|
Fiscal Policy
In economics and political science, fiscal policy is the use of government revenue collection ( taxes or tax cuts) and expenditure to influence a country's economy. The use of government revenue expenditures to influence macroeconomic variables developed in reaction to the Great Depression of the 1930s, when the previous laissez-faire approach to economic management became unworkable. Fiscal policy is based on the theories of the British economist John Maynard Keynes, whose Keynesian economics theorised that government changes in the levels of taxation and government spending influence aggregate demand and the level of economic activity. Fiscal and monetary policy are the key strategies used by a country's government and central bank to advance its economic objectives. The combination of these policies enables these authorities to target inflation (which is considered "healthy" at the level in the range 2%–3%) and to increase employment. Additionally, it is designed to try t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economics
Economics () is the social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyzes what's viewed as basic elements in the economy, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyzes the economy as a system where production, consumption, saving, and investment interact, and factors affecting it: employment of the resources of labour, capital, and land, currency inflation, economic growth, and public policies that have impact on these elements. Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, describing "what is", and normative economics, advocating "what ought to be"; between economic theory and applied economics; between ratio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Income Distribution
In economics, income distribution covers how a country's total GDP is distributed amongst its population. Economic theory and economic policy have long seen income and its distribution as a central concern. Unequal distribution of income causes economic inequality which is a concern in almost all countries around the world. Classical economists such as Adam Smith (1723–1790), Thomas Malthus (1766–1834), and David Ricardo (1772–1823) concentrated their attention on factor income-distribution, that is, the distribution of income between the primary factors of production (land, labour and capital). Modern economists have also addressed issues of income distribution, but have focused more on the distribution of income across individuals and households. Important theoretical and policy concerns include the balance between income inequality and economic growth, and their often inverse relationship. The Lorenz curve can represent the distribution of income within a society ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
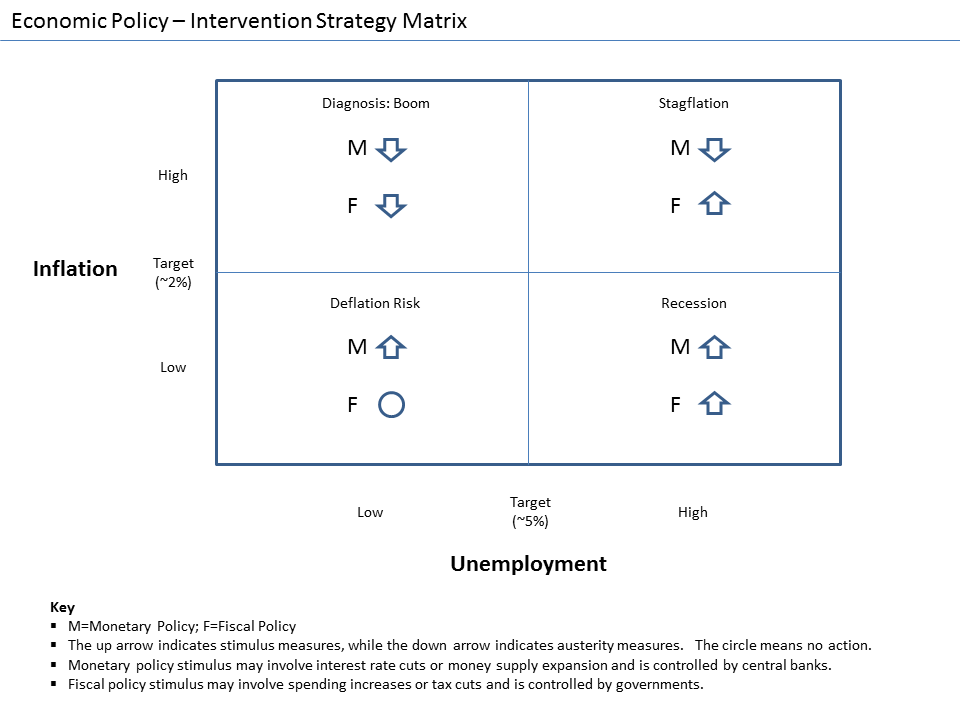
Recession
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction when there is a general decline in economic activity. Recessions generally occur when there is a widespread drop in spending (an adverse demand shock). This may be triggered by various events, such as a financial crisis, an external trade shock, an adverse supply shock, the bursting of an economic bubble, or a large-scale anthropogenic or natural disaster (e.g. a pandemic). In the United States, a recession is defined as "a significant decline in economic activity spread across the market, lasting more than a few months, normally visible in real GDP, real income, employment, industrial production, and wholesale-retail sales." The European Union has adopted a similar definition. In the United Kingdom, a recession is defined as negative economic growth for two consecutive quarters. Governments usually respond to recessions by adopting expansionary macroeconomic policies, such as increasing money supply and decreasing int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taylor & Francis
Taylor & Francis Group is an international company originating in England that publishes books and academic journals. Its parts include Taylor & Francis, Routledge, F1000 Research or Dovepress. It is a division of Informa plc, a United Kingdom–based publisher and conference company. Overview The company was founded in 1852 when William Francis joined Richard Taylor in his publishing business. Taylor had founded his company in 1798. Their subjects covered agriculture, chemistry, education, engineering, geography, law, mathematics, medicine, and social sciences. Francis's son, Richard Taunton Francis (1883–1930), was sole partner in the firm from 1917 to 1930. In 1965, Taylor & Francis launched Wykeham Publications and began book publishing. T&F acquired Hemisphere Publishing in 1988, and the company was renamed Taylor & Francis Group to reflect the growing number of imprints. Taylor & Francis left the printing business in 1990, to concentrate on publishing. In 1998 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Journal Of Economic Education
''The Journal of Economic Education'' (''JEE'') offers original peer-reviewed articles on teaching economics. The inaugural issue appeared in the fall of 1969. At the time, G.L. Bach ( Stanford University) wrote in the ''American Economic Review Papers and Proceedings'' (1971) that the ''JEE'' was to be the forum for scholarly work in economic education, primarily at the undergraduate level in colleges and universities, but including junior colleges and, to some extent, the high schools. In the early days, the Council for Economic Education (then call the Joint Council and later the National Council) oversaw publication of the ''JEE'', and members of the American Economic Association Committee on Economic Education served as the editorial board, with Henry Villard (City University of New York) serving as editor. The Council for Economic Education assigned the ''JEE'' copyright and publishing responsibility to the nonprofit Heldref Publications in 1981. The Council, however, re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discretionary Policy
In macroeconomics, discretionary policy is an economic policy based on the ''ad hoc'' judgment of policymakers as opposed to policy set by predetermined rules. For instance, a central banker could make decisions on interest rates on a case-by-case basis instead of allowing a set rule, such as Friedman's k-percent rule, an inflation target following the Taylor rule, or a nominal income target to determine interest rates or the money supply. In practice, most policy actions are discretionary in nature. "Discretionary policy" can refer to decision making in both monetary policy and fiscal policy. The opposite is a ''commitment policy''. Arguments against Monetarist economists in particular have been opponents of the use of discretionary policy. According to Milton Friedman, the dynamics of change associated with the passage of time presents a timing problem for public policy. The reason this poses a problem is because a long and variable time lag exists between: # the need for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve System (often shortened to the Federal Reserve, or simply the Fed) is the central banking system of the United States of America. It was created on December 23, 1913, with the enactment of the Federal Reserve Act, after a series of financial panics (particularly the panic of 1907) led to the desire for central control of the monetary system in order to alleviate financial crises. Over the years, events such as the Great Depression in the 1930s and the Great Recession during the 2000s have led to the expansion of the roles and responsibilities of the Federal Reserve System. U.S. Congress, Congress established three key objectives for monetary policy in the Federal Reserve Act: maximizing employment, stabilizing prices, and moderating long-term interest rates. The first two objectives are sometimes referred to as the Federal Reserve's dual mandate. Its duties have expanded over the years, and currently also include supervising and bank regulation, regulating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procyclical And Countercyclical Variables
Procyclical and countercyclical variables are variables that fluctuate in a way that is positively or negatively correlated with business cycle fluctuations in gross domestic product (GDP). The scope of the concept may differ between the context of macroeconomic theory and that of economic policy–making. The concept is often encountered in the context of a government's approach to spending and taxation. A 'procyclical fiscal policy' can be summarised simply as governments choosing to increase government spending and reduce taxes during an economic expansion, but reduce spending and increase taxes during a recession. A 'countercyclical' fiscal policy takes the opposite approach: reducing spending and raising taxes during a boom period, and increasing spending and cutting taxes during a recession. Business cycle theory Procyclical In business cycle theory and finance, any economic quantity that is positively correlated with the overall state of the economy is said to be procyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full Employment
Full employment is a situation in which there is no cyclical or deficient-demand unemployment. Full employment does not entail the disappearance of all unemployment, as other kinds of unemployment, namely structural and frictional, may remain. For instance, workers who are "between jobs" for short periods of time as they search for better employment are not counted against full employment, as such unemployment is frictional rather than cyclical. An economy with full employment might also have unemployment or underemployment where part-time workers cannot find jobs appropriate to their skill level, as such unemployment is considered structural rather than cyclical. Full employment marks the point past which expansionary fiscal and/or monetary policy cannot reduce unemployment any further without causing inflation. Some economists define full employment somewhat differently, as the unemployment rate at which inflation does not continuously increase. Advocacy of avoiding accelerating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stimulus (economics)
In economics, stimulus refers to attempts to use monetary policy or fiscal policy (or stabilization policy in general) to stimulate the economy. Stimulus can also refer to monetary policies such as lowering interest rates and quantitative easing. A stimulus is sometimes colloquially referred to as "priming the pump" or "pump priming". Concept During a recession, production and employment are far below their sustainable potential due to lack of demand. It is hoped that increasing demand will stimulate growth and that any adverse side effects from stimulus will be mild. Fiscal stimulus refers to increasing government consumption or transfers or lowering taxes, increasing the rate of growth of public debt. Supporters of Keynesian economics assume the stimulus will cause sufficient economic growth to fill that gap partially or completely via the multiplier effect. Monetary stimulus refers to lowering interest rates, quantitative easing, or other ways of increasing the amount o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Economic Association
The American Economic Association (AEA) is a learned society in the field of economics. It publishes several peer-reviewed journals acknowledged in business and academia. There are some 23,000 members. History and Constitution The AEA was established in 1885 in Saratoga Springs, New York by younger progressive economists trained in the German historical school, including Richard T. Ely, Edwin Robert Anderson Seligman and Katharine Coman, the only woman co-founder; since 1900 it has been under the control of academics. The purposes of the Association are: 1) The encouragement of economic research, especially the historical and statistical study of the actual conditions of industrial life; 2) The issue of publications on economic subjects; 3) The encouragement of perfect freedom of economic discussion. The Association as such will take no partisan attitude, nor will it commit its members to any position on practical economic questions. The Association publishes one of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquidity Trap
A liquidity trap is a situation, described in Keynesian economics, in which, "after the rate of interest has fallen to a certain level, liquidity preference may become virtually absolute in the sense that almost everyone prefers holding cash rather than holding a debt (financial instrument) which yields so low a rate of interest." Keynes, John Maynard (1936) '' The General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money'', United Kingdom: Palgrave Macmillan, 2007 edition, A liquidity trap is caused when people hoard cash because they expect an adverse event such as deflation, insufficient aggregate demand, or war. Among the characteristics of a liquidity trap are interest rates that are close to zero and changes in the money supply that fail to translate into changes in the price level. Krugman, Paul R. (1998)"It's baack: Japan's Slump and the Return of the Liquidity Trap," Brookings Papers on Economic Activity Origin and definition of the term John Maynard Keynes, in his 1936 '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)