|
Fish In Chinese Mythology
Fish are an important motif in Chinese mythology. There are various myths involving fish. Chinese mythology refers to those myths found in the historical geographic area of China. The geographic area of "China" is of course a concept which has evolved of changed through history. Fish in Chinese mythology include myths in Chinese and other languages, as transmitted by Han Chinese as well as other officially recognized 56 minority ethnic groups in China. The Chinese word for "fish", ''yu'', is a homophone for "abundance", "plenty", and "affluence" (yu 餘); therefore, fishes are a symbol of wealth. The Chinese dragon is the head of the fish clan. The act of fishing is also an important motif in Chinese mythology and culture. Cultural significance and symbolism Yu (fish) Fishes are a symbol of wealth in Chinese culture. The Chinese character for fish is yu (). It is pronounced with a different tone in modern Chinese, 裕 (yù) means "abundance". Alternatively, 餘, meaning "over, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carp Jumping The Dragon Gate
Carp are various species of oily fish, oily freshwater fish from the family Cyprinidae, a very large group of fish native to Europe and Asia. While carp is consumed in many parts of the world, they are generally considered an invasive species in parts of Africa, Australia and most of the United States. Biology The cypriniformes (family Cyprinidae) are traditionally grouped with the Characiformes, Siluriformes, and Gymnotiformes to create the superorder Ostariophysi, since these groups share some common features. These features include being found predominantly in fresh water and possessing Weberian ossicles, an anatomical structure derived from the first five anterior-most vertebrae, and their corresponding ribs and neural crests. The third anterior-most pair of ribs is in contact with the extension of the bony labyrinth, labyrinth and the posterior with the swim bladder. The function is poorly understood, but this structure is presumed to take part in the transmission of vibr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Longmen (Shanxi)
Lóngmén Shān, Mount Longmen or Longmen Mountain is a mountain in Shanxi province, China. In March–April 2010, the Wangjialing coal mine flood occurred here. Geography Lóngmén Shān is where the Yellow River abruptly leaves the vast, rugged expanse of the Loess Plateau that spreads out in the mountain's north and west to enter a plain which connects both to the nearby Linfen Basin in the east and to the Guanzhong Plain further southwest. The mountain is thus a part of the Loess Plateau's southern edge. At the same time, it forms the south-western extreme point of the Lüliang Mountains, a range that runs parallel to the river as it flows south. The spot at Lóngmén Shān's southwestern tip where the Yellow River breaks through is called Yǔménkǒu (, “ Yu's doorway, or gate”). Here, three bridges span the Yellow River. As there are no other nearby bridges either upstream or downstream, this is the only dry connection from Xiangning County and Hejin (in Shanxi provinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Bronze Inscriptions
Chinese bronze inscriptions, also commonly referred to as bronze script or bronzeware script, are writing in a variety of Chinese scripts on ritual bronzes such as ''zhōng'' bells and '' dǐng'' tripodal cauldrons from the Shang dynasty (2nd millennium BC) to the Zhou dynasty (11th–3rd century BC) and even later. Early bronze inscriptions were almost always cast (that is, the writing was done with a stylus in the wet clay of the piece-mold from which the bronze was then cast), while later inscriptions were often engraved after the bronze was cast. The bronze inscriptions are one of the earliest scripts in the Chinese family of scripts, preceded by the oracle bone script. Terminology For the early Western Zhou to early Warring States period, the bulk of writing which has been unearthed has been in the form of bronze inscriptions. As a result, it is common to refer to the variety of scripts of this period as "bronze script", even though there is no single such script. The term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oracle Bone Script
