|
Fern Cave National Wildlife Refuge
Fern Cave National Wildlife Refuge is a National Wildlife Refuge located in northeastern Alabama, near Paint Rock, Alabama in Jackson County. Despite receiving more than 1,200 visitors per year, the facility is unstaffed; it is administered by the Wheeler National Wildlife Refuge in Decatur, Alabama. Topography Most of the Fern Cave NWR is on the western side of Nat Mountain between Scottsboro and Huntsville, Alabama. The Paint Rock River, a tributary of the Tennessee River borders the northwestern side of the refuge. Elevation ranges from the relative flat area around the Paint Rock River valley to a 1,500+ foot elevation at the top of the mountain. Fern Cave Fern Cave NWR is named after the eponymous cave located in the region; in it, explorers found an abundance of American hart's-tongue ferns (''Asplenium scolopendrium'' var. ''americanum''); in the modern day, the variation/subspecies is considered federally endangered. The fern population in the cave has been drastic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jackson County, Alabama
Jackson County is the northeasternmost county in the U.S. state of Alabama. As of the 2020 census, the population was 52,579. The county seat is Scottsboro. The county was named for Andrew Jackson, general in the United States Army and afterward President of the United States of America. Jackson County is a prohibition or dry county, but three cities within the county (Bridgeport, Scottsboro, and Stevenson) are "wet", allowing alcohol sales. Jackson County comprises the Scottsboro, AL Micropolitan Statistical Area, And Jackson county is included in the Scottsboro-Fort Payne combined statistical areas. It is the site of Russell Cave National Monument, an archeological site with evidence of 8,000 years of human occupation in the Southeast. History Jackson County was established on December 13, 1819, after the federal government arranged a treaty to remove the Cherokee from the area and extinguish their land claims. The hilly and mountainous terrain of the Appalachians made th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squirrel
Squirrels are members of the family Sciuridae, a family that includes small or medium-size rodents. The squirrel family includes tree squirrels, ground squirrels (including chipmunks and prairie dogs, among others), and flying squirrels. Squirrels are indigenous to the Americas, Eurasia, and Africa, and were introduced by humans to Australia. The earliest known fossilized squirrels date from the Eocene epoch, and among other living rodent families, the squirrels are most closely related to the mountain beaver and to the dormice. Etymology The word ''squirrel'', first attested in 1327, comes from the Anglo-Norman which is from the Old French , the reflex of a Latin word , which was taken from the Ancient Greek word (; from ) 'shadow-tailed', referring to the long bushy tail which many of its members have. The native Old English word for the squirrel, , survived only into Middle English (as ) before being replaced. The Old English word is of Common Germanic origin, cognat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
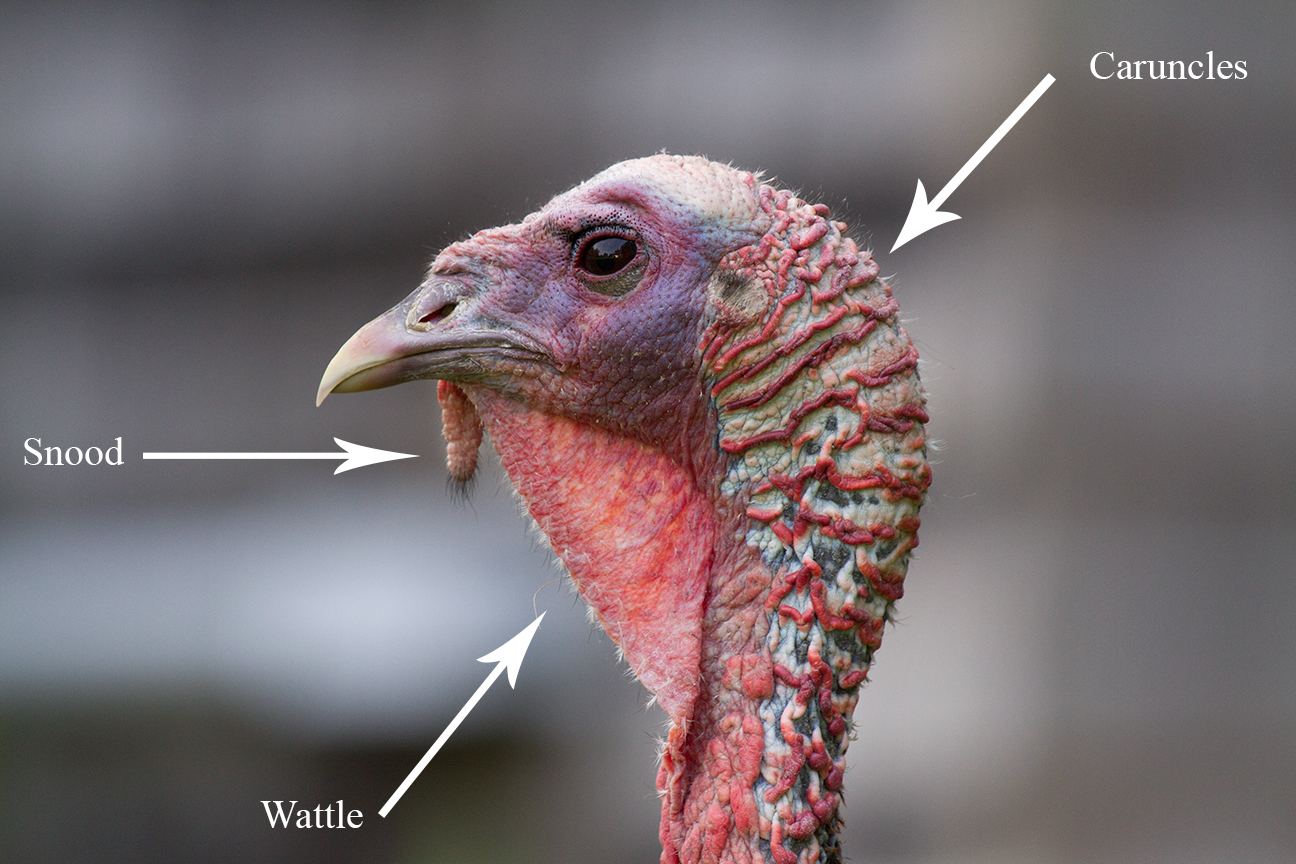
Wild Turkey
The wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo'') is an Upland game bird, upland ground bird native to North America, one of two extant species of Turkey (bird), turkey and the heaviest member of the order Galliformes. It is the ancestor to the domestic turkey, which was originally derived from a southern Mexican subspecies of wild turkey (not the related ocellated turkey). Description Adult wild turkeys have long reddish-yellow to grayish-green legs. The body feathers are generally blackish and dark, sometimes grey brown overall with a coppery sheen that becomes more complex in adult males. Adult males, called toms or gobblers, have a large, featherless, reddish head, red throat, and red Wattle (anatomy), wattles on the throat and neck. The head has fleshy growths called Caruncle (bird anatomy) , caruncles. Juvenile males are called jakes; the difference between an adult male and a juvenile is that the jake has a very short beard and his tail fan has longer feathers in the middle. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White-tailed Deer
The white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), also known as the whitetail or Virginia deer, is a medium-sized deer native to North America, Central America, and South America as far south as Peru and Bolivia. It has also been introduced to New Zealand, all the Greater Antilles in the Caribbean (Cuba, Jamaica Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ..., Hispaniola, and Puerto Rico), and some countries in Europe, such as the Czech Republic, Finland, France, Germany, Romania and Serbia. In the Americas, it is the most widely distributed wild ungulate. In North America, the species is widely distributed east of the Rocky Mountains as well as in southwestern Arizona and most of Mexico, except Baja California peninsula, Lower California. It is mostly displaced by the black ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Bullhead Catfish
The yellow bullhead (''Ameiurus natalis'') is a species of bullhead catfish, a ray-finned fish that lacks scales. Description The yellow bullhead is a medium-sized member of the catfish family. It is typically yellow-olive to slate black on the back and may appear mottled depending on its habitat. The sides are lighter and more yellowish, while the underside of the head and body are bright yellow, yellow white, or bright white. The rear edge of its caudal fin is rounded. The anal fin is much longer than those of other bullheads, having anywhere between 24 and 27 rays. The yellow bullhead, though less common, can be easily distinguished from the brown bullhead and black bullhead by the group of white barbels or "whiskers" under its chin. Yellow bullheads are medium-sized bullheads that rarely grow larger than , but can reach up to . Yellow bullheads range in size from 6 to 14 inches, and can live up to 12 years. Diet The yellow bullhead is a voracious scavenger that will almost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bluegill
The bluegill (''Lepomis macrochirus''), sometimes referred to as "bream", "brim", "sunny", or "copper nose" as is common in Texas, is a species of North American freshwater fish, native to and commonly found in streams, rivers, lakes, ponds and wetlands east of the Rocky Mountains. It is the type species of the genus ''Lepomis'' (true sunfish), from the family Centrarchidae (sunfishes, crappies and black basses) in the order Perciformes (perch-like fish). Bluegills can grow up to long and about . While their color can vary from population to population, they typically have a very distinctive coloring, with deep blue and purple on the face and gill cover, dark olive-colored bands down the side, and a fiery orange to yellow belly. They are omnivorous and will consume anything they can fit in their mouth, but mostly feed on small aquatic insects and baitfishes. The fish are important prey for bass, other larger sunfish, northern pike and muskellunge, walleye, trout, herons, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banded Sculpin
The banded sculpin (''Cottus carolinae'') is a freshwater fish dwelling mostly in small to moderate sized streams in areas of swift current. Young and juvenile ''C. carolinae'' can mainly be found in pools, riffles, and other shallow habitats while adults tend to prefer deeper waters. ''C. carolinae'' primarily eats insects and insect larvae, but their large mouths enable them to eat prey nearly as large as themselves, including other sculpin. To prevent predation, including by other fish, the color and pattern of the sculpin tends to match its environment. Most ''Cottus carolinae'' are mottled brown with dark vertical banding and usually reach about three inches in length. They have a broad head which rather quickly narrows into a slim body, giving them the appearance of a tadpole reaching adulthood. ''Cottus carolinae'' has proven to be useful as a representative species for the effects of mining related impacts on fishing communities since it has been proven that their density ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northern Slimy Salamander
The northern slimy salamander (''Plethodon glutinosus'') is a species of terrestrial plethodontid salamander found throughout much of the eastern two-thirds of the United States. Common names The northern slimy salamander is called "slimy" because it produces sticky slime from glands on its lower back and tail in order to defend itself from predators. It is also sometimes referred to as the viscid salamander, grey-spotted salamander, slippery salamander, or sticky salamander, depending on which source is consulted. Description The northern slimy salamander is typically an overall black in color, with numerous silvery spots or gold spots across its back. It is usually in total length (including tail), but can grow to 20.6 cm (8.1 in). Males are not easily distinguished from females, though females tend to be slightly larger. It has 15-17 costal grooves. Taxonomy ''P. glutinosus'' is one of 57 species in the genus ''Plethodon'' and was one of the first of its cogener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spotted-tail Salamander
The spotted-tail salamander (''Eurycea lucifuga''), also known as a "cave salamander", is a species of brook salamander. Description The spotted-tail salamander is a relatively large lungless salamander, ranging in total length from 10 to 20 cm (4 to 8 in). The tail makes up a significant proportion of the total length, up to 60–65%. Post-metamorphic individuals have orange to reddish orange backs and a pale, unmarked ventral surface. The dorsal surface of the body is heavily marked with irregularly spaced spots and dashes. The limbs of the spotted-tail salamander are long. There are 14–15 costal grooves on the side of the body. This species has a prehensile tail. Habitat and distribution Spotted-tail salamanders are typically found in areas with exposed limestone or other calcareous rock, particularly in crevices of rock faces, bluffs and caves. This species is also frequently found hundreds of metres from the mouths of caves, far beyond the twilight zone of the cave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambarus Unestami
''Cambarus unestami'', the blackbarred crayfish, is a species of crayfish in the family Cambaridae. It is native to Alabama and Georgia in the United States. The IUCN The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natu ... conservation status of ''Cambarus unestami'' is "LC", least concern, with no immediate threat to the species' survival. The IUCN status was reviewed in 2010. References Further reading * * * Cambaridae Freshwater crustaceans of North America Articles created by Qbugbot Crustaceans described in 1969 Taxa named by Horton H. Hobbs Jr. {{Crayfish-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Cavefish
''Typhlichthys subterraneus'', the southern cavefish, is a species of cavefish in the family Amblyopsidae endemic to karst regions of the eastern United States. Taxonomy ''T. subterraneus'' is a one of five obligate troglobitic species in Amblyopsidae. ''T. subterraneus'' is currently the only member of the genus ''Typhlichthys'', but it may be a cryptic species complex. The southern cavefish was described by Charles Frédéric Girard in 1859 from a well near Bowling Green, Warren County, Kentucky. Later, Eigenmann in 1905 described both ''T. osborni'' and ''T. wyandotte'' based on differences in head width and eye diameter. ''Typhlichthys osborni'' was described from Horse Cave, Kentucky, whereas ''T. wyandotte'' was described from a well near Corydon, Indiana, that was later destroyed. In 2002, a well-like entrance into a cave on the property of a car dealership in Corydon was discovered and is believed to represent the type locality. Regardless, this species is generally cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_(3679650501).jpg)