|
Fibular Dimelia Diplopodia Syndrome
The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity is small, placed toward the back of the head of the tibia, below the knee joint and excluded from the formation of this joint. Its lower extremity inclines a little forward, so as to be on a plane anterior to that of the upper end; it projects below the tibia and forms the lateral part of the ankle joint. Structure The bone has the following components: * Lateral malleolus * Interosseous membrane connecting the fibula to the tibia, forming a syndesmosis joint * The superior tibiofibular articulation is an arthrodial joint between the lateral condyle of the tibia and the head of the fibula. * The inferior tibiofibular articulation (tibiofibular syndesmosis) is formed by the rough, convex surface of the medial side of the lower end ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superior Tibiofibular Joint
The proximal tibiofibular articulation (also called superior tibiofibular joint) is an arthrodial joint between the lateral condyle of the tibia and the head of the fibula. The contiguous surfaces of the bones present flat, oval facets covered with cartilage and connected together by an articular capsule and by anterior and posterior ligaments. When the term ''tibiofibular articulation'' is used without a modifier, it refers to the proximal, not the distal (i.e., inferior) tibiofibular articulation. Clinical significance Injuries to the proximal tibiofibular joint are uncommon and usually associated with other injuries to the lower leg. Dislocations can be classified into the following five types: * Anterolateral dislocation (most common) * Posteromedial dislocation * Superior dislocation (uncommon, associated with shortened tibia fractures or severe ankle injuries) * Inferior dislocation (rare, associated with lengthened tibia fractures or avulsion of the foot, usuall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Condyle Of Tibia
The lateral condyle is the lateral portion of the upper extremity of tibia. It serves as the insertion for the biceps femoris muscle (small slip). Most of the tendon of the biceps femoris inserts on the fibula. See also * Gerdy's tubercle * Medial condyle of tibia The medial condyle is the medial (or inner) portion of the upper extremity of tibia. It is the site of insertion for the semimembranosus muscle. See also * Lateral condyle of tibia * Medial collateral ligament The medial collateral ligament ... Additional images File:Gray258.png, Bones of the right leg. Anterior surface. File:Slide2bib.JPG, Right knee in extension. Deep dissection. Posterior view. File:Slide2cocc.JPG, Right knee in extension. Deep dissection. Posterior view. References External links * * * () Bones of the lower limb Tibia {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biceps Femoris
The biceps femoris () is a muscle of the thigh located to the posterior, or back. As its name implies, it has two parts, one of which (the long head) forms part of the hamstrings muscle group. Structure It has two heads of origin: *the ''long head'' arises from the lower and inner impression on the posterior part of the tuberosity of the ischium. This is a common tendon origin with the semitendinosus muscle, and from the lower part of the sacrotuberous ligament. *the ''short head'', arises from the lateral lip of the linea aspera, between the adductor magnus and vastus lateralis extending up almost as high as the insertion of the gluteus maximus, from the lateral prolongation of the linea aspera to within 5 cm. of the lateral condyle; and from the lateral intermuscular septum. The two muscle heads joint together distally and unite in an intricate fashion. The fibers of the long head form a fusiform belly, which passes obliquely downward and lateralward across the sciat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability to withstand significant amounts of tension. Tendons are similar to ligaments; both are made of collagen. Ligaments connect one bone to another, while tendons connect muscle to bone. Structure Histologically, tendons consist of dense regular connective tissue. The main cellular component of tendons are specialized fibroblasts called tendon cells (tenocytes). Tenocytes synthesize the extracellular matrix of tendons, abundant in densely packed collagen fibers. The collagen fibers are parallel to each other and organized into tendon fascicles. Individual fascicles are bound by the endotendineum, which is a delicate loose connective tissue containing thin collagen fibrils and elastic fibres. Groups of fascicles are bounded by the epitenon, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Process (anatomy)
In anatomy, a process ( la, processus) is a projection or outgrowth of tissue from a larger body. For instance, in a vertebra, a process may serve for muscle attachment and leverage (as in the case of the transverse and spinous processes), or to fit (forming a synovial joint), with another vertebra (as in the case of the articular processes).Moore, Keith L. et al. (2010) ''Clinically Oriented Anatomy'', 6th Ed, p.442 fig. 4.2 The word is used even at the microanatomic level, where cells can have processes such as cilia or pedicels. Depending on the tissue, processes may also be called by other terms, such as ''apophysis'', ''tubercle'', or ''protuberance''. Examples Examples of processes include: *The many processes of the human skull: ** The mastoid and styloid processes of the temporal bone ** The zygomatic process of the temporal bone ** The zygomatic process of the frontal bone ** The orbital, temporal, lateral, frontal, and maxillary processes of the zygomatic bone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lateral Condyle Of Tibia
The lateral condyle is the lateral portion of the upper extremity of tibia. It serves as the insertion for the biceps femoris muscle (small slip). Most of the tendon of the biceps femoris inserts on the fibula. See also * Gerdy's tubercle * Medial condyle of tibia The medial condyle is the medial (or inner) portion of the upper extremity of tibia. It is the site of insertion for the semimembranosus muscle. See also * Lateral condyle of tibia * Medial collateral ligament The medial collateral ligament ... Additional images File:Gray258.png, Bones of the right leg. Anterior surface. File:Slide2bib.JPG, Right knee in extension. Deep dissection. Posterior view. File:Slide2cocc.JPG, Right knee in extension. Deep dissection. Posterior view. References External links * * * () Bones of the lower limb Tibia {{musculoskeletal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartilaginous
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck and the bronchial tubes, and the intervertebral discs. In other taxa, such as chondrichthyans, but also in cyclostomes, it may constitute a much greater proportion of the skeleton. It is not as hard and rigid as bone, but it is much stiffer and much less flexible than muscle. The matrix of cartilage is made up of glycosaminoglycans, proteoglycans, collagen fibers and, sometimes, elastin. Because of its rigidity, cartilage often serves the purpose of holding tubes open in the body. Examples include the rings of the trachea, such as the cricoid cartilage and carina. Cartilage is composed of specialized cells called chondrocytes that produce a large amount of collagenous extracellular matrix, abundant ground substance that is rich in proteoglyc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prenatal Development
Prenatal development () includes the development of the embryo and of the fetus during a viviparous animal's gestation. Prenatal development starts with fertilization, in the germinal stage of embryonic development, and continues in fetal development until birth. In human pregnancy, prenatal development is also called antenatal development. The development of the human embryo follows fertilization, and continues as fetal development. By the end of the tenth week of gestational age the embryo has acquired its basic form and is referred to as a fetus. The next period is that of fetal development where many organs become fully developed. This fetal period is described both topically (by organ) and chronologically (by time) with major occurrences being listed by gestational age. The very early stages of embryonic development are the same in all mammals, but later stages of development, and the length of gestation varies. Terminology In the human: Different terms are used to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ossified
Ossification (also called osteogenesis or bone mineralization) in bone remodeling is the process of laying down new bone material by Cell (biology), cells named osteoblasts. It is synonymous with bone tissue formation. There are two processes resulting in the formation of normal, healthy bone tissue: Intramembranous ossification is the direct laying down of bone into the primitive connective tissue (mesenchyme), while endochondral ossification involves cartilage as a precursor. In fracture healing, endochondral osteogenesis is the most commonly occurring process, for example in fractures of long Bone, bones treated by plaster of Paris, whereas fractures treated by open reduction and internal fixation with metal plates, screws, pins, rods and nails may heal by intramembranous osteogenesis. Heterotopic ossification is a process resulting in the formation of bone tissue that is often atypical, at an extraskeletal location. Calcification is often confused with ossification. Calci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
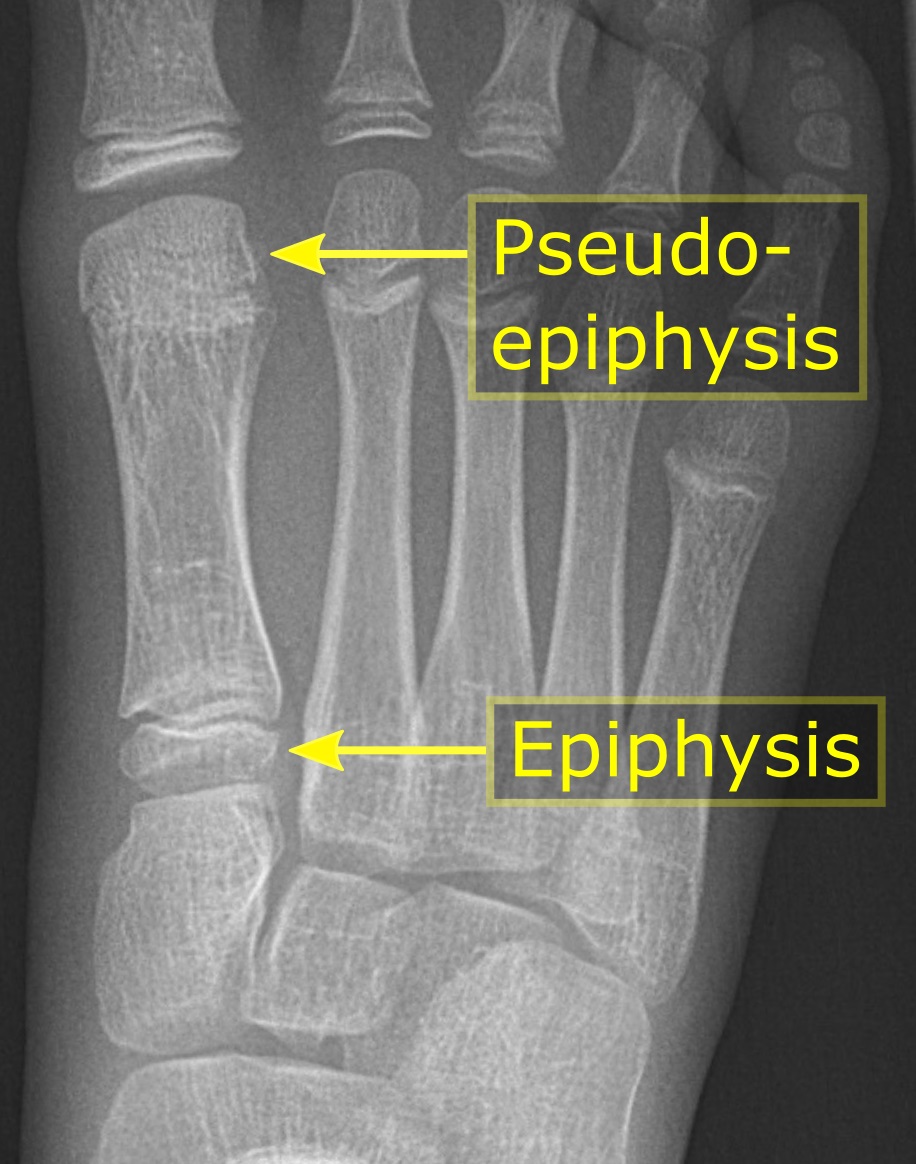
Epiphysis
The epiphysis () is the rounded end of a long bone, at its joint with adjacent bone(s). Between the epiphysis and diaphysis (the long midsection of the long bone) lies the metaphysis, including the epiphyseal plate (growth plate). At the joint, the epiphysis is covered with articular cartilage; below that covering is a zone similar to the epiphyseal plate, known as subchondral bone. The epiphysis is filled with red bone marrow, which produces erythrocytes (red blood cells). Structure There are four types of epiphysis: # Pressure epiphysis: The region of the long bone that forms the joint is a pressure epiphysis (e.g. the head of the femur, part of the hip joint complex). Pressure epiphyses assist in transmitting the weight of the human body and are the regions of the bone that are under pressure during movement or locomotion. Another example of a pressure epiphysis is the head of the humerus which is part of the shoulder complex. condyles of femur and tibia also comes under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Periosteum
The periosteum is a membrane that covers the outer surface of all bones, except at the articular surfaces (i.e. the parts within a joint space) of long bones. Endosteum lines the inner surface of the medullary cavity of all long bones. Structure The periosteum consists of an outer fibrous layer, and an inner cambium layer (or osteogenic layer). The fibrous layer is of dense irregular connective tissue, containing fibroblasts, while the cambium layer is highly cellular containing progenitor cells that develop into osteoblasts. These osteoblasts are responsible for increasing the width of a long bone and the overall size of the other bone types. After a bone fracture, the progenitor cells develop into osteoblasts and chondroblasts, which are essential to the healing process. The outer fibrous layer and the inner cambium layer is differentiated under electron micrography. As opposed to osseous tissue, the periosteum has nociceptors, sensory neurons that make it very sensitive to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fibular Artery
In anatomy, the fibular artery, also known as the peroneal artery, supplies blood to the lateral compartment of the leg. It arises from the tibial-fibular trunk. Structure The fibular artery arises from the bifurcation of tibial-fibular trunk into the fibular and posterior tibial arteries in the upper part of the leg proper, just below the knee. It runs towards the foot in the deep posterior compartment of the leg, just medial to the fibula. It supplies a perforating branch to both the lateral and anterior compartments of the leg; it also provides a nutrient artery to the fibula. Some sources claim that the fibular artery arises directly from the posterior tibial artery, but vascular and plastic surgeons note the clinical significance of the tibial-fibular trunk. The fibular artery is accompanied by small veins (venae comitantes) known as fibular veins. Branches Communication branch to posterior tibial artery. Perforating branch to anterior lateral malleolar artery. A calcan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)