Oracle bone script () is an ancient form of Chinese characters that were engraved on oracle bonesanimal bones or turtle plastrons used in pyromantic divination. Oracle bone script was used in the late 2nd millennium BC, and is the earliest known form of Chinese writing. The vast majority of oracle bone inscriptions, of which about 150,000 pieces have been discovered, were found at the Yinxu site located in Xiaotun Village, Anyang, Henan Province. The latest significant discovery is the Huayuanzhuang storage of 1,608 pieces, 579 of which were inscribed, found near Xiaotun in 1993. They record pyromantic divinations of the last nine kings of the Shang dynasty, beginning with Wu Ding, whose accession is dated by different scholars at 1250 BC or 1200 BC. Oracle bone inscriptions of Wu Ding's reign have been radiocarbon dated to 1254–1197 BC±10 years. After the Shang were overthrown by the Zhou dynasty in c. 1046 BC, divining with milfoil became more common, and a much smaller ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radical (Chinese Character)
A Chinese radical () or indexing component is a graphical component of a Chinese character under which the character is traditionally listed in a Chinese dictionary. This component is often a semantic indicator similar to a morpheme, though sometimes it may be a phonetic component or even an artificially extracted portion of the character. In some cases the original semantic or phonological connection has become obscure, owing to changes in character meaning or pronunciation over time. The English term "radical" is based on an analogy between the structure of characters and inflection of words in European languages. Radicals are also sometimes called "classifiers", but this name is more commonly applied to grammatical classifiers (measure words). History In the earliest Chinese dictionaries, such as the '' Erya'' (3rd century BC), characters were grouped together in broad semantic categories. Because the vast majority of characters are phono-semantic compounds (), comb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guanyin
Guanyin () is a Bodhisattva associated with compassion. She is the East Asian representation of Avalokiteśvara ( sa, अवलोकितेश्वर) and has been adopted by other Eastern religions, including Chinese folk religion. She was first given the appellation of "Goddess of Mercy" or "Mercy Goddess" by Jesuit missionaries in China. Guanyin is short for Guanshiyin, which means " he One WhoPerceives the Sounds of the World." On the 19th day of the sixth lunar month, Guanyin's attainment of Buddhahood is celebrated. Some Buddhists believe that when one of their adherents departs from this world, they are placed by Guanyin in the heart of a lotus, and then sent to the western pure land of Sukhāvatī. Guanyin is often referred to as the "most widely beloved Buddhist Divinity" with miraculous powers to assist all those who pray to her, as is mentioned in the ''Pumen chapter'' of ''Lotus Sutra'' and ''Kāraṇḍavyūha Sūtra''. Several large temples in East Asia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhou Dynasty
The Zhou dynasty ( ; Old Chinese ( B&S): *''tiw'') was a royal dynasty of China that followed the Shang dynasty. Having lasted 789 years, the Zhou dynasty was the longest dynastic regime in Chinese history. The military control of China by the royal house, surnamed Ji, lasted initially from 1046 until 771 BC for a period known as the Western Zhou, and the political sphere of influence it created continued well into the Eastern Zhou period for another 500 years. The establishment date of 1046 BC is supported by the Xia–Shang–Zhou Chronology Project and David Pankenier, but David Nivison and Edward L. Shaughnessy date the establishment to 1045 BC. During the Zhou dynasty, centralized power decreased throughout the Spring and Autumn period until the Warring States period in the last two centuries of the dynasty. In the latter period, the Zhou court had little control over its constituent states that were at war with each other until the Qin state consolidated power and forme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jiang Ziya
Jiang Ziya ( century BC – century BC), also known by several other names, was a Chinese noble who helped kings Wen and Wu of Zhou overthrow the Shang in ancient China. Following their victory at Muye, he continued to serve as a Zhou minister. He remained loyal to the regent Duke of Zhou during the Rebellion of the Three Guards; following the Duke's punitive raids against the restive Eastern Barbarians or ''Dongyi'', Jiang was enfeoffed with their territory as the marchland of Qi. He established his seat at Yingqiu (in modern Linzi). Names The first marquis of Qi bore the given name Shang. The nobility of ancient China bore two surnames, an ancestral name and a clan name. His were Jiang (姜) and Lü (呂), respectively. He had two courtesy names, Shangfu (尚父; lit. "Esteemed Father") and Ziya (lit. "Master Ivory, Master Tusk"), which were used for respectful address by his peers. The names Jiang Shang and Jiang Ziya became the most common after th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
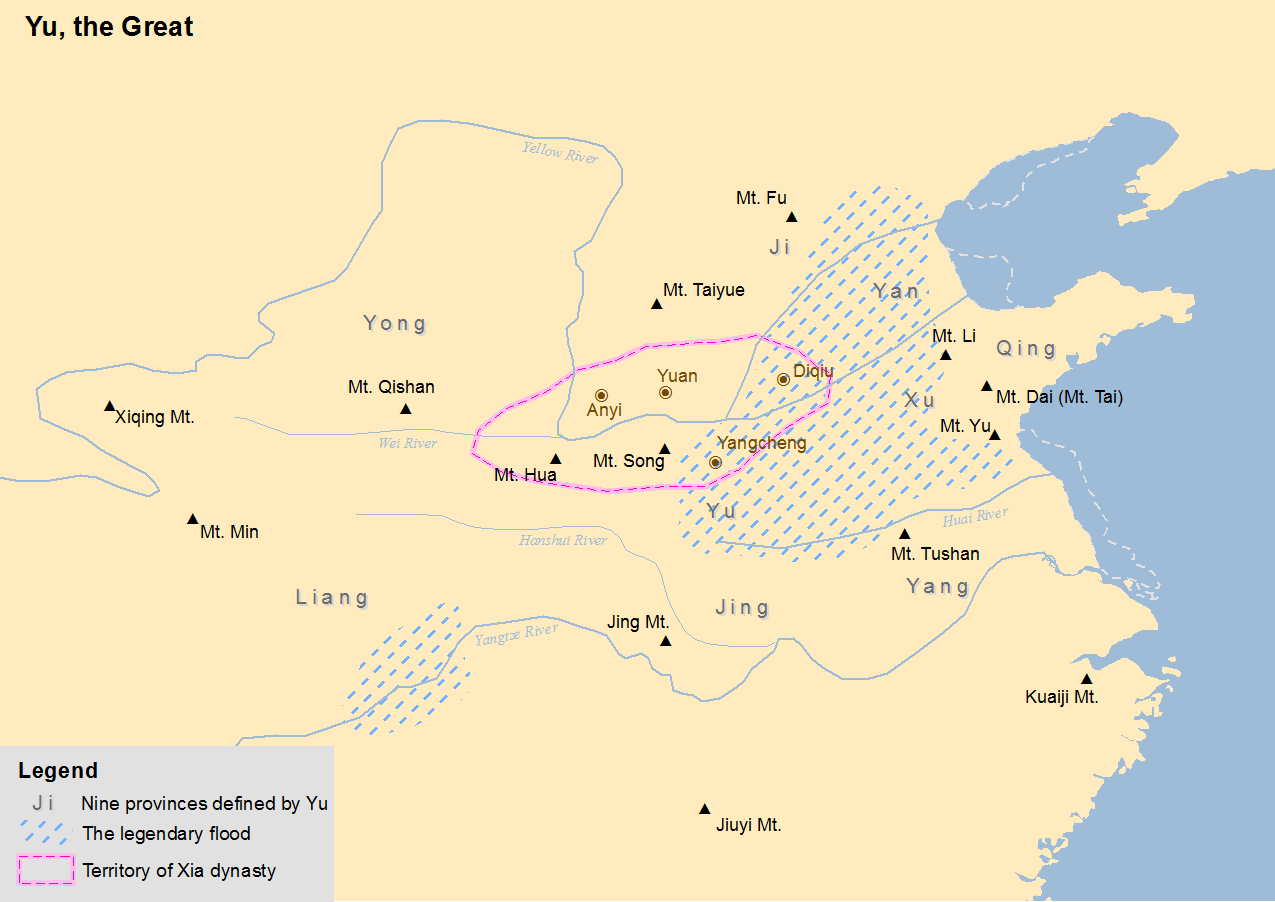
Great Flood (China)
The Great Flood of Gun-Yu (), also known as the Gun-Yu myth, was a major flood in ancient China that allegedly continued for at least two generations, which resulted in great population displacements among other disasters, such as storms and famine. People left their homes to live on the high hills and mounts, or nest on the trees. According to mythological and historical sources, it is traditionally dated to the third millennium BCE, or about 2300-2200 BCE, during the reign of Emperor Yao. However, archaeological evidence of an outburst flood at Jishi Gore on the Yellow River, comparable to similar severe events in the world in the past 10,000 years, has been dated to about 1920 BCE (a few centuries later than the traditional beginning of the Xia dynasty which came after Emperors Shun and Yao), and is suggested to have been the basis for the myth. Treated either historically or mythologically, the story of the Great Flood and the heroic attempts of the various human charact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fuxi
Fuxi or Fu Hsi (伏羲 ~ 伏犧 ~ 伏戲) is a culture hero in Chinese legend and mythology, credited along with his sister and wife Nüwa with creating humanity and the invention of music, hunting, fishing, domestication, and cooking as well as the Cangjie system of writing Chinese characters around 2,000BC. Fuxi was counted as the first of the Three Sovereigns at the beginning of the Chinese dynastic period. Origin Pangu was said to be the creation god in Chinese mythology. He was a giant sleeping within an egg of chaos. As he awoke, he stood up and divided the sky and the earth. Pangu then died after standing up, and his body turned into rivers, mountains, plants, animals, and everything else in the world, among which is a powerful being known as Huaxu (華胥). Huaxu gave birth to a twin brother and sister, Fuxi and Nüwa. Fuxi and Nüwa are said to be creatures that have faces of human and bodies of snakes. Fuxi was known as the "original god", and he was said to have be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |