|
Filchner Station
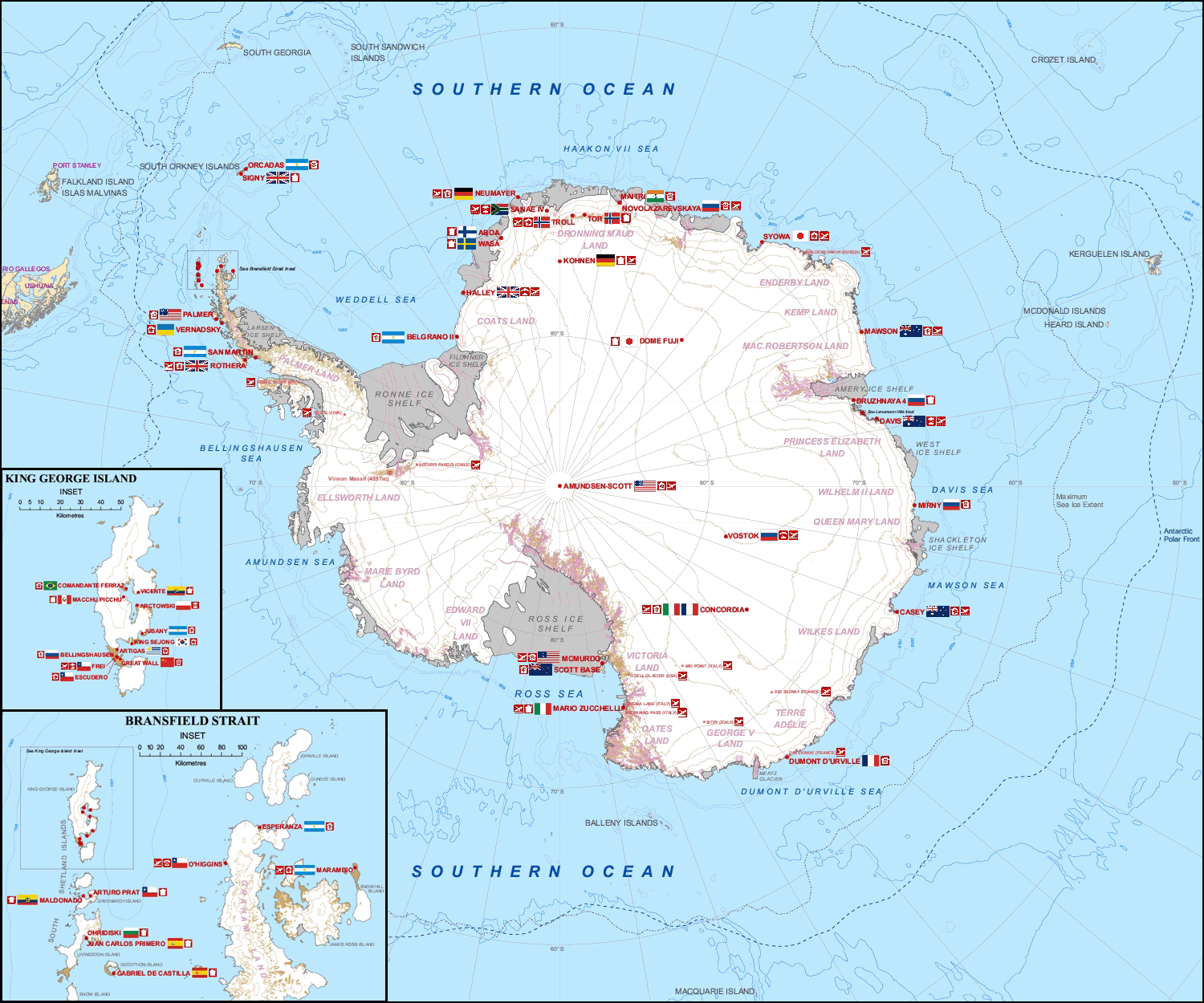
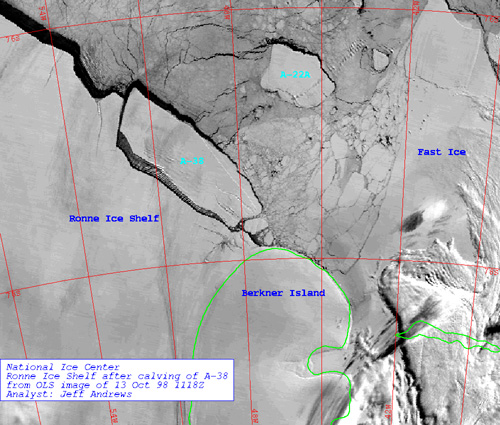
Filchner Station was a German research station in the Antarctic. Administered by the Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research, it was established in February 1982 on the Filchner–Ronne Ice Shelf. The first station in Antarctica to be mounted on jacks, the structure was raised each year to allow for the increase in height of the shelf by snowfall. It was also relocated around southwards each year to account for drift of the ice shelf. In October 1998, Filchner Station was stranded on iceberg A-38 when it broke away from the ice shelf. Research operations were cancelled and an emergency salvage operation was carried out that removed the majority of the station by February 1999. Establishment and operation The Filchner Station was established by the West German Alfred Wegener Institute for Polar and Marine Research (AWI) in February 1982. The station consisted of steel containers housing living quarters and laboratories. The station was the first in the Antarcti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Stations In Antarctica
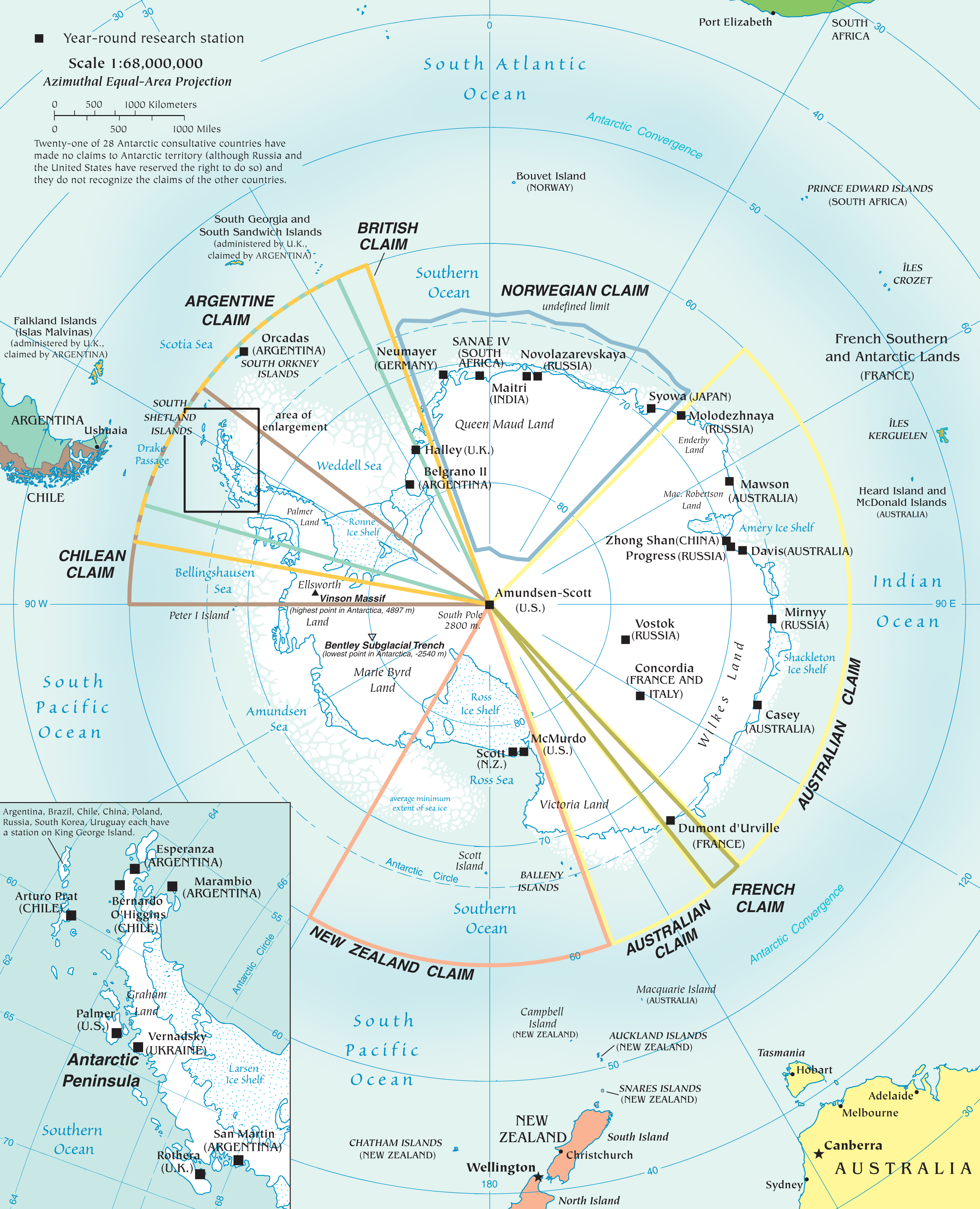
Multiple governments have set up permanent research stations in Antarctica and these bases are widely distributed. Unlike the drifting ice stations set up in the Arctic, the research stations of the Antarctic are constructed either on rock or on ice that is (for practical purposes) fixed in place. Many of the stations are demographics of Antarctica, staffed throughout the year. A total of 42 countries (as of October 2006), all signatories to the Antarctic Treaty System, Antarctic Treaty, operate seasonal (summer) and year-round research stations on the continent. The population of people performing and supporting scientific research on the continent and nearby islands varies from approximately 4,000 during the summer season to 1,000 during winter (June). In addition to these permanent stations, approximately Antarctic field camps, 30 field camps are established each summer to support specific projects. History First bases During the Heroic Age of Antarctic Exploration in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teniente R
A lieutenant ( , ; abbreviated Lt., Lt, LT, Lieut and similar) is a commissioned officer rank in the armed forces of many nations. The meaning of lieutenant differs in different militaries (see comparative military ranks), but it is often subdivided into senior (first lieutenant) and junior (second lieutenant and even third lieutenant) ranks. In navies, it is often equivalent to the army rank of captain; it may also indicate a particular post rather than a rank. The rank is also used in fire services, emergency medical services, security services and police forces. Lieutenant may also appear as part of a title used in various other organisations with a codified command structure. It often designates someone who is "second-in-command", and as such, may precede the name of the rank directly above it. For example, a "lieutenant master" is likely to be second-in-command to the "master" in an organisation using both ranks. Political uses include lieutenant governor in various gov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1982 Establishments In Antarctica
__NOTOC__ Year 198 (CXCVIII) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Sergius and Gallus (or, less frequently, year 951 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 198 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire *January 28 **Publius Septimius Geta, son of Septimius Severus, receives the title of Caesar. **Caracalla, son of Septimius Severus, is given the title of Augustus. China *Winter – Battle of Xiapi: The allied armies led by Cao Cao and Liu Bei defeat Lü Bu; afterward Cao Cao has him executed. By topic Religion * Marcus I succeeds Olympianus as Patriarch of Constantinople (until 211). Births * Lu Kai (or Jingfeng), Chinese official and general (d. 269) * Quan Cong, Chinese general and advisor (d. 24 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germany And The Antarctic
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the List of European countries by population, second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated between the Baltic Sea, Baltic and North Sea, North seas to the north, and the Alps to the south; it covers an area of , with a population of almost 84 million within its 16 States of Germany, constituent states. Germany borders Denmark to the north, Poland and the Czech Republic to the east, Austria and Switzerland to the south, and France, Luxembourg, Belgium, and the Netherlands to the west. The nation's capital and List of cities in Germany by population, most populous city is Berlin and its financial centre is Frankfurt; the largest urban area is the Ruhr. Various Germanic peoples, Germanic List of ancient Germanic peoples, tribes have inhabited the northern parts of modern Germany since classical anti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Outposts Of Antarctica
''Outposts: Journeys to the surviving relics of the British Empire'' is a book by Simon Winchester. It details his travels to each of the remaining dependencies of the British Empire and was first published in 1985 in Britain by Hodder and Stoughton under the title ''Outposts'' and in the United States by Prentice Hall as ''The Sun Never Sets: Travels to the Remaining Outposts of the British Empire''. It was reprinted in 2003 with a new foreword written to address the changing political climate and attitudes in relation to the British Empire, most importantly concerning the handover of Hong Kong to China and, more generally, the rise of globalism. Publication history *''Outposts: Journeys to the Surviving Relics of the British Empire'' (1985), Hodder & Stoughton *''The Sun Never Sets: Travels to the Remaining Outposts of the British Empire'' (1985), Prentice Hall *''Outposts: Journeys to the Surviving Relics of the British Empire'' revised ed. (2003), Penguin Penguins (ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctic Treaty
russian: link=no, Договор об Антарктике es, link=no, Tratado Antártico , name = Antarctic Treaty System , image = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty.svgborder , image_width = 180px , caption = Flag of the Antarctic Treaty System , type = Condominium , date_drafted = , date_signed = December 1, 1959"Antarctic Treaty" in ''The New Encyclopædia Britannica''. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica Inc., 15th edn., 1992, Vol. 1, p. 439. , location_signed = Washington, D.C., United States , date_sealed = , date_effective = June 23, 1961 , condition_effective = Ratification of all 12 signatories , date_expiration = , signatories = 12 , parties = 55 , depositor = Federal government of the United States , languages = English, French, Russian, and Spanish , wikisource = Antarctic Treaty The Antarctic Treaty a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ice Calving
Ice calving, also known as glacier calving or iceberg calving, is the breaking of ice chunks from the edge of a glacier.Essentials of Geology, 3rd edition, Stephen Marshak It is a form of ice ablation or ice disruption. It is the sudden release and breaking away of a mass of ice from a glacier, iceberg, ice front, ice shelf, or crevasse. The ice that breaks away can be classified as an iceberg, but may also be a growler, bergy bit, or a crevasse wall breakaway.Glossary of Glacier Terms Ellin Beltz, 2006. Retrieved July 2009. Calving of glaciers is often accompanied by a loud cracking or booming sound before blocks of ice up to high break loose and crash into the water. The entry of the ice into the water causes large, and often hazardous waves. The waves formed in locations like |
Iceberg A-38
A-38 was a large iceberg that split from the Filchner-Ronne Ice Shelf in Antarctica in October 1998. Soon after formation it split into two pieces, A-38A and A-38B, which drifted westwards on the Weddell Gyre. The icebergs moved north along the Antarctic Peninsula and reached its tip in February 2003. A-38A and A-38B increased speed in open sea and grounded in shallower waters to the east of South Georgia Island in December 2003. A-38A broke up into three pieces in March 2004 and drifted north where it decayed. A-38B split into two in April, with the eastern portion, now known as A-38G, drifting north and west to decay. The remainder of A-38B remained grounded, interfering with the foraging routes of seals and penguins in South Georgia, resulting in the deaths of their young. On 20 August A38-B broke into two, with the new portion drifting north and breaking up. The remainder of A-38B continued to break up through September 2004 and had completely decayed by 2005. Calv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand Antarctic Society
New Zealand Antarctic Society was formed in 1933 by New Zealand businessman Arthur Leigh Hunt and Antarctic explorers Rear Admiral Richard E. Byrd and Sir Douglas Mawson Sir Douglas Mawson OBE FRS FAA (5 May 1882 – 14 October 1958) was an Australian geologist, Antarctic explorer, and academic. Along with Roald Amundsen, Robert Falcon Scott, and Sir Ernest Shackleton, he was a key expedition leader during .... Its aims are: * to bring together people interested in the region * to share knowledge of the region * to foster interest in the region * to seek and support protection of the Antarctic environment * to promote New Zealand's interests in the region Since 1956 it has published a quarterly magazine, ''Antarctic''. A set of Ross Dependency postage stamps celebrated the society's 50th anniversary in 1983. The national office is now in Auckland. References External links * 1934 establishments in New Zealand Environmental studies organizations Explorati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rothera Research Station
The Rothera Research Station is a British Antarctic Survey (BAS) base on the Antarctic Peninsula, located at Rothera Point, Adelaide Island. Rothera also serves as the capital of the British Antarctic Territory, a British Overseas Territory. History and current activities Rothera station was established in 1975 to replace Adelaide station (1961-1977) where the skiway had deteriorated. The opening of the Bonner Laboratory in 1996/1997 marked the start of new activities in biological sciences in the Antarctic peninsula. These included scuba diving and experiments conducted in the Bonner Laboratory throughout the year. The first Bonner Lab burned down in the winter of 2001 after an electrical fault; it was rebuilt and opened in December 2003. Meteorological research using satellite data intercepted at the Rothera ground station also continues year round. In January 2017, it was announced that the Rothera Research Station will receive £100m in funding from the government. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest continent, being about 40% larger than Europe, and has an area of . Most of Antarctica is covered by the Antarctic ice sheet, with an average thickness of . Antarctica is, on average, the coldest, driest, and windiest of the continents, and it has the highest average elevation. It is mainly a polar desert, with annual precipitation of over along the coast and far less inland. About 70% of the world's freshwater reserves are frozen in Antarctica, which, if melted, would raise global sea levels by almost . Antarctica holds the record for the lowest measured temperature on Earth, . The coastal regions can reach temperatures over in summer. Native species of animals include mites, nematodes, penguins, seals and tardigrades. Where vegetation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neumayer-Station II
Neumayer-Station or Neumayer-Station II was a permanent German Antarctic research base on Atka Bay. It opened in 1992, replacing the old Georg-von-Neumayer-Station. On February 20, 2009, it was replaced by the new permanent research base Neumayer-Station III. See also * List of Antarctic research stations * List of Antarctic field camps Many Antarctic research stations support satellite field camps which are, in general, seasonal camps. The type of field camp can vary – some are permanent structures used during the annual Antarctic summer, whereas others are little more than te ... Germany and the Antarctic Princess Astrid Coast Outposts of Queen Maud Land 1992 establishments in Antarctica 2009 disestablishments in Antarctica {{PrincessAstridCoast-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |