|
First Schools' War
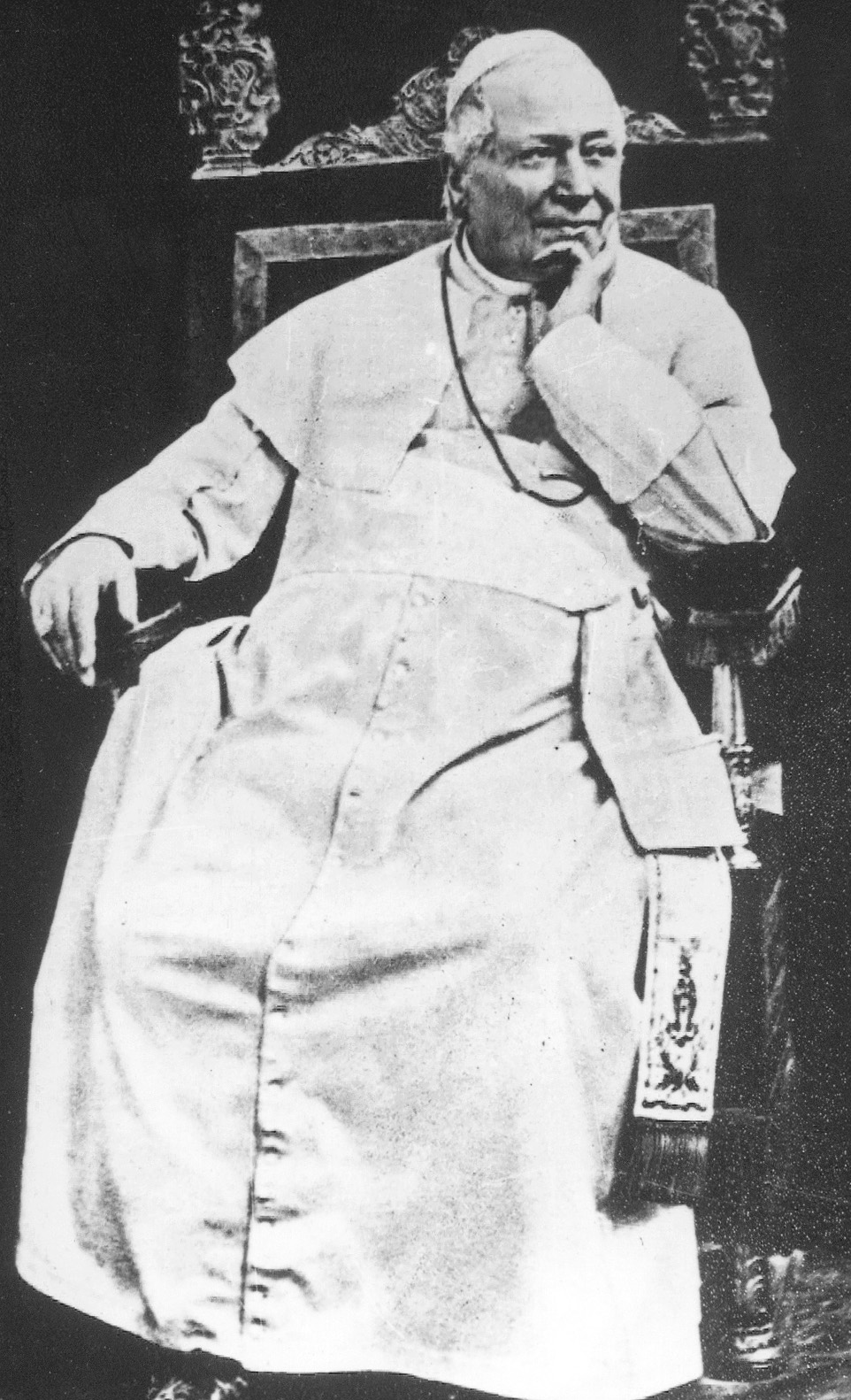
The First School War (french: Première guerre scolaire, nl, Eerste schoolstrijd) was a political crisis in Belgium over the issue of religion in education. The School War marks the high water mark of the conflict between the conservative Catholic Party, and the secular Liberal Party. The war lasted from 1879 to 1884 and resulted in a period of nearly fifty years of Catholic political dominance. It was followed by a Second School War between 1950 and 1959. Background In the preceding centuries, education in Belgium had been dominated by the Catholic Church. In 1842, a new education law formalized religious education in primary schools, while also conceding the freedom of education guaranteed in Article 17 of the Constitution of 1831: Under the terms of Article 6 of the Education Act of 1842: In practice, the interpretation of the law varied and, since the vast majority of the Belgian population was Catholic, the Church was allowed considerable influence in schools. The quali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schoolstrijd (Belgium, 1950s)
{{Disambig ...
