|
Firoozbakht's Conjecture
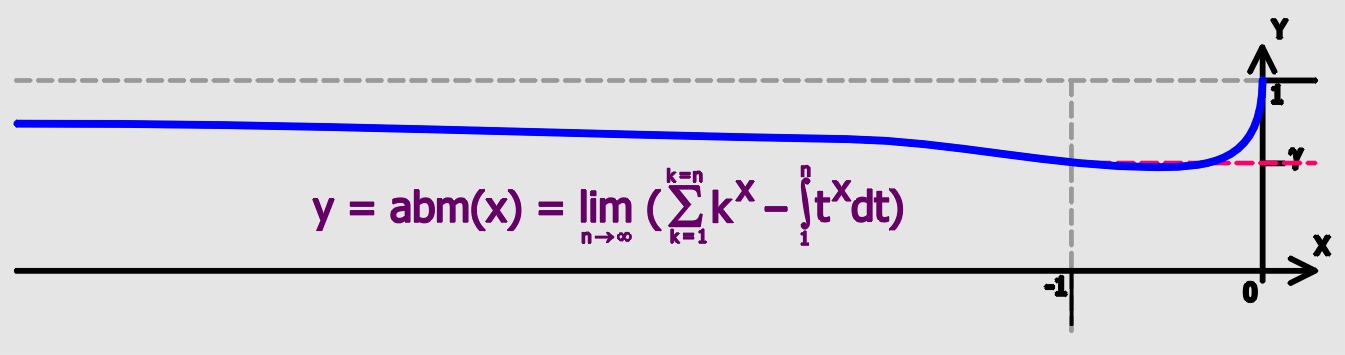
In number theory, Firoozbakht's conjecture (or the Firoozbakht conjecture) is a conjecture about the distribution of prime numbers. It is named after the Iranian mathematician Farideh Firoozbakht who stated it first in 1982. The conjecture states that p_^ (where p_n is the ''n''th prime) is a strictly decreasing function of ''n'', i.e., :\sqrt +10, where \gamma denotes the Euler–Mascheroni constant. Two related conjectures (see the comments of ) are :\left(\frac\right)^n < e, which is weaker, and : which is stronger. See also * * Andrica's conjecture * |
Wikipedia Primegaps
Wikipedia is a multilingual free online encyclopedia written and maintained by a community of volunteers, known as Wikipedians, through open collaboration and using a wiki-based editing system. Wikipedia is the largest and most-read reference work in history. It is consistently one of the 10 most popular websites ranked by Similarweb and formerly Alexa; Wikipedia was ranked the 5th most popular site in the world. It is hosted by the Wikimedia Foundation, an American non-profit organization funded mainly through donations. Wikipedia was launched by Jimmy Wales and Larry Sanger on January 15, 2001. Sanger coined its name as a blend of ''wiki'' and ''encyclopedia''. Wales was influenced by the "spontaneous order" ideas associated with Friedrich Hayek and the Austrian School of economics after being exposed to these ideas by the libertarian economist Mark Thornton. Initially available only in English, versions in other languages were quickly developed. Its combined edition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helmut Maier
Helmut Maier (born 17 October 1953) is a German mathematician and professor at the University of Ulm, Germany. He is known for his contributions in analytic number theory and mathematical analysis and particularly for the so-called Maier's matrix method as well as Maier's theorem for primes in short intervals. He has also done important work in exponential sums and trigonometric sums over special sets of integers and the Riemann zeta function. Education Helmut Maier graduated with a Diploma in Mathematics from the University of Ulm in 1976, under the supervision of Hans-Egon Richert. He received his PhD from the University of Minnesota in 1981, under the supervision of J. Ian Richards. Research and academic positions Maier's PhD thesis was an extension of his paper ''Chains of large gaps between consecutive primes''. In this paper Maier applied for the first time what is now known as Maier's matrix method. This method later on led him and other mathematicians to the discovery of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oppermann's Conjecture
Oppermann's conjecture is an unsolved problem in mathematics on the distribution of prime numbers.. It is closely related to but stronger than Legendre's conjecture, Andrica's conjecture, and Brocard's conjecture. It is named after Danish mathematician Ludvig Oppermann, who announced it in an unpublished lecture in March 1877. Statement The conjecture states that, for every integer ''x'' > 1, there is at least one prime number between : ''x''(''x'' − 1) and ''x''2, and at least another prime between : ''x''2 and ''x''(''x'' + 1). It can also be phrased equivalently as stating that the prime-counting function must take unequal values at the endpoints of each range.. That is: : ''π''(''x''2 − x) < ''π''(''x''2) < ''π''(''x''2 + ''x'') for ''x'' > 1 with ''π''(''x'') being the number of prime numbers less than or equal to ''x''. The end points of these two ranges are a square between two pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legendre's Conjecture
Legendre's conjecture, proposed by Adrien-Marie Legendre, states that there is a prime number between n^2 and (n+1)^2 for every positive integer n. The conjecture is one of Landau's problems (1912) on prime numbers; , the conjecture has neither been proved nor disproved. Prime gaps If Legendre's conjecture is true, the gap between any prime ''p'' and the next largest prime would be O(\sqrt p), as expressed in big O notation. It is one of a family of results and conjectures related to prime gaps, that is, to the spacing between prime numbers. Others include Bertrand's postulate, on the existence of a prime between n and 2n, Oppermann's conjecture on the existence of primes between n^2, n(n+1), and (n+1)^2, Andrica's conjecture and Brocard's conjecture on the existence of primes between squares of consecutive primes, and Cramér's conjecture that the gaps are always much smaller, of the order (\log p)^2. If Cramér's conjecture is true, Legendre's conjecture would follow for all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andrica's Conjecture
Andrica's conjecture (named afteDorin Andrica is a conjecture regarding the gaps between prime numbers. The conjecture states that the inequality :\sqrt - \sqrt < 1 holds for all , where is the ''n''th prime number. If denotes the ''n''th , then Andrica's conjecture can also be rewritten as : Empirical evidence Imran Ghory has used data on the largest prime gaps to confirm the conjecture for up to 1.3002 × 1016.''Prime Numbers: The Most Mysterious Figures in Math'', John Wiley & Sons, Inc., 2005, p. 13. Using a table of maximal gaps and the above gap inequality, the con ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prime Number Theorem
In mathematics, the prime number theorem (PNT) describes the asymptotic distribution of the prime numbers among the positive integers. It formalizes the intuitive idea that primes become less common as they become larger by precisely quantifying the rate at which this occurs. The theorem was proved independently by Jacques Hadamard and Charles Jean de la Vallée Poussin in 1896 using ideas introduced by Bernhard Riemann (in particular, the Riemann zeta function). The first such distribution found is , where is the prime-counting function (the number of primes less than or equal to ''N'') and is the natural logarithm of . This means that for large enough , the probability that a random integer not greater than is prime is very close to . Consequently, a random integer with at most digits (for large enough ) is about half as likely to be prime as a random integer with at most digits. For example, among the positive integers of at most 1000 digits, about one in 2300 is prime ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euler–Mascheroni Constant
Euler's constant (sometimes also called the Euler–Mascheroni constant) is a mathematical constant usually denoted by the lowercase Greek letter gamma (). It is defined as the limiting difference between the harmonic series and the natural logarithm, denoted here by \log: :\begin \gamma &= \lim_\left(-\log n + \sum_^n \frac1\right)\\ px&=\int_1^\infty\left(-\frac1x+\frac1\right)\,dx. \end Here, \lfloor x\rfloor represents the floor function. The numerical value of Euler's constant, to 50 decimal places, is: : History The constant first appeared in a 1734 paper by the Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler, titled ''De Progressionibus harmonicis observationes'' (Eneström Index 43). Euler used the notations and for the constant. In 1790, Italian mathematician Lorenzo Mascheroni used the notations and for the constant. The notation appears nowhere in the writings of either Euler or Mascheroni, and was chosen at a later time perhaps because of the constant's connection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonard Adleman
Leonard Adleman (born December 31, 1945) is an American computer scientist. He is one of the creators of the RSA encryption algorithm, for which he received the 2002 Turing Award, often called the Nobel prize of Computer science. He is also known for the creation of the field of DNA computing. Biography Leonard M. Adleman was born to a JewishLeonard (Len) Max Adleman 2002 Recipient of the ACM Turing Award Interviewed by Hugh Williams, August 18, 2016 amturing.acm.org family in . His family had originally immigrated to the United States from modern-day |
János Pintz
János Pintz (born 20 December 1950 in Budapest) is a Hungary, Hungarian mathematician working in analytic number theory. He is a fellow of the Alfréd Rényi Institute of Mathematics, Rényi Mathematical Institute and is also a member of the Hungarian Academy of Sciences. In 2014, he received the Cole Prize. Mathematical results Pintz is best known for proving in 2005 (with Daniel Goldston and Cem Yıldırım) that :: \liminf_\frac=0 where p_n denotes the ''n''th prime number. In other words, for every ε > 0, there exist infinitely many pairs of consecutive primes ''p''''n'' and ''p''''n''+1 that are closer to each other than the average distance between consecutive primes by a factor of ε, i.e., ''p''''n''+1 − ''p''''n'' < ε log ''p''''n''. This result was originally reported in 2003 by Daniel Goldston and Cem Yıldırım but was later retracted. Pintz joined the team and comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Number Theory
Number theory (or arithmetic or higher arithmetic in older usage) is a branch of pure mathematics devoted primarily to the study of the integers and arithmetic function, integer-valued functions. German mathematician Carl Friedrich Gauss (1777–1855) said, "Mathematics is the queen of the sciences—and number theory is the queen of mathematics."German original: "Die Mathematik ist die Königin der Wissenschaften, und die Arithmetik ist die Königin der Mathematik." Number theorists study prime numbers as well as the properties of mathematical objects made out of integers (for example, rational numbers) or defined as generalizations of the integers (for example, algebraic integers). Integers can be considered either in themselves or as solutions to equations (Diophantine geometry). Questions in number theory are often best understood through the study of Complex analysis, analytical objects (for example, the Riemann zeta function) that encode properties of the integers, primes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cramér's Conjecture
In number theory, Cramér's conjecture, formulated by the Swedish mathematician Harald Cramér in 1936, is an estimate for the size of gaps between consecutive prime numbers: intuitively, that gaps between consecutive primes are always small, and the conjecture quantifies asymptotically just how small they must be. It states that :p_-p_n=O((\log p_n)^2),\ where ''p''''n'' denotes the ''n''th prime number, ''O'' is big O notation, and "log" is the natural logarithm. While this is the statement explicitly conjectured by Cramér, his heuristic actually supports the stronger statement :\limsup_ \frac = 1, and sometimes this formulation is called Cramér's conjecture. However, this stronger version is not supported by more accurate heuristic models, which nevertheless support the first version of Cramér's conjecture. Neither form has yet been proven or disproven. Conditional proven results on prime gaps Cramér gave a conditional proof of the much weaker statement that :p_-p_n = O(\s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |