|
Fiscal Illusion
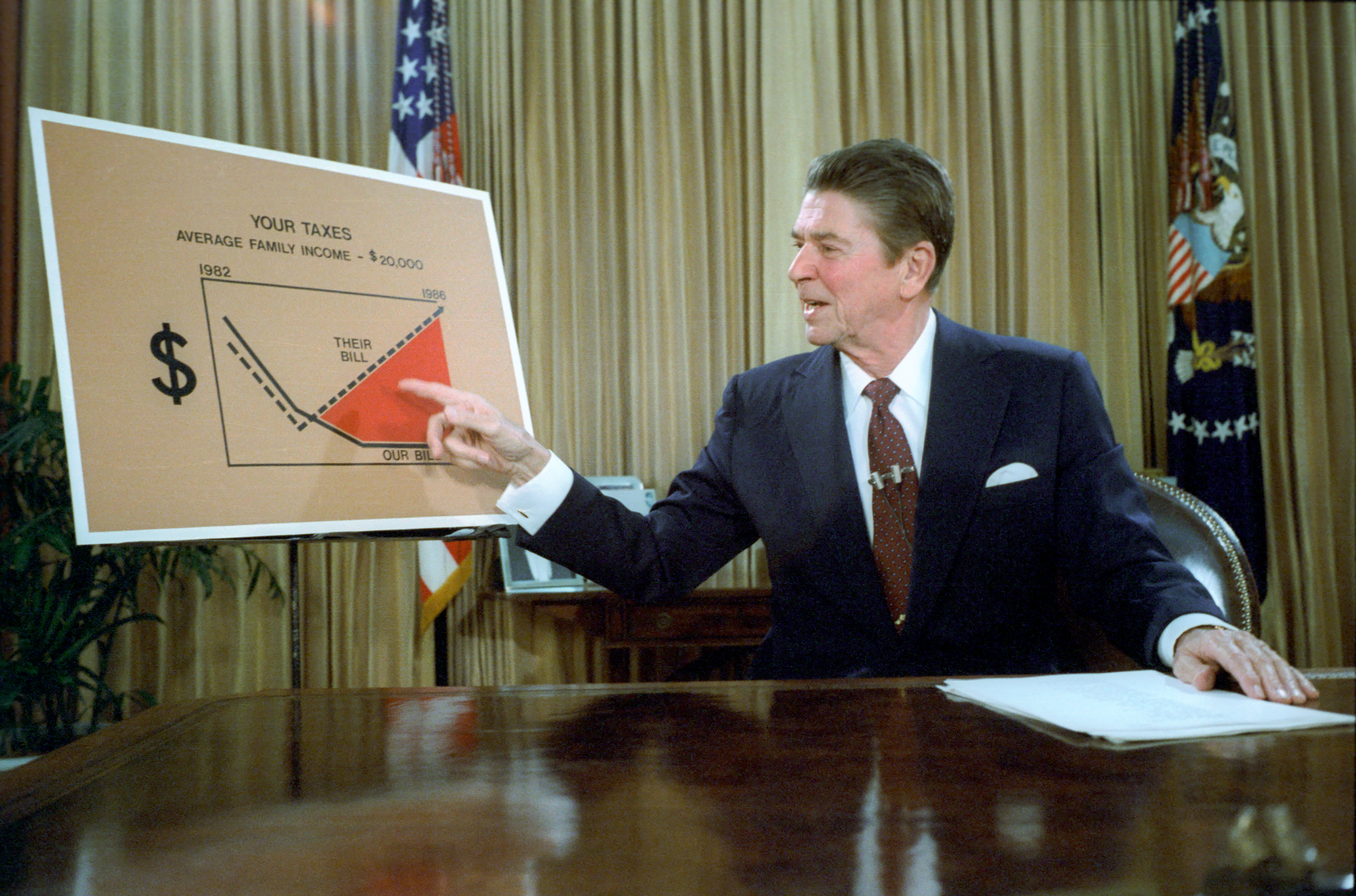
In public choice theory, fiscal illusion is a failure to accurately perceive the amount of government expenditure. The theory of fiscal illusion was first developed by the Italian economist Amilcare Puviani in his 1903 book ''Teoria della illusione finanziaria'' (''Theory of Financial Illusion'' (not yet translated into English, but translated into German in 1960 under the title ''Die Illusionen in der öffentlichen Finanzwirtschaft'', Berlin: Duncker & Humblot, 1960)). Fiscal illusion occurs when government revenues are not completely transparent or are not fully perceived by taxpayers; then the cost of government is seen to be less than it actually is. Since some or all taxpayers benefit from government expenditures from these unobserved or hidden revenues, the public's appetite for government expenditures increases, thus providing politicians incentive to expand the size of government. Overview Fiscal illusion has been used to explain the flypaper effect often seen when a hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Public Choice
Public choice, or public choice theory, is "the use of economic tools to deal with traditional problems of political science".Gordon Tullock, The New Palgrave: A Dictionary of Economics, [1987] 2008, "public choice," ''The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics''. . Its content includes the study of political behavior. In political science, it is the subset of positive political theory that studies self-interested Agent (economics), agents (voters, politicians, bureaucrats) and their interactions, which can be represented in a number of ways – using (for example) standard constrained utility maximization, game theory, or decision theory. It is the origin and intellectual foundation of contemporary work in political economy.Alberto Alesina, Torsten Persson, Guido Tabellini, 2006. “Reply to Blankart and Koester's Political Economics versus Public Choice Two Views of Political Economy in Competition,” Kyklos, 59(2), pp. 201–208 In popular use, "public choice" is often used as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Expenditure
Public expenditure is spending made by the government of a country on collective needs and wants, such as pension, provisions, security, infrastructure, etc. Until the 19th century, public expenditure was limited as laissez faire philosophies believed that money left in private hands could bring better returns. In the 20th century, John Maynard Keynes argued the role of public expenditure in determining levels of income and distribution in the economy. Since then, government expenditures has shown an increasing trend. Sources of government revenue include taxes, and non-tax revenues. In the 17th and the 18th centuries, public expenditure was considered a wastage of money. Thinkers believed government should stay with their traditional functions of spending on defense and maintaining law and order. Theories of public expenditure Several theories of taxation exist in public economics. Governments at all levels (national, regional and local) need to raise revenue from a variety ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amilcare Puviani