School struggle can refer to: * School struggle (Netherlands) (19th and 20th century) * First School War (Belgium, 1880s) * Second School War The Second School War (french: Deuxième guerre scolaire, nl, Tweede schoolstrijd) was a political crisis in Belgium over the issue of religion in education. The conflict lasted between 1950 and 1959 and was ended by a cross-party agreement, know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
19th Century In Belgium
19 (nineteen) is the natural number following 18 and preceding 20. It is a prime number. Mathematics 19 is the eighth prime number, and forms a sexy prime with 13, a twin prime with 17, and a cousin prime with 23. It is the third full reptend prime, the fifth central trinomial coefficient, and the seventh Mersenne prime exponent. It is also the second Keith number, and more specifically the first Keith prime. * 19 is the maximum number of fourth powers needed to sum up to any natural number, and in the context of Waring's problem, 19 is the fourth value of g(k). * The sum of the squares of the first 19 primes is divisible by 19. *19 is the sixth Heegner number. 67 and 163, respectively the 19th and 38th prime numbers, are the two largest Heegner numbers, of nine total. * 19 is the third centered triangular number as well as the third centered hexagonal number. : The 19th triangular number is 190, equivalently the sum of the first 19 non-zero integers, that is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1879 In Belgium
The following lists events that happened during 1879 in the Kingdom of Belgium. Incumbents *Monarch: Leopold II *Prime Minister: Walthère Frère-Orban Events * 2 March – Castle in Tervuren burns down. * 17 April – Firedamp explosion at Agrappe Mine in Frameries. * 1 July – Law secularising primary education passes, triggering First School War Publications ;Periodicals * ''Almanach de Poche de Bruxelles'' (Brussels, H. Manceaux) * ''Bulletin de la Société belge de géographie'', 3 (Brussels, Secrétariat de la Société Belge de Géographie) ;Books * Hendrik Conscience, ''Het wassen beeld'' * Léon Vanderkindere, ''Le siècle des Artevelde: études sur la civilisation morale & politique de la Flandre & du Brabant'' (Brussels, A.-N. Lebègue). Art and architecture * Leuven railway station rebuilt Births * 5 February – Jules De Bisschop, Olympic rower (died 1954) * 15 February – Camille Van Hoorden, footballer (died 1919) * 28 April – Edgard Tytgat, paint ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secularism In Belgium
Religion in Belgium is diversified, with Christianity, in particular, the Catholic Church, representing the largest community, though it has experienced a significant decline since the 1960s (when it was the nominal religion of over 80% of the population). Belgium's policy separates the state from the churches, and freedom of religion of the citizens is guaranteed by the country's constitution. According to the Eurobarometer poll carried out by the European Commission in December 2018, the share of Christians increased by 10% points from 52.5% in 2009 to 62.8% in 9 years, with Catholicism being the largest denomination at 57.1%. Protestants comprised 2.3% and Orthodox Christians comprised 0.6%. Non-religious people comprised 29.3% of the population and were divided between those who primarily identified as atheists (9.1%) or as agnostics (20.2%). A further 6.8% of the population was Muslim and 1.1% were believers in other religions. On the other hand, the following Eurobaro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Education In Belgium
Education in Belgium is regulated and for the most part financed by one of the three communities: Flemish, French and German-speaking. Each community has its own school system, with small differences among them. The federal government plays a very small role: it decides directly the age for mandatory schooling and indirectly the financing of the communities. The schools can be divided in three groups ( nl, netten; french: réseaux): # Schools owned by the communities (''GO! Onderwijs van de Vlaamse gemeenschap''; ''Wallonie-Bruxelles Enseignement'') # Subsidized public schools (''officieel gesubsidieerd onderwijs''; ''réseau officiel subventionné''), organized by provinces, municipalities or the Brussels French Community Commission # Subsidized free schools (''vrij gesubsidieerd onderwijs''; ''réseau libre subventionné''), mainly organized by an organization affiliated to the Catholic church The latter is the largest group, both in number of schools and in number of pupils. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political History Of Belgium
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with Decision-making, making decisions in Social group, groups, or other forms of Power (social and political), power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or Social status, status. The branch of social science that studies politics and government is referred to as political science. It may be used positively in the context of a "political solution" which is compromising and nonviolent, or descriptively as "the art or science of government", but also often carries a negative connotation.. The concept has been defined in various ways, and different approaches have fundamentally differing views on whether it should be used extensively or limitedly, empirically or normatively, and on whether conflict or co-operation is more essential to it. A variety of methods are deployed in politics, which include promoting one's own political views among people, negotiation with other political subje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Education In Belgium
Education in Belgium is regulated and for the most part financed by one of the three communities: Flemish, French and German-speaking. Each community has its own school system, with small differences among them. The federal government plays a very small role: it decides directly the age for mandatory schooling and indirectly the financing of the communities. The schools can be divided in three groups ( nl, netten; french: réseaux): # Schools owned by the communities (''GO! Onderwijs van de Vlaamse gemeenschap''; ''Wallonie-Bruxelles Enseignement'') # Subsidized public schools (''officieel gesubsidieerd onderwijs''; ''réseau officiel subventionné''), organized by provinces, municipalities or the Brussels French Community Commission # Subsidized free schools (''vrij gesubsidieerd onderwijs''; ''réseau libre subventionné''), mainly organized by an organization affiliated to the Catholic church The latter is the largest group, both in number of schools and in number of pupils. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kulturkampf
(, 'culture struggle') was the conflict that took place from 1872 to 1878 between the Catholic Church led by Pope Pius IX and the government of Prussia led by Otto von Bismarck. The main issues were clerical control of education and ecclesiastical appointments. A unique feature of , compared to other struggles between the state and the Catholic Church in other countries, was Prussia's anti-Polish component. By extension the term is sometimes used to describe any conflict between secular and religious authorities or deeply opposing values, beliefs between sizable factions within a nation, community, or other group. Background Europe and the Catholic Church Under the influence of new emerging philosophies and ideologies, such as the enlightenment, realism, positivism, materialism, nationalism, secularism, and liberalism, the role of religion in society and the relationship between society and established churches underwent profound changes in the 18th and 19th centuries. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jules Ferry Laws
The Jules Ferry Laws are a set of French laws which established free education in 1881, then mandatory and ''laic'' (secular) education in 1882. Jules Ferry, a lawyer holding the office of Minister of Public Instruction in the 1880s, is widely credited for creating the modern Republican school (''l'école républicaine''). The dual system of state and church schools that were largely staffed by religious officials was replaced by state schools and lay school teachers. The educational reforms enacted by Jules Ferry are often attributed to a broader anti-clerical campaign in France. History French education during the 19th century was marked by two distinct and segregated systems, the first being a secondary school system and the second a primary school system. However, in each of these systems, the Catholic Church provided an alternative to secular schooling that was often the only option for families in economically depressed regions of France. Although the Republican party is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholicism In Belgium
The Catholic Church in Belgium, part of the global Catholic Church in Belgium, is under the spiritual leadership of the Pope, the curia in Rome and the Episcopal Conference of Bishops. Dioceses There are eight dioceses, including one archdiocese, seat of the archiepiscopal residence and St. Rumbolds Cathedral, located in the old Flemish city of Mechelen (Malines in French). The Belgian church also oversees the Basilica of the Sacred Heart, the National Basilica of Belgium. In 2009, Cardinal André-Mutien Léonard was appointed new archbishop of Mecheln-Brussels and thus Belgium's new primate, but only after the 450th anniversary celebration of the Mechelen-Brussels archdiocese and the canonisation of Fr. Damien De Veuster of Molokai. Both events were led by Cardinal Godfried Danneels, his predecessor as Archbishop and Primate between 1979 and 2010. Before his appointment, Léonard was Bishop of Namur. Since 2015, the Archbishop of Mechelen-Brussels and primate of all Belgi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Social Teaching
Catholic social teaching, commonly abbreviated CST, is an area of Catholic doctrine concerning matters of human dignity and the common good in society. The ideas address oppression, the role of the state (polity), state, subsidiarity, social organization, concern for social justice, and issues of wealth distribution. Its foundations are widely considered to have been laid by Pope Leo XIII's 1891 encyclical, encyclical letter ''Rerum novarum'', which advocated economic distributism. Its roots can be traced to the writings of Catholic theologians such as St. Thomas Aquinas and St. Augustine of Hippo. It is also derived from concepts present in the Bible and cultures of the ancient Near East. According to Pope John Paul II, the foundation of social justice "rests on the threefold cornerstones of human dignity, solidarity and subsidiarity". According to Pope Benedict XVI, its purpose "is simply to help purify reason and to contribute, here and now, to the acknowledgment and attainm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)


