|
Flanker Task
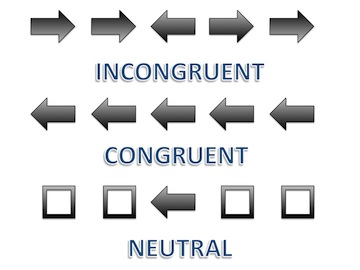
In cognitive psychology, the Eriksen flanker task is a set of response inhibition tests used to assess the ability to suppress responses that are inappropriate in a particular context. The target is flanked by non-target stimuli which correspond either to the same directional response as the target (''congruent'' flankers), to the opposite response (''incongruent'' flankers), or to neither (''neutral'' flankers). The task is named for American psychologists Barbara. A. Eriksen & Charles W. Eriksen, who first published the task in 1974, and for the flanker stimuli that surround the target. In the tests, a directional response (usually left or right) is assigned to a central target stimulus. Various forms of the task are used to measure information processing and selective attention. Procedure and method In an Eriksen Flanker Task there are three types of stimuli used: #Congruent stimulus- Flankers call for the same response as the target, and may appear identical. Also referred t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cognitive Psychology
Cognitive psychology is the scientific study of mental processes such as attention, language use, memory, perception, problem solving, creativity, and reasoning. Cognitive psychology originated in the 1960s in a break from behaviorism, which held from the 1920s to 1950s that unobservable mental processes were outside the realm of empirical science. This break came as researchers in linguistics and cybernetics, as well as applied psychology, used models of mental processing to explain human behavior. Work derived from cognitive psychology was integrated into other branches of psychology and various other modern disciplines like cognitive science, linguistics, and economics. The domain of cognitive psychology overlaps with that of cognitive science, which takes a more interdisciplinary approach and includes studies of non-human subjects and artificial intelligence. History Philosophically, ruminations on the human mind and its processes have been around since the times of the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol (drug)
Alcohol, sometimes referred to by the chemical name ''ethanol'', is a depressant drug that is the active ingredient in drinks such as beer, wine, and distilled spirits (hard liquor). It is one of the oldest and most commonly consumed recreational drugs, causing the characteristic effects of alcohol intoxication ("drunkenness"). Among other effects, alcohol produces happiness and euphoria, decreased anxiety, increased sociability, sedation, impairment of cognitive, memory, motor, and sensory function, and generalized depression of central nervous system (CNS) function. Ethanol is only one of several types of alcohol, but it is the only type of alcohol that is found in alcoholic beverages or commonly used for recreational purposes; other alcohols such as methanol and isopropyl alcohol are significantly more toxic. A mild, brief exposure to isopropanol, being only moderately more toxic than ethanol, is unlikely to cause any serious harm. Methanol, being profoundly more t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cocktail Party Effect
The cocktail party effect is the phenomenon of the brain's ability to focus one's auditory attention on a particular stimulus while filtering out a range of other stimuli, such as when a partygoer can focus on a single conversation in a noisy room. Listeners have the ability to both segregate different stimuli into different streams, and subsequently decide which streams are most pertinent to them. It has been proposed that one's sensory memory subconsciously parses all stimuli and identifies discrete pieces of information by classifying them by salience. This effect is what allows most people to "tune into" a single voice and "tune out" all others. This phenomenon is often described in terms of "selective attention" or " selective hearing". It may also describe a similar phenomenon that occurs when one may immediately detect words of importance originating from unattended stimuli, for instance hearing one's name among a wide range of auditory input. An inability to segregate s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Effect
The Simon effect is the difference in accuracy or reaction time between trials in which stimulus and response are on the same side and trials in which they are on opposite sides, with responses being generally slower and less accurate when the stimulus and response are on opposite sides. The task is similar in concept to the ''Stroop Effect''. The Stroop Color and Word Test (SCWT) can be used to assess the ability to inhibit cognitive interference that occurs when the processing of a specific stimulus feature impedes the simultaneous processing of a second stimulus attribute. The Simon effect is an extension of this effect, but the interference in this task is generated by spatial features rather than features of the stimuli themselves. Original experiment In Simon's original study, two lights (the stimulus) were placed on a rotating circular panel. This device would be rotated at varying degrees (away from the horizontal plane). Simon wished to see if an alteration of the spatial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stroop Effect
---- ---- Naming the font color of a printed word is an easier and quicker task if word meaning and font color are congruent. If two words are both printed in red, the average time to say "red" in response to the written word "green" is greater than the time to say "red" in response to the written word "mouse". In psychology, the Stroop effect is the delay in reaction time between congruent and incongruent stimuli. The effect has been used to create a psychological test (the Stroop test) that is widely used in clinical practice and investigation. A basic task that demonstrates this effect occurs when there is a mismatch between the name of a color (e.g., "blue", "green", or "red") and the color it is printed on (i.e., the word "red" printed in blue ink instead of red ink). When asked to name the color of the word it takes longer and is more prone to errors when the color of the ink does not match the name of the color. The effect is named after John Ridley Stroop, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Event-related Potential
An event-related potential (ERP) is the measured brain response that is the direct result of a specific sensory, cognitive, or motor event. More formally, it is any stereotyped electrophysiological response to a stimulus. The study of the brain in this way provides a noninvasive means of evaluating brain functioning. ERPs are measured by means of electroencephalography (EEG). The magnetoencephalography (MEG) equivalent of ERP is the ERF, or event-related field. Evoked potentials and induced potentials are subtypes of ERPs. History With the discovery of the electroencephalogram (EEG) in 1924, Hans Berger revealed that one could measure the electrical activity of the human brain by placing electrodes on the scalp and amplifying the signal. Changes in voltage can then be plotted over a period of time. He observed that the voltages could be influenced by external events that stimulated the senses. The EEG proved to be a useful source in recording brain activity over the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Task Switching (psychology)
Task switching, or set-shifting, is an executive function that involves the ability to ''unconsciously'' shift attention between one task and another. In contrast, cognitive shifting is a very similar executive function, but it involves ''conscious'' (not unconscious) change in attention. Together, these two functions are subcategories of the broader cognitive flexibility concept. Task switching allows a person to rapidly and efficiently adapt to different situations. It is often studied by cognitive and experimental psychologists, and can be tested experimentally using tasks like the Wisconsin Card Sorting Test. Deficits in task switching are commonly observed in patients with Parkinson's disease, and in those on the autism spectrum. Background and history Human behavior and cognition are characterized by the ability to adapt to a dynamic environment, whether in attention, action, or both. This ability to shift attention and action adaptively has been investigated in the la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priming (psychology)
Priming is a phenomenon whereby exposure to one stimulus influences a response to a subsequent stimulus, without conscious guidance or intention. The priming effect refers to the positive or negative effect of a rapidly presented stimulus (priming stimulus) on the processing of a second stimulus (target stimulus) that appears shortly after. Generally speaking, the generation of priming effect depends on the existence of some positive or negative relationship between priming and target stimuli. For example, the word ''nurse'' is recognized more quickly following the word ''doctor'' than following the word ''bread''. Priming can be perceptual, associative, repetitive, positive, negative, affective, semantic, or conceptual. Priming effects involve word recognition, semantic processing, attention, unconscious processing, and many other issues, and are related to differences in various writing systems. Research, however, has yet to firmly establish the duration of priming effects, yet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acute Tryptophan Depletion
Acute tryptophan depletion (ATD) is a technique used extensively to study the effect of low serotonin in the brain. This experimental approach reduces the availability of tryptophan, an amino acid Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha ... which serves as the precursor to serotonin. The lack of mood-lowering effects after ATD in healthy subjects seems to contradict a direct causal relationship between acutely decreased serotonin levels and depression, although mood-lowering effects are observed in certain vulnerable individuals. References Serotonin {{Neuroscience-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. Approximately 90% of the serotonin that the body produces is in the intestinal tract. Biochemically, the indoleamine molecule derives from the amino acid tryptophan, via the (rate-limiting) hydroxylation of the 5 position on the ring (forming the intermediate 5-hydroxytryptophan), and then decarboxylation to produce serotonin. Serotonin is primarily found in the enteric nervous system located in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract). However, it is also produced in the central nervous system (CNS), specifically in the raphe nuclei located in the brainstem, Merkel cells located in the skin, pulmonary neuroendocrine cells and taste receptor cells in the tongue. Additionally, serotonin is stored in blood platelets a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Exercise
Exercise is a body activity that enhances or maintains physical fitness and overall health and wellness. It is performed for various reasons, to aid growth and improve strength, develop muscles and the cardiovascular system, hone athletic skills, weight loss or maintenance, improve health, or simply for enjoyment. Many individuals choose to exercise outdoors where they can congregate in groups, socialize, and improve well-being as well as mental health. In terms of health benefits, the amount of recommended exercise depends upon the goal, the type of exercise, and the age of the person. Even doing a small amount of exercise is healthier than doing none. Classification Physical exercises are generally grouped into three types, depending on the overall effect they have on the human body: * Aerobic exercise is any physical activity that uses large muscle groups and causes the body to use more oxygen than it would while resting. The goal of aerobic exercise is to increas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's disease (PD), or simply Parkinson's, is a long-term degenerative disorder of the central nervous system that mainly affects the motor system. The symptoms usually emerge slowly, and as the disease worsens, non-motor symptoms become more common. The most obvious early symptoms are tremor, rigidity, slowness of movement, and difficulty with walking. Cognitive and behavioral problems may also occur with depression, anxiety, and apathy occurring in many people with PD. Parkinson's disease dementia becomes common in the advanced stages of the disease. Those with Parkinson's can also have problems with their sleep and sensory systems. The motor symptoms of the disease result from the death of cells in the substantia nigra, a region of the midbrain, leading to a dopamine deficit. The cause of this cell death is poorly understood, but involves the build-up of misfolded proteins into Lewy bodies in the neurons. Collectively, the main motor symptoms are also k ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)



