|
First Messenian War
The First Messenian War was a war between Messenia and Sparta. It began in 743 BC and ended in 724 BC, according to the dates given by Pausanias (geographer), Pausanias. The war continued the rivalry between the Achaeans (tribe), Achaeans and the Dorians that had been initiated by the purported Return of the Heracleidae. Both sides utilized an explosive incident to settle the rivalry by full-scale war. The war was prolonged into 20 years. The result was a Spartan victory. Messenia was depopulated by emigration of the Achaeans to other states. Those who did not emigrate were reduced socially to helots, or serfs. Their descendants were held in hereditary servitude for centuries until the Spartan state finally needed them for defense. Dates Pausanias' standard dates Pausanias (geographer), Pausanias says that the opening campaign was a surprise attack on Ampheia by a Spartan force commanded by Alcmenes, List of kings of Sparta#Agiad dynasty, Agiad king of Sparta, in the second yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messenian Wars
Messenian Wars refers to the wars between Messenia and Sparta in the 8th and 7th centuries BC as well as the 4th century BC. *First Messenian War *Second Messenian War *Third Messenian War The helots (; el, εἵλωτες, ''heílotes'') were a subjugated population that constituted a majority of the population of Laconia and Messenia – the territories ruled by Sparta. There has been controversy since antiquity as to their ex ... {{Authority control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
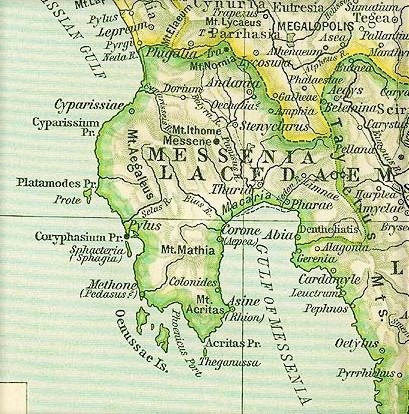
Koroni
Koroni or Corone ( el, Κορώνη) is a town and a former Communities and Municipalities of Greece, municipality in Messenia, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Pylos-Nestoras, of which it is a municipal unit. Known as ''Corone'' by the Republic of Venice, Venetians and Ottomans, the town of Koroni (pop. 1,397 in 2011) sits on the southwest peninsula of the Peloponnese on the Gulf of Messinia in southern Greece, by road southwest of Kalamata. The town is nestled on a hill below a Venetian castle and reaches to the edge of the gulf. The town was the seat of the former municipality of Koróni, which has a land area of and a population of 4,366 (2011 census). The municipal unit consists of the communities Akritochori, Charakopio, Chrysokellaria, Falanthi, Kaplani, Kompoi, Koroni, Vasilitsi, Vounaria and Iamia of Koroni, Iamia. It also includes the uninhabited island of Venétiko. History The town was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ithome
Mount Ithome (Greek: Ἰθώμη) or Ithomi, previously Vourkano(s) ( el, Βουρκάνο(ς)) or Voulcano(s) ( el, Βουλκάνο(ς)), is the northernmost of twin peaks in Messenia, Greece. Mount Ithome rises to about , about over Valyra, the seat of Ithomi, the former municipality. The other peak is Mount Eva ( el, Εύα), , connected to Mount Ithomi by a thin ridge long. Mount Ithome is north of Kalamata on the Gulf of Messenia, east of Pylos, seat of Bronze Age Messenia, and north of Messini, modern namesake of ancient Messene, nestled under the cliffs of Mount Ithome. From the top the whole valley of the Pamisos river can be viewed eastward to Mount Taygetus and southward to the Gulf of Messenia. The site is highly defensible and yet off the main road; in this case, the Kalamata-Pylos road. Etymology Ithome Like most ancient names the etymology of ''Ithome'' is not certain. It is also the name of a town in Thessaly, although Reece notes evidence that the one ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arcadia (ancient Region)
Arcadia ( el, Ἀρκαδία) is a region in the central Peloponnese. It takes its name from the mythological character Arcas, and in Greek mythology it was the home of the gods Hermes and Pan. In European Renaissance arts, Arcadia was celebrated as an unspoiled, harmonious wilderness; as such, it was referenced in popular culture. The modern regional unit of the same name more or less overlaps with the historical region, but is slightly larger. History Arcadia was gradually linked in a loose confederation that included all the Arcadian towns and was named League of the Arcadians. In the 7th century BC, it successfully faced the threat of Sparta and the Arcadians managed to maintain their independence. They participated in the Persian Wars alongside other Greeks by sending forces to Thermopylae and Plataea. During the Peloponnesian War, Arcadia allied with Sparta and Corinth. In the following years, during the period of the Hegemony of Thebes, the Theban general Epaminondas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merope (mythology)
Merope ( grc, Μερόπη) was a Queen of Messenia in Greek mythology, daughter of King Cypselus of Arcadia and wife of Cresphontes, the Heraclid king of Messenia. After the murder of her husband and her two older children by Polyphontes (another Heraclid), Merope was forced to marry the murderer, but she managed to save her youngest son Aepytus, whom she sent secretly to Aetolia. Several years later, when Aepytus grew up, he killed Polyphontes with the collaboration of Merope, and he took revenge for the murder of his relatives and the insult to his mother. Euripides' ''Cresphontes'' Euripides based his lost tragedy ''Cresphontes'' (, ''Kresphóntēs'') on this myth. According to Hyginus' description of the plot (''Fabulae'' 137), Merope's son (in this version also named Cresphontes), once grown, set in motion the plan to avenge his father's death by presenting himself ''incognito'' to Polyphontes as his own killer, claiming the price Polyphontes had put on his head. As the t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thera
Santorini ( el, Σαντορίνη, ), officially Thira (Greek language, Greek: Θήρα ) and classical Greek Thera (English language, English pronunciation ), is an island in the southern Aegean Sea, about 200 km (120 mi) southeast from the Greece, Greek mainland. It is the largest island of a small circular archipelago, which bears the Santorini caldera, same name and is the remnant of a caldera. It forms the southernmost member of the Cyclades group of islands, with an area of approximately 73 km2 (28 sq mi) and a 2011 census population of 15,550. The municipality of Santorini includes the inhabited islands of Santorini and Therasia, as well as the uninhabited islands of Nea Kameni, Palaia Kameni, Aspronisi and Christiana Island, Christiana. The total land area is 90.623 km2 (34.990 sq mi). Santorini is part of the Thira (regional unit), Thira regional unit. The island was the site of one of the largest volcanic eruptions in recorded h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurotas (river)
The Eurotas ( grc, Εὐρώτας) or Evrotas (modern Greek: ) is the main river of Laconia and one of the major rivers of the Peloponnese, in Greece. The river's springs are located just northwest of the border between Laconia and Arcadia (regional unit), Arcadia, at Skortsinos. The river is also fed by underwater springs at Pellana and by tributaries coursing down from Taygetos, Mt. Taygetos and Parnon, Mt. Parnon, which flank the Eurotas valley to the west and east, respectively. The river is long, flowing in a north-south direction and emptying into the Laconian Gulf. Its drainage basin is . Etymology The classical Eurotas was changed to Iri in the Middle Ages and only changed back to Eurotas in recent times. Eurotas, however, is not the most ancient name of the river. It does not appear in the works of Homer, which purport to recount the stories and geography of Mycenaean Greece. In that legendary time, the Dorians are not known to have been present in the Eurotas Valley. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mycenae
Mycenae ( ; grc, Μυκῆναι or , ''Mykē̂nai'' or ''Mykḗnē'') is an archaeological site near Mykines in Argolis, north-eastern Peloponnese, Greece. It is located about south-west of Athens; north of Argos; and south of Corinth. The site is inland from the Saronic Gulf and built upon a hill rising above sea level. In the second millennium BC, Mycenae was one of the major centres of Greek civilization, a military stronghold which dominated much of southern Greece, Crete, the Cyclades and parts of southwest Anatolia. The period of Greek history from about 1600 BC to about 1100 BC is called Mycenaean in reference to Mycenae. At its peak in 1350 BC, the citadel and lower town had a population of 30,000 and an area of 32 hectares. The first correct identification of Mycenae in modern literature was during a survey conducted by Francesco Grimani, commissioned by the Provveditore Generale of the Kingdom of the Morea in 1700, who used Pausanias's description of the Lio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neleides
Neleides or Nelides ( (Nηλείδης); also Neleiades (Νηληιάδης), Neleius, and in the plural Neleidae; grc-gre, Νηλεῖδαι) was a patronymic of ancient Greece derived from Neleus, son of the Greek god Poseidon, and was used to refer to his descendants. In literature, this name typically designated either Nestor, the son of Neleus, or Antilochus, his grandson.Herodotus, v. 65 One notable offshoot of this family line was the Alcmaeonidae The Alcmaeonidae or Alcmaeonids ( grc-gre, Ἀλκμαιωνίδαι ; Attic: ) were a wealthy and powerful noble family of ancient Athens, a branch of the Neleides who claimed descent from the mythological Alcmaeon, the great-grandson of Nes .... Notes References *{{SmithDGRBM Pylian characters in Greek mythology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristodemus
In Greek mythology, Aristodemus (Ancient Greek: Ἀριστόδημος) was one of the Heracleidae, son of Aristomachus and brother of Cresphontes and Temenus. He was a great-great-grandson of Heracles and helped lead the fifth and final attack on Mycenae in the Peloponnese. Aristodemus and his brothers complained to the oracle that its instructions had proved fatal to those who had followed them; the oracle had told Hyllas to attack through the narrow passage when the third fruit was ripe. They received the answer that by the "third fruit" the "third generation" was meant, and that the "narrow passage" was not the isthmus of Corinth, but the straits of Rhium. They accordingly built a fleet at Naupactus, but before they set sail, Aristodemus was struck by lightning (or shot by Apollo) and the fleet destroyed, because one of the Heraclidae had slain an Acarnanian soothsayer. His brothers were later able to conquer the Peloponnese. By his wife Argia, daughter of King Autesion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cresphontes
In Greek mythology, Cresphontes (; grc, Κρεσφόντης) was a son of Aristomachus, husband of Merope, father of Aepytus and brother of Temenus and Aristodemus. He was a great-great-grandson of Heracles and helped lead the fifth and final attack on Mycenae in the Peloponnesus. He became king of Messene. Cresphontes and his brothers complained to the oracle that its instructions had proved fatal to those who had followed them (the oracle had told Hyllus to attack through the narrow passage when the third fruit was ripe). They received the answer that by the "third fruit" the "third generation" was meant, and that the "narrow passage" was not the isthmus of Corinth, but the straits of Rhium. They accordingly built a fleet at Naupactus, but before they set sail, Aristodemus was struck by lightning (or shot by Apollo) and the fleet destroyed, because one of the Heraclidae had slain an Acarnanian soothsayer. The oracle, being again consulted by Temenus, bade him offer an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temenus
In Greek mythology, Temenus ( el, Τήμενος, ''Tḗmenos'') was a son of Aristomachus and brother of Cresphontes and Aristodemus. Temenus was a great-great-grandson of Heracles and helped lead the fifth and final attack on Mycenae in the Peloponnese. He became King of Argos. He was the father of Ceisus, Káranos, Phalces(who was said to be founder of SciyonPausaniasbr>2.6.7/ref>), Agraeus, and Hyrnetho. Káranos was the first king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia and founder of the royal Macedonian dynasty–the Temenid or Argead dynasty–which culminated in the sons of Alexander the Great five centuries later. Conquest of the Peloponnese Temenus and his brothers complained to the oracle that its instructions had proved fatal to those who had followed them (the oracle had told Hyllas to attack through the narrow passage when the third fruit was ripe). They received the answer that by the "third fruit" the "third generation" was meant, and that the " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)