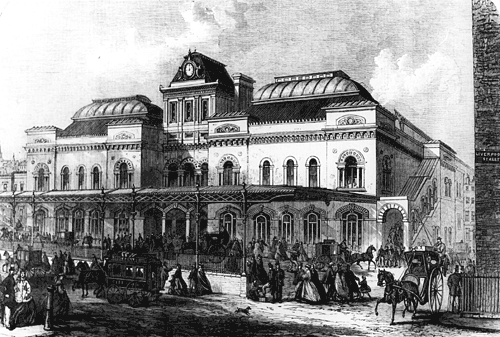|
Finchley Central Tube Station
Finchley Central is a London Underground station in the Church End area of Finchley, north London. The station is located on the High Barnet branch of the Northern line, between West Finchley and East Finchley stations; it is the junction for the short branch to Mill Hill East. The station is around 7 miles north-northwest of Charing Cross and is in Travelcard Zone 4. The station was opened on 22 August 1867 as part of the Great Northern Railway's line between Finsbury Park and Edgware stations. As part of London Underground's Northern Heights plan, Northern line trains started serving the station in 1940 and main line passenger services ended in 1941. History Original station Finchley Central station was built by the Edgware, Highgate and London Railway (EH&LR) on its line from Finsbury Park to Edgware. As construction of the line was nearing completion and before it opened it was purchased in July 1867 by the larger Great Northern Railway (GNR), whose main line from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Underground
The London Underground (also known simply as the Underground or by its nickname the Tube) is a rapid transit system serving Greater London and some parts of the adjacent ceremonial counties of England, counties of Buckinghamshire, Essex and Hertfordshire in England. The Underground has its origins in the Metropolitan Railway, the world's first underground passenger railway. Opened on 10 January 1863, it is now part of the Circle line (London Underground), Circle, District line, District, Hammersmith & City line, Hammersmith & City and Metropolitan lines. The first line to operate underground electric locomotive, electric traction trains, the City & South London Railway in 1890, is now part of the Northern line. The network has expanded to 11 lines, and in 2020/21 was used for 296 million passenger journeys, making it List of metro systems, one of the world's busiest metro systems. The 11 lines collectively handle up to 5 million passenger journeys a day and serve 272 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finchley Central Station On Ordnance Survey Map, 1873
Finchley () is a large district of north London, England, in the London Borough of Barnet. Finchley is on high ground, north of Charing Cross. Nearby districts include: Golders Green, Muswell Hill, Friern Barnet, Whetstone, Mill Hill and Hendon. It is predominantly a residential suburb, with three town centres: North Finchley, East Finchley and Finchley Church End (Finchley Central). Made up of four wards, the population of Finchley counted 65,812 as of 2011. History Finchley probably means "Finch's clearing" or "finches' clearing" in late Anglo-Saxon; the name was first recorded in the early 13th century. Finchley is not recorded in Domesday Book, but by the 11th century its lands were held by the Bishop of London. In the early medieval period the area was sparsely populated woodland, whose inhabitants supplied pigs and fuel to London. Extensive cultivation began about the time of the Norman conquest. By the 15th and 16th centuries the woods on the eastern side of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexandra Palace Railway Station (1873–1954)
Alexandra Palace is a closed railway station in the grounds of Alexandra Palace in the Muswell Hill area of north London. It is one of a number of stations to have held the name at various times and should not be confused with the current Alexandra Palace station which is on the East Coast Main Line to the east of the closed station. The former station was the terminus of a short branch line from Highgate. The preceding station on the branch was . The station was located immediately adjacent to the north side of the Palace buildings. Nothing remains of the tracks or island platform today, which have been removed and covered by a car park, but the small station building remains and is in use as a community centre. History The station was built by the Muswell Hill Railway (MHR) and opened on 24 May 1873 along with the Palace. However, when the Palace burned down only two weeks after opening, the train service was considerably reduced and from 1 August 1873 was stopped for alm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Passenger Transport Board
The London Passenger Transport Board was the organisation responsible for local public transport in London and its environs from 1933 to 1948. In common with all London transport authorities from 1933 to 2000, the public name and brand was London Transport. History The London Passenger Transport Board (LPTB) was established pursuant to the London Passenger Transport Act 1933 enacted on 13 April 1933. The bill had been introduced by Herbert Morrison, who was Transport Minister in the Labour Government until 1931. Because the legislation was a hybrid bill it had been possible to allow it to 'roll over' into the new parliament under the incoming National Government. The new government, although dominated by Conservatives, decided to continue with the bill, with no serious changes, despite its extensive transfer of private undertakings into the public sector. On 1 July 1933, the LPTB came into being, covering the "London Passenger Transport Area". The LPTB's financial structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North London Railway
The North London Railway (NLR) company had lines connecting the northern suburbs of London with the East and West India Docks further east. The main east to west route is now part of London Overground's North London Line. Other NLR lines fell into disuse but were later revived as part of the Docklands Light Railway, and London Overground's East London Line. The company was originally called the East & West India Docks & Birmingham Junction Railway (E&WID&BJR) from its start in 1850, until 1853. in 1909 it entered into an agreement with the London and North Western Railway which introduced common management, and the NLR was taken over completely by the LNWR in 1922. The LNWR itself became part of the LMS from the start of 1923. The railways were nationalised in 1948 and most LMS lines, including the North London route, then came under the control of the London Midland Region of British Railways. History The East & West India Docks & Birmingham Junction Railway was incorporated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canonbury Railway Station
Canonbury railway station serves the districts of Canonbury and Highbury within the London Borough of Islington in north London. It is on London Overground's North London line and East London line. The station and all trains serving it are operated by London Overground, and the station is in Travelcard Zone 2. This location of the station is close to the boundary with the London Borough of Hackney. History The station was originally named "Newington Road and Balls Pond Road" when opened in 1858 by the North London Railway, and was sited east of the present station on the east side of Newington Green Road. The station was renamed "Canonbury" in July 1870 and then resited to its present location, the west side of Douglas Road (now Wallace Road), in December of the same year. The Victorian main building was demolished in 1969, although the building was fully intact. In 2007, the ticket office was extensively refurbished, as part of the station upgrade programme delivered throu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Widened Lines
The Widened Lines (also known as the City Widened Lines; formerly known as the Moorgate Line) is a double-track railway line forming part of the Thameslink route between St Pancras and within Central London. For most of their life the Widened Lines ran from King's Cross to , and were completed in 1866 when the Metropolitan Railway was widened from two to four tracks between King's Cross and Farringdon (hence the ''widened'' name) and a four-track railway opened from there to Moorgate. The tracks were owned by the Metropolitan Railway but were used mainly by other railway companies. Connections to the Great Northern Railway (GNR) at King's Cross and London, Chatham and Dover Railway (LC&DR) at Farringdon allowed cross-London services to run. There was very soon a connection to the Midland Railway at St Pancras, near King's Cross. In the early 20th century competition led to the cross-London services being withdrawn, although the GNR and Midland services into Moorgate survived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broad Street Railway Station (England)
Broad Street was a major terminal station in the City of London, adjacent to Liverpool Street station. It served as the main terminus of the North London Railway (NLR) network, running from 1865 to 1986. During its lifetime, it catered for mainly local suburban services around London, and over time struggled to compete with other modes of transport, leading to its closure. The station was built as a joint venture by the NLR and the London and North Western Railway (LNWR) in order to have a station serving freight closer to the City. It was immediately successful for both goods and passenger services and saw a significant increase in NLR traffic. Usage peaked in the early 20th century, after which it suffered from competition of London trams,_buses,_and_particularly_the_London_Underground.html" ;"title=""type": ..., buses, and particularly the London Underground">"type": ..., buses, and particularly the London Underground network. Patronage gradually fell and services decreased, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
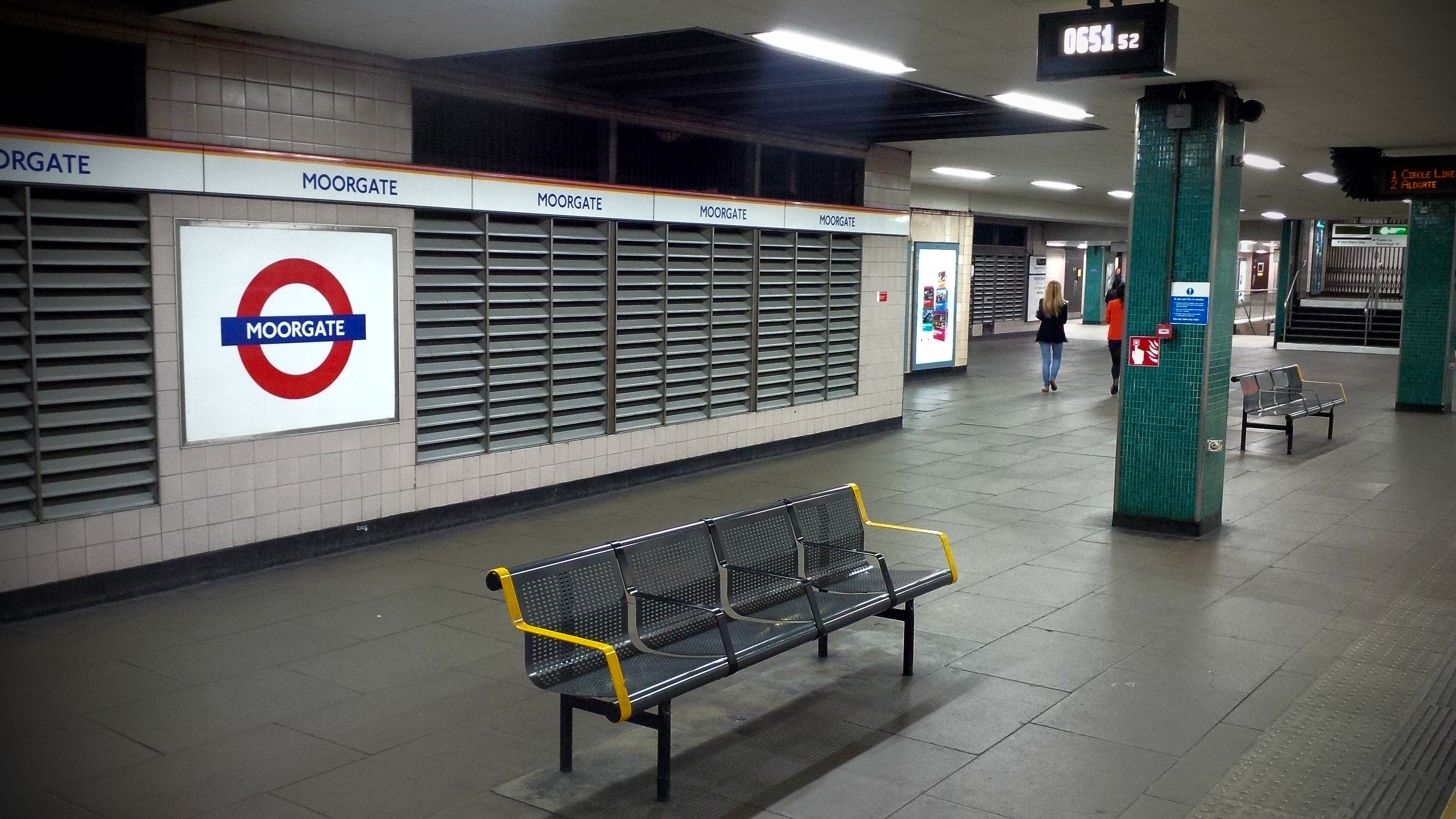
Moorgate Station
Moorgate is a central London railway terminus and connected London Underground station on Moorgate in the City of London. Main line railway services for Hertford, Welwyn Garden City, Stevenage and Letchworth are operated by Great Northern, while the Underground station is served by the Circle, Hammersmith & City, Metropolitan and Northern lines. The station was opened as Moorgate Street in 1865 by the Metropolitan Railway. In 1900, the City & South London Railway added the station to its network, and the Great Northern & City Railway began serving the station in 1904. In 1975, the Northern City Line platforms were the site of the Moorgate tube crash – at the time, the worst peacetime accident in the history of the London Underground – in which 43 people were killed. Thameslink branch services were withdrawn in the early 21st century, and in 2022 a new ticket hall was built connected to the newly opened Elizabeth line at , with through access to the rest of Liverpool Str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Four (British Railway Companies)
"Big Four" was a name used to describe the four largest railway companies in the United Kingdom in the period 1923–1947. The name was coined by ''The Railway Magazine'' in its issue of February 1923: "The Big Four of the New Railway Era". The Big Four were: * Great Western Railway (GWR) * London, Midland and Scottish Railway (LMS) * London and North Eastern Railway (LNER) * Southern Railway (SR) The companies were formed as a result of the Railways Act 1921, in a process known as "The Grouping" (of the railways), which came into effect on 1 January 1923. On 1 January 1948 the companies were nationalised to form British Rail, British Railways as a result of the Transport Act 1947. Characterisation The three larger companies relied heavily on freight (especially coal), as well as long-distance passenger traffic. The Southern Railway, in contrast, was predominantly a passenger railway, which, despite its small size, carried more than a quarter of the total UK passenger tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Railways Act 1921
The Railways Act 1921 (c. 55), also known as the Grouping Act, was an Act of Parliament enacted by the British government and intended to stem the losses being made by many of the country's 120 railway companies, by "grouping" them into four large companies dubbed the " Big Four". This was intended to move the railways away from internal competition, and retain some of the benefits which the country had derived from a government-controlled railway during and after the Great War of 1914–1918. The provisions of the Act took effect from the start of 1923. History The British railway system had been built up by more than a hundred railway companies, large and small, and often, particularly locally, in competition with each other. The parallel railways of the East Midlands and the rivalry between the South Eastern Railway and the London, Brighton and South Coast Railway at Hastings were two examples of such local competition. During the First World War the railways were under st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chain (unit)
The chain is a unit of length equal to 66 feet (22 yards). It is subdivided into 100 links (PDF) or 4 rods. There are 10 chains in a furlong, and 80 chains in one statute mile. In metric terms, it is 20.1168 m long. By extension, chainage (running distance) is the distance along a curved or straight survey line from a fixed commencing point, as given by an odometer. The chain has been used for several centuries in England and in some other countries influenced by English practice. In the United Kingdom, there were 80 chains to the mile, but until the early nineteenth century the Scottish and Irish customary miles were longer than the statute mile; consequently a Scots chain was about 74 (imperial) feet, an Irish chain 84 feet. These longer chains became obsolete following the adoption of the imperial system of units in 1824. Definition The UK statute chain is 22 yards, which is . This unit is a statute measure in the United Kingdom, defined in the Weights and Measures Act 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |