|
Federative Committee On Anatomical Terminology
The Federative International Programme for Anatomical Terminology (FIPAT) is a group of experts who review, analyze, and discuss the terms of the morphological structures of the human body. It was created by the International Federation of Associations of Anatomists (IFAA) and was previously known as the Federative Committee on Anatomical Terminology (FCAT) and the Federative International Committee on Anatomical Terminology (FICAT). Origins and history This Committee was created in 1989, at the XIII International Congress of Anatomists, held in Rio de Janeiro (Brazil). It followed the old International Anatomical Nomenclature Committee (IANC). The professionals involved are renowned professors and researchers with knowledge of medical terminology. They hold periodic meetings in different countries on a rotating basis, where they study morphological terminology: anatomical, histological and embryology of the human being. The results of this committee were published in 1998 i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphology (biology)
Morphology is a branch of biology dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features. This includes aspects of the outward appearance (shape, structure, colour, pattern, size), i.e. external morphology (or eidonomy), as well as the form and structure of the internal parts like bones and organs, i.e. internal morphology (or anatomy). This is in contrast to physiology, which deals primarily with function. Morphology is a branch of life science dealing with the study of gross structure of an organism or taxon and its component parts. History The etymology of the word "morphology" is from the Ancient Greek (), meaning "form", and (), meaning "word, study, research". While the concept of form in biology, opposed to function, dates back to Aristotle (see Aristotle's biology), the field of morphology was developed by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (1790) and independently by the German anatomist and physiologist Karl Friedrich Burdach ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histology
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology which studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into ''organology'', the study of organs, ''histology'', the study of tissues, and ''cytology'', the study of cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms. Biological tissues Animal tissue classification There are four basic types of animal tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. All animal tissues are considered to be subtypes of these four principal tissue types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nomina Anatomica
''Nomina Anatomica'' (''NA'') was the international standard on human anatomic terminology from 1895 until it was replaced by ''Terminologia Anatomica'' in 1998. In the late nineteenth century some 30,000 terms for various body parts were in use. The same structures were described by different names, depending (among other things) on the anatomist's school and national tradition. Vernacular translations of Latin and Greek, as well as various eponymous terms, were barriers to effective international communication. There was disagreement and confusion among anatomists regarding anatomical terminology. Editions The first and last entries in the following table are not NA editions, but they are included for the sake of continuity. Although these early editions were authorized by different bodies, they are sometimes considered part of the same series. Before these codes of terminology, approved at anatomists congresses, the usage of anatomical terms was based on authoritative work ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terminologia Anatomica
''Terminologia Anatomica'' is the international standard for human anatomical terminology. It is developed by the Federative International Programme on Anatomical Terminology, a program of the International Federation of Associations of Anatomists (IFAA). The second edition was released in 2019 and approved and adopted by the IFAA General Assembly in 2020. ''Terminologia Anatomica'' supersedes the previous standard, ''Nomina Anatomica''. It contains terminology for about 7500 human anatomical structures. Categories of anatomical structures ''Terminologia Anatomica'' is divided into 16 chapters grouped into five parts. The official terms are in Latin. Although equivalent English-language terms are provided, as shown below, only the official Latin terms are used as the basis for creating lists of equivalent terms in other languages. Part I Chapter 1: General anatomy # General terms # Reference planes # Reference lines # Human body positions # Movements # Parts of human body ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
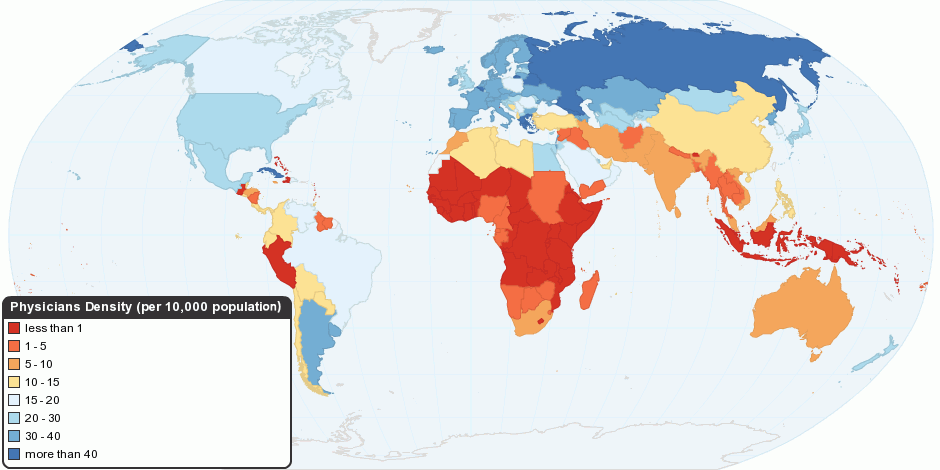
Medical Care
Health care or healthcare is the improvement of health via the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, amelioration or cure of disease, illness, injury, and other physical and mental impairments in people. Health care is delivered by health professionals and allied health fields. Medicine, dentistry, pharmacy, midwifery, nursing, optometry, audiology, psychology, occupational therapy, physical therapy, athletic training, and other health professions all constitute health care. It includes work done in providing primary care, secondary care, and tertiary care, as well as in public health. Access to health care may vary across countries, communities, and individuals, influenced by social and economic conditions as well as health policies. Providing health care services means "the timely use of personal health services to achieve the best possible health outcomes". Factors to consider in terms of health care access include financial limitations (such as insurance coverage), geograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teaching
Teaching is the practice implemented by a ''teacher'' aimed at transmitting skills (knowledge, know-how, and interpersonal skills) to a learner, a student, or any other audience in the context of an educational institution. Teaching is closely related to ''learning'', the student's activity of appropriating this knowledge. Teaching is part of the broader concept of ''education Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Va ...''.Naïl Ver, Adeline Paul and Farid Malki, ''Professeur des écoles : droits, responsabilités, carrière'', Retz Éditions, 2014, 223 p. Methods Profession Training References {{Authority control ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research
Research is "creativity, creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion on past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, Discovery (observation), discovery, interpretation (philosophy), interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemology, epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Specialist
A medical specialty is a branch of medical practice that is focused on a defined group of patients, diseases, skills, or philosophy. Examples include those branches of medicine that deal exclusively with children (paediatrics), cancer (oncology), laboratory medicine (pathology), or primary care (family medicine). After completing medical school or other basic training, physicians or surgeons and other clinicians usually further their medical education in a specific specialty of medicine by completing a multiple-year residency to become a specialist. History of medical specialization To a certain extent, medical practitioners have long been specialized. According to Galen, specialization was common among Roman physicians. The particular system of modern medical specialties evolved gradually during the 19th century. Informal social recognition of medical specialization evolved before the formal legal system. The particular subdivision of the practice of medicine into various special ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe. Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for scientific reasoning is tens of thousands of years old. The earliest written records in the history of science come from Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200 BCE. Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but was preserved in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age and later by the efforts of Byzantine Greek scholars who brought Greek m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Language
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe. Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for scientific reasoning is tens of thousands of years old. The earliest written records in the history of science come from Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200 BCE. Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but was preserved in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age and later by the efforts of Byzantine Greek scholars who brought Greek man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terminology
Terminology is a group of specialized words and respective meanings in a particular field, and also the study of such terms and their use; the latter meaning is also known as terminology science. A ''term'' is a word, compound word, or multi-word expressions that in specific contexts is given specific meanings—these may deviate from the meanings the same words have in other contexts and in everyday language. Terminology is a discipline that studies, among other things, the development of such terms and their interrelationships within a specialized domain. Terminology differs from lexicography, as it involves the study of concepts, conceptual systems and their labels (''terms''), whereas lexicography studies words and their meanings. Terminology is a discipline that systematically studies the "labelling or designating of concepts" particular to one or more subject fields or domains of human activity. It does this through the research and analysis of terms in context for the pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embryology
Embryology (from Greek ἔμβρυον, ''embryon'', "the unborn, embryo"; and -λογία, '' -logia'') is the branch of animal biology that studies the prenatal development of gametes (sex cells), fertilization, and development of embryos and fetuses. Additionally, embryology encompasses the study of congenital disorders that occur before birth, known as teratology. Early embryology was proposed by Marcello Malpighi, and known as preformationism, the theory that organisms develop from pre-existing miniature versions of themselves. Aristotle proposed the theory that is now accepted, epigenesis. Epigenesis is the idea that organisms develop from seed or egg in a sequence of steps. Modern embryology, developed from the work of Karl Ernst von Baer, though accurate observations had been made in Italy by anatomists such as Aldrovandi and Leonardo da Vinci in the Renaissance. Comparative embryology Preformationism and epigenesis As recently as the 18th century, the prevailin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |