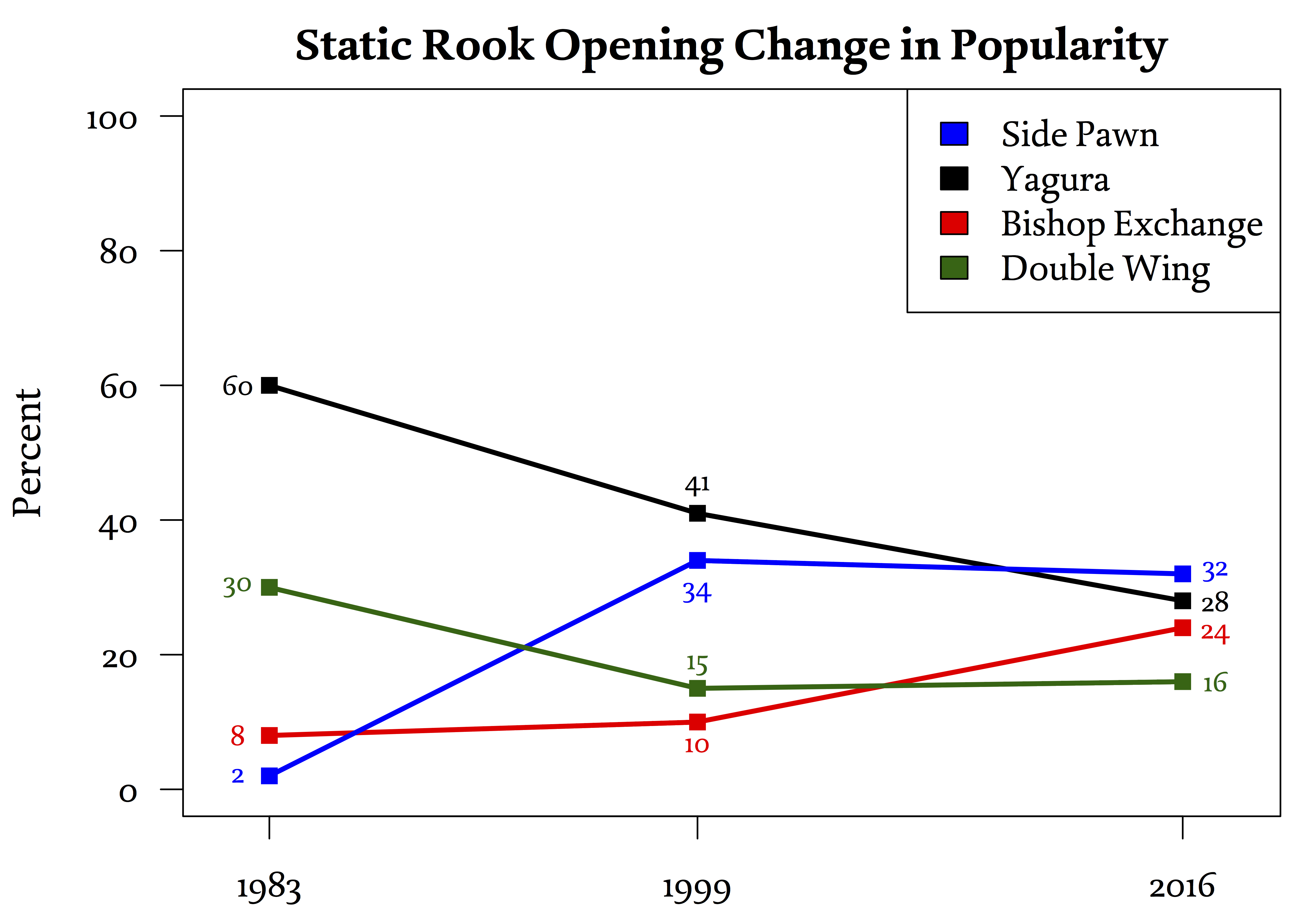
Central Rook
In shogi, Central Rook (中飛車 ''nakabisha'') is a subclass of Ranging Rook openings in which the rook is positioned on the fifth (central) file. However, since the central file can be thought of as the dividing line between Ranging Rook and Static Rook positions, it is also possible to find Static Rook positions using a rook that has been moved to the central file. These strategies are generally categorized as subclasses of the particular Static Rook opening. For example, Central Rook Yagura (矢倉中飛車) is a Yagura opening that uses a central rook. The term 中飛車 without modification refers to Ranging Rook Central Rook strategies while Static Rook central rook strategies have another word modifying 中飛車. Central Rook subcategories Ranging Rook strategies like Central Rook are also traditionally played by White against Black's Static Rook position. However, in the modern era (that is, later than the Edo period), Normal Central Rook is played by both White a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi Opening
A shogi opening ( ) is the sequence of initial moves of a shogi game before the middle game. The more general Japanese term for the beginning of the game is ()''.'' A '' jōseki'' () is the especially recommended sequence of moves for a given opening that was considered balanced play at one point in time for both sides by professional players. (However, some ''s'' have become outdated when they are reevaluated to no longer give balanced play.) ''s'' also typically include commentary about the possible reasons to deviate from the especially regarding blunders. Note that not all openings have ''s''. For example, trap openings like Demon Slayer, while they may have standard moves, are considered to favor one player and are not balanced play. Thus, the Demon Slayer opening is not a jōseki. Introduction The very first opening moves in most games are pawn pushes. In particular, most games start with two types of pawn pushes. A player can move the rook pawn forward (P-26) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Castle (shogi)
In shogi, castles ( ja, 囲い, translit=kakoi) are strong defensive configurations of pieces that protect the king ( ja, 玉). In contrast to the special castling move in western chess, shogi castles are structures that require making multiple individual moves with more than one piece. Introduction Usually the pieces involved in constructing castles are golds ( ja, 金), silvers ( ja, 銀), and pawns ( ja, 歩). Typically, they also require moving the king from its starting position – often to the left or right side of the board. The simplest castle involves two pieces and requires three moves, but it is more common to move at least three different pieces. For example, a simple Mino castle requires moving the king, the rook ( ja, 飛), a silver, and two golds for a total of six moves. Others such as the Static Rook Bear-in-the-hole castle are more complex, which requires moving the king, a pawn, the bishop ( ja, 角), a lance ( ja, 香), a silver, and two golds for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mino Castle
The Mino castle (美濃囲い ''minō gakoi'' or 本美濃囲い ''hon minō gakoi'') is a castle used in shogi. Mino castle is a very commonly used defensive formation that may be used within both Ranging Rook and Static Rook positions against both Ranging Rook and Static Rook opponents. The castle has several variants and may be the initial springboard for other further castle developments (such as the Silver Crown castle variants and the Right Fortress). Due to its popularity, several methods of attacking the Mino castle have been well studied. History The Mino castle was first developed for White in Lance handicap games by , the 10th Lifetime Meijin. The adjacent diagram shows the first recorded example of a Mino castle by Sōkan III in 1765. A major innovation was the adaption of Mino for use in even games by (1795–1839), who was a student of the 9th Lifetime Meijin, , and the second strongest historical player of his time as evaluated by today's standard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Rook Silver Horns
In shogi, Silver Horns Central Rook (ツノ銀中飛車 ''tsuno gin nakabisha'') is a type of Central Rook opening that uses the Silver Horn formation where the right and left silver are positioned at the ears of the player's rook, which is positioned on the bottom rank. Silver Horns uses a Kimura Mino (木村美濃) castle instead of the usual Mino castle. Formation This ranging rook opening is characterized by moving the rook to the 5th file, and then placing the left silver at 67 (43, if playing White). If the opponent opts for a quick game, the game is played with the position as is, in which case it is called Incomplete Silver Horns (片ツノ銀 ''kata tsuno gin''). In case of a slow game, the right silver is placed at 47 (63, if playing White), the right gold at 38 (72) or 48 (62), and the king at 28 (82) or 38 (72) (this castle is called Kimura Mino). The left gold is often set at 78 (32). As can be seen in the accompanying diagrams, this leads to a symmetrical stance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheerful Central Rook
In shogi, Cheerful Central Rook (ゴキゲン中飛車 ''gokigen nakabisha'', also Gokigen Central Rook or Go-As-You-Please Central Rook) is a type of Central Rook opening in which the Central Rook player's bishop diagonal remains open. This is a more aggressive strategy since the bishops may be exchanged at any time during the opening. (See: Ranging Rook#Types of Ranging Rook.) Cheerful Central Rook is played against a Static Rook opponent. White's variation 1.P-76 P-34 2.P-26. Open bishop diagonals. Black plays Static Rook. 2...P-54. White pushes the central pawn – the signature move of Cheerful Central Rook. 3.P-25. Rook pawn advance. 3...R-52. Central Rook move. Early pawn push After White swings their rook to the central file, pushing the second file pawn by Black (4.P-24) in order to trade the pawns off and get a pawn in hand is thought to be a mistake (although not quite a blunder) here since it will result in a position judged to be better for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranging Rook
Ranging Rook or Swinging Rook (振り飛車 ''furibisha'') openings in shogi position the rook to the center or left of the player's board to support an attack there. Ranging Rook strategies used in Ranging Rook vs Static Rook are among the oldest of shogi strategies attested in the historical documents that first describe the rules of shogi around 1600. Description Types of Ranging Rook Traditionally, Ranging Rook has been used as a defensive strategy for White against Static Rook openings played by Black. White's rook can be moved flexibly to counteract Black's attacks. These types of White openings are named simply Ranging Rook (振り飛車 ''furibisha''). In describing the game positions of both opponents, the term is Static Rook vs Ranging Rook (居飛車対振り飛車 ''ibisha tai furibisha''). In these games, Black has the initiative, and White quickly builds a defense by castling the king and seeks counterattacking opportunities. By default, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi Openings
, also known as Japanese chess, is a Abstract strategy game, strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as chess, Western chess, ''chaturanga, Xiangqi'', Indian chess, and ''janggi''. ''Shōgi'' means general's (''shō'' ) board game (''gi'' ). Western chess is sometimes called (''Seiyō Shōgi'' ) in Japan. Shogi was the earliest chess-related historical game to allow captured pieces to be returned to the board by the capturing player. This drop rule is speculated to have been invented in the 15th century and possibly connected to the practice of 15th century Mercenary#15th to 18th centuries, mercenaries switching loyalties when captured instead of being killed. The earliest predecessor of the game, chaturanga, originated in India in the sixth century, and the game was likely transmitted to Japan via China or Korea sometime after the Nara period."Shogi". ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2002. Shogi in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranging Rook Openings
Length measurement, distance measurement, or range measurement (ranging) refers to the many ways in which length, distance, or range can be measured. The most commonly used approaches are the rulers, followed by transit-time methods and the interferometer methods based upon the speed of light. For objects such as crystals and diffraction gratings, diffraction is used with X-rays and electron beams. Measurement techniques for three-dimensional structures very small in every dimension use specialized instruments such as ion microscopy coupled with intensive computer modeling. Standard rulers The ruler the simplest kind of length measurement tool: lengths are defined by printed marks or engravings on a stick. The metre was initially defined using a ruler before more accurate methods became available. Gauge blocks are a common method for precise measurement or calibration of measurement tools. For small or microscopic objects, microphotography where the length is calibrated usi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |