|
Field Recording
Field recording is the term used for an audio recording produced outside a recording studio, and the term applies to recordings of both natural and human-produced sounds. It also applies to sound recordings like electromagnetic fields or vibrations using different microphones like a passive magnetic antenna for electromagnetic recordings or contact microphones. For underwater field recordings, a field recordist uses hydrophones to capture the sounds and/or movements of whales, or other aquatic organisms. These recordings are very useful for sound designers. Field recording of natural sounds, also called phonography (a term chosen to illustrate its similarities to photography), was originally developed as a documentary adjunct to research work in the field, and foley work for film. With the introduction of high-quality, portable recording equipment, it has subsequently become an evocative artform in itself. In the 1970s, both processed and natural phonographic recordings, (p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matmos - Rose Has Teeth In The Mouth Of A Beast - Martin Mics Cows
Matmos is an experimental electronic music duo originally from San Francisco but now residing in Baltimore. M. C. (Martin) Schmidt and Drew Daniel are the core members, but they frequently include other artists on their records and in their performances, including notably J Lesser. Apart from releasing twelve full-length studio albums and numerous collaborative works, Matmos is also well known for their collaboration with Icelandic singer and musician Björk, both on studio recordings and live tours. After being signed to Matador Records for nine years, Matmos signed with Thrill Jockey in 2012. The name ''Matmos'' refers to the seething lake of evil slime beneath the city Sogo in the 1968 film '' Barbarella''. Notable work In 1998, Matmos remixed the Björk single Alarm Call. Subsequently, Matmos worked with Björk on her albums ''Vespertine'' (2001) and ''Medúlla'' (2004), as well as her ''Vespertine'' and ''Greatest Hits'' tours. In November 2004, Matmos spent 97 hours in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nagra
Nagra is a brand of portable audio recorders produced from 1951 in Switzerland. Beginning in 1997 a range of high-end equipment aimed at the audiophile community was introduced, and Nagra expanded the company’s product lines into new markets. Originally a product of the Kudelski Group, Nagra recorders are now developed, produced and sold by independently-owned company ''Audio Technology Switzerland S.A.'', based in Romanel-sur-Lausanne. History The machines were initially designed by Polish inventor Stefan Kudelski, and his company won numerous technical awards for their precision and reliability. Nagra means " twill record" in Polish, Kudelski's mother language. Nagra-brand tape recorders were the ''de facto'' standard sound recording systems for motion picture and (non-video) single-camera television production from the 1960s until the 1990s. Synchronization Originally, a physical sync lead tethered the Nagra recorder to the camera (putting a pulse from the camera onto t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase (waves)
In physics and mathematics, the phase of a periodic function F of some real variable t (such as time) is an angle-like quantity representing the fraction of the cycle covered up to t. It is denoted \phi(t) and expressed in such a scale that it varies by one full turn as the variable t goes through each period (and F(t) goes through each complete cycle). It may be measured in any angular unit such as degrees or radians, thus increasing by 360° or 2\pi as the variable t completes a full period. This convention is especially appropriate for a sinusoidal function, since its value at any argument t then can be expressed as \phi(t), the sine of the phase, multiplied by some factor (the amplitude of the sinusoid). (The cosine may be used instead of sine, depending on where one considers each period to start.) Usually, whole turns are ignored when expressing the phase; so that \phi(t) is also a periodic function, with the same period as F, that repeatedly scans the same range of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
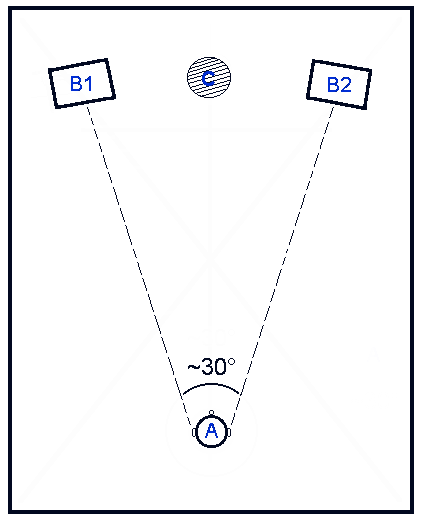
Binaural Hearing
Sound localization is a listener's ability to identify the location or origin of a detected sound in direction and distance. The sound localization mechanisms of the mammalian auditory system have been extensively studied. The auditory system uses several cues for sound source localization, including time difference and level difference (or intensity difference) between the ears, and spectral information. These cues are also used by other animals, such as birds and reptiles, but there may be differences in usage, and there are also localization cues which are absent in the human auditory system, such as the effects of ear movements. Animals with the ability to localize sound have a clear evolutionary advantage. How sound reaches the brain Sound is the perceptual result of mechanical vibrations traveling through a medium such as air or water. Through the mechanisms of compression and rarefaction, sound waves travel through the air, bounce off the pinna and concha of the exter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directivity
In electromagnetics, directivity is a parameter of an antenna or optical system which measures the degree to which the radiation emitted is concentrated in a single direction. It is the ratio of the radiation intensity in a given direction from the antenna to the radiation intensity averaged over all directions.IEEE Std 145-2013, IEEE Standard for Definitions of Terms for Antennas, IEEE Therefore, the directivity of a hypothetical isotropic radiator is 1, or 0 dBi. An antenna's directivity is greater than its gain by an efficiency factor, radiation efficiency. Directivity is an important measure because many antennas and optical systems are designed to radiate electromagnetic waves in a single direction or over a narrow-angle. By the principle of reciprocity, the directivity of an antenna when receiving is equal to its directivity when transmitting. The directivity of an actual antenna can vary from 1.76 dBi for a short dipole to as much as 50 dBi for a large dish antenna. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decibel
The decibel (symbol: dB) is a relative unit of measurement equal to one tenth of a bel (B). It expresses the ratio of two values of a power or root-power quantity on a logarithmic scale. Two signals whose levels differ by one decibel have a power ratio of 101/10 (approximately ) or root-power ratio of 10 (approximately ). The unit expresses a relative change or an absolute value. In the latter case, the numeric value expresses the ratio of a value to a fixed reference value; when used in this way, the unit symbol is often suffixed with letter codes that indicate the reference value. For example, for the reference value of 1 volt, a common suffix is " V" (e.g., "20 dBV"). Two principal types of scaling of the decibel are in common use. When expressing a power ratio, it is defined as ten times the logarithm in base 10. That is, a change in ''power'' by a factor of 10 corresponds to a 10 dB change in level. When expressing root-power quantities, a change in ''ampl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tablet Computer
A tablet computer, commonly shortened to tablet, is a mobile device, typically with a mobile operating system and touchscreen display processing circuitry, and a rechargeable battery in a single, thin and flat package. Tablets, being computers, do what other personal computers do, but lack some input/output (I/O) abilities that others have. Modern tablets largely resemble modern smartphones, the only differences being that tablets are relatively larger than smartphones, with screens or larger, measured diagonally, and may not support access to a cellular network. Unlike laptops which have traditionally run off operating systems usually designed for desktops, tablets usually run mobile operating systems, alongside smartphones. The touchscreen display is operated by Gesture recognition, gestures executed by finger or digital pen (stylus), instead of the Computer mouse, mouse, touchpad, and Keyboard (computing), keyboard of larger computers. Portable computers can be classifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smartphone
A smartphone is a portable computer device that combines mobile telephone and computing functions into one unit. They are distinguished from feature phones by their stronger hardware capabilities and extensive mobile operating systems, which facilitate wider software, internet (including web browsing over mobile broadband), and multimedia functionality (including music, video, cameras, and gaming), alongside core phone functions such as voice calls and text messaging. Smartphones typically contain a number of metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit (IC) chips, include various sensors that can be leveraged by pre-included and third-party software (such as a magnetometer, proximity sensors, barometer, gyroscope, accelerometer and more), and support wireless communications protocols (such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, or satellite navigation). Early smartphones were marketed primarily towards the enterprise market, attempting to bridge the functionality of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flash Memory
Flash memory is an electronic non-volatile computer memory storage medium that can be electrically erased and reprogrammed. The two main types of flash memory, NOR flash and NAND flash, are named for the NOR and NAND logic gates. Both use the same cell design, consisting of floating gate MOSFETs. They differ at the circuit level depending on whether the state of the bit line or word lines is pulled high or low: in NAND flash, the relationship between the bit line and the word lines resembles a NAND gate; in NOR flash, it resembles a NOR gate. Flash memory, a type of floating-gate memory, was invented at Toshiba in 1980 and is based on EEPROM technology. Toshiba began marketing flash memory in 1987. EPROMs had to be erased completely before they could be rewritten. NAND flash memory, however, may be erased, written, and read in blocks (or pages), which generally are much smaller than the entire device. NOR flash memory allows a single machine word to be written to an era ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
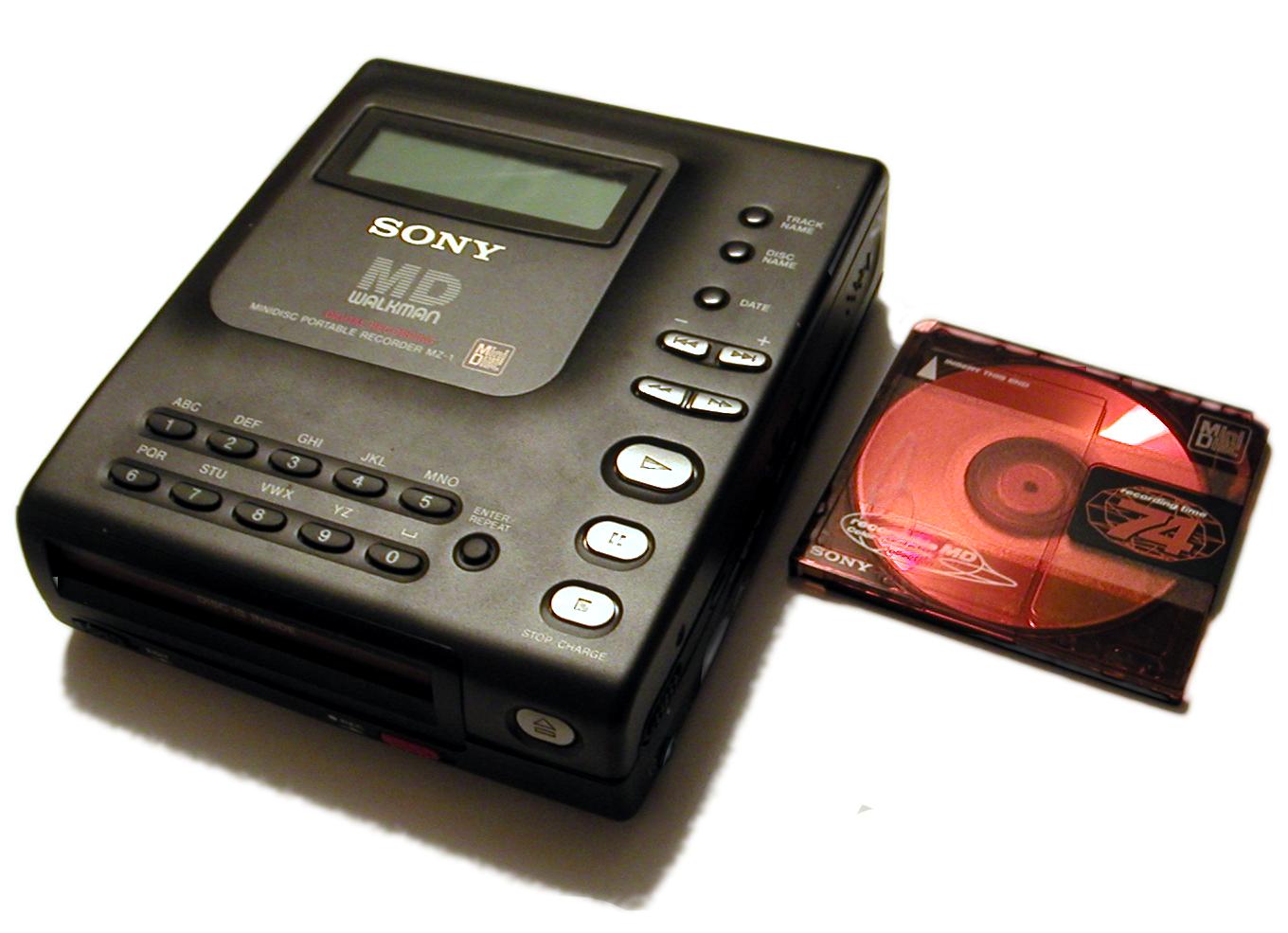
MiniDisc
MiniDisc (MD) is an erasable magneto-optical disc-based data storage format offering a capacity of 60, 74, and later, 80 minutes of digitized audio. Sony announced the MiniDisc in September 1992 and released it in November of that year for sale in Japan and in December in Europe, North America, and other countries. The music format was based on ATRAC audio data compression, Sony's own proprietary compression code. Its successor, Hi-MD, would later introduce the option of linear PCM digital recording to meet audio quality comparable to that of a compact disc. MiniDiscs were very popular in Japan and found moderate success in Europe; although it was designed to be the successor of the cassette tape, it did not manage to mass replace it globally. By March 2011 Sony had sold 22 million MD players. Sony has ceased development of MD devices, with the last of the players sold by March 2013. Market history In 1983, just a year after the introduction of the Compact Disc, Kees ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Compact Cassette
The Digital Compact Cassette (DCC) is a magnetic tape sound recording format introduced by Philips and Matsushita Electric in late and marketed as the successor to the standard analog Compact Cassette. It was also a direct competitor to Sony's MiniDisc (MD), but neither format toppled the then-ubiquitous analog cassette despite their technical superiority, and DCC was discontinued in . Another competing format, the Digital Audio Tape (DAT), had by also failed to sell in large quantities to consumers, although it was popular as a professional digital audio storage format. The DCC form factor is similar to the analog compact cassette (CC), and DCC recorders and players can play back either type: analog as well as DCC. This backward compatibility was intended to allow users to adopt digital recording without rendering their existing tape collections obsolete, but because DCC recorders couldn't record (only play back) analog cassettes, it effectively forced consumers to either ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compact Audio Cassette
The Compact Cassette or Musicassette (MC), also commonly called the tape cassette, cassette tape, audio cassette, or simply tape or cassette, is an analog magnetic tape recording format for audio recording and playback. Invented by Lou Ottens and his team at the Dutch company Philips in 1963, Compact Cassettes come in two forms, either already containing content as a prerecorded cassette (''Musicassette''), or as a fully recordable "blank" cassette. Both forms have two sides and are reversible by the user. Although other tape cassette formats have also existed - for example the Microcassette - the generic term ''cassette tape'' is normally always used to refer to the Compact Cassette because of its ubiquity. Its uses have ranged from portable audio to home recording to data storage for early microcomputers; the Compact Cassette technology was originally designed for dictation machines, but improvements in fidelity led to it supplanting the stereo 8-track cartridge and reel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)