__NOTOC__ Hamilcar ( xpu, 𐤇𐤌𐤋𐤊 , ,. or , , " Melqart is Gracious"; grc-gre, Ἁμίλκας, ''Hamílkas'';) was a common Carthaginian masculine given name. The name was particularly common among the ruling families of ancient Carthage. People named Hamilcar include: * Hamilcar the Magonid, "King" of Carthage, led the Carthaginian forces at the Battle of Himera in 480BC during the First Sicilian War * Hamilcar, a general against Timoleon of Syracuse * Hamilcar, a brother of Gisco, possibly brother of Hanno II, with whom he was executed in the middle of the 4th centuryBC * Hamilcar the Rhodian, possibly a Carthaginian spy in the entourage of Alexander the Great, executed when returning to Carthage. * Hamilcar, son of Gisgo and grandson of Hanno the Great, led a campaign against Agathocles of Syracuse during the Third Sicilian War. He defeated Agathocles in the Battle of the Himera River in 311 BC. He was captured during the Siege of Syracuse and then killed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flypaper Effect
The flypaper effect is a concept from the field of public finance that suggests that a government grant to a recipient municipality increases the level of local public spending more than an increase in local income of an equivalent size. When a dollar of exogenous grants to a community leads to significantly greater public spending than an equivalent dollar of citizen income: money sticks where it hits, like a fly to flypaper. Grants to the government will stay in the hands of the government and income to individuals will stay with these individuals. Founding The concept was first described in a metaphorical way by Arthur Okun in response to the research of his colleague Edward Gramlich, which was published in 1979 as ''The Stimulative Effects of Intergovernmental Grants''. Gramlich, together with Courant and Rubinfeld, sought an explanation for the phenomenon that nonmatching grants stimulate much more local spending per dollar of grant than does income going to private citizens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deficit Spending
Within the budgetary process, deficit spending is the amount by which spending exceeds revenue over a particular period of time, also called simply deficit, or budget deficit; the opposite of budget surplus. The term may be applied to the budget of a government, private company, or individual. Government deficit spending was first identified as a necessary economic tool by John Maynard Keynes in the wake of the Great Depression. It is a central point of controversy in economics, as discussed below. Controversy Government deficit spending is a central point of controversy in economics, with prominent economists holding differing views. The mainstream economics position is that deficit spending is desirable and necessary as part of countercyclical fiscal policy, but that there should not be a structural deficit (i.e., permanent deficit): The government should run deficits during recessions to compensate for the shortfall in aggregate demand, but should run surpluses in boom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CATO Institute
The Cato Institute is an American libertarian think tank headquartered in Washington, D.C. It was founded in 1977 by Ed Crane, Murray Rothbard, and Charles Koch, chairman of the board and chief executive officer of Koch Industries.Koch Industries is the second largest privately held company by revenue in the United States. Cato was established to have a focus on public advocacy, media exposure and societal influence. According to the ''2020 Global Go To Think Tank Index Report'' (Think Tanks and Civil Societies Program, University of Pennsylvania), Cato is number 27 in the "Top Think Tanks Worldwide" and number 13 in the "Top Think Tanks in the United States". The Cato Institute is libertarian in its political philosophy, and advocates a limited role for government in domestic and foreign affairs as well as a strong protection of civil liberties. This includes support for lowering or abolishing most taxes, opposition to the Federal Reserve system and the Affordable Care Act, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Niskanen
William Arthur Niskanen (; March 13, 1933 – October 26, 2011) was an American economist. He was one of the architects of President Ronald Reagan's economic program and contributed to public choice theory. He was also a long-time chairman of the Cato Institute, a libertarian think-tank. Early life and education Niskanen was born and raised in Bend, Oregon. He received his B.A. from Harvard University in 1954. He pursued graduate study of economics at the University of Chicago, where his teachers included Milton Friedman and other prominent economists who were then revolutionizing economics, public policy, and law with ideas that would come to be known as the Chicago school of economics. Niskanen received his M.A. in 1955 and his doctorate in 1962, writing his dissertation on the economics of alcoholic beverage sales.T. Rees Shapiro. "William A. Niskanen Jr., economist and former Cato Institute chairman, dies." ''Washington Post''. November 1, 2011. https://www.washingtonpost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Starve The Beast
"Starve the beast" is a political strategy employed by American conservatives to limit government spending by cutting taxes, to deprive the federal government of revenue in a deliberate effort to force it to reduce spending. The term "the beast", in this context, refers to the United States federal government and the programs it funds, using mainly American taxpayer dollars, particularly social programs such as education, welfare, Social Security, Medicare, and Medicaid. On July 14, 1978, economist and future Federal Reserve chairman Alan Greenspan testified to the Senate Finance Committee: "Let us remember that the basic purpose of any tax cut program in today's environment is to reduce the momentum of expenditure growth by restraining the amount of revenue available and trust that there is a political limit to deficit spending." Before his election as President, then-candidate Ronald Reagan foreshadowed the strategy during the 1980 US Presidential debates, saying "John An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empirical
Empirical evidence for a proposition is evidence, i.e. what supports or counters this proposition, that is constituted by or accessible to sense experience or experimental procedure. Empirical evidence is of central importance to the sciences and plays a role in various other fields, like epistemology and law. There is no general agreement on how the terms ''evidence'' and ''empirical'' are to be defined. Often different fields work with quite different conceptions. In epistemology, evidence is what justifies beliefs or what determines whether holding a certain belief is rational. This is only possible if the evidence is possessed by the person, which has prompted various epistemologists to conceive evidence as private mental states like experiences or other beliefs. In philosophy of science, on the other hand, evidence is understood as that which ''Scientific method#Confirmation, confirms'' or ''disconfirms'' Hypothesis#Scientific hypothesis, scientific hypotheses and arbitrates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
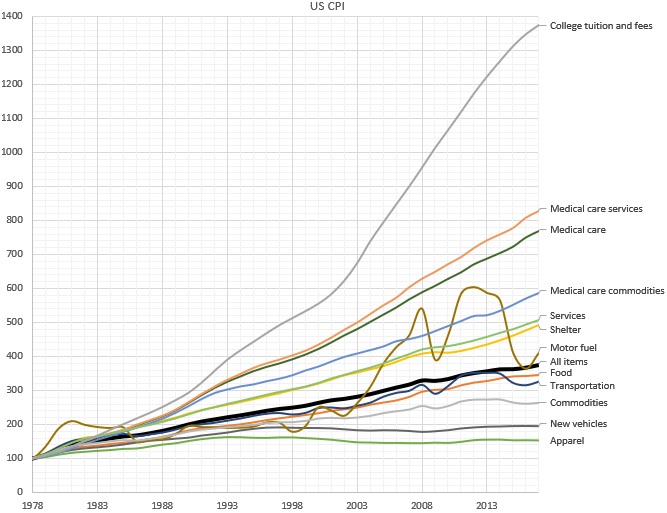
Baumol's Cost Disease
Baumol's cost disease, also known as the Baumol effect, is the rise of wages in jobs that have experienced little or no increase in labor productivity, in response to rising salaries in other jobs that have experienced higher productivity growth. The phenomenon was described by William J. Baumol and William G. Bowen in the 1960s and is an example of cross elasticity of demand. The rise of wages in jobs without productivity gains derives from the requirement to compete for workers with jobs that have experienced productivity gains and so can naturally pay higher salaries, just as classical economics predicts. For instance, if the retail sector pays its managers 19th-century-style wages, retail managers may decide to quit to get jobs in the automobile sector, where wages are higher because of higher labor productivity. Thus, retail managers' salaries increase not due to labor productivity increases in the retail sector but due to productivity and corresponding wage increases in oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Money Illusion
In economics, money illusion, or price illusion, is a cognitive bias where money is thought of in nominal, rather than real terms. In other words, the face value (nominal value) of money is mistaken for its purchasing power (real value) at a previous point in time. Viewing purchasing power as measured by the nominal value is false, as modern fiat currencies have no intrinsic value and their real value depends purely on the price level. The term was coined by Irving Fisher in ''Stabilizing the Dollar''. It was popularized by John Maynard Keynes in the early twentieth century, and Irving Fisher wrote an important book on the subject, ''The Money Illusion'', in 1928. The existence of money illusion is disputed by monetary economists who contend that people act rationally (i.e. think in real prices) with regard to their wealth. Eldar Shafir, Peter A. Diamond, and Amos Tversky (1997) have provided empirical evidence for the existence of the effect and it has been shown to affect beha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyler Cowen
Tyler Cowen (; born January 21, 1962) is an American economist, columnist and blogger. He is a professor at George Mason University, where he holds the Holbert L. Harris chair in the economics department. He hosts the economics blog ''Marginal Revolution'', together with co-author Alex Tabarrok. Cowen and Tabarrok also maintain the website Marginal Revolution University, a venture in online education. Cowen writes the "Economic Scene" column for ''The New York Times'' and since July 2016 has been a regular opinion columnist at ''Bloomberg Opinion''. He also writes for such publications as ''The New Republic'', ''The Wall Street Journal'', ''Forbes'', ''Newsweek'' and the ''Wilson Quarterly''. He serves as general director of George Mason's Mercatus Center, a university research center that focuses on the market economy. Since 2015, he has hosted the podcast ''Conversations with Tyler''. In September, 2018, Tyler and his team at George Mason University launched Emergent Ventures, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |