|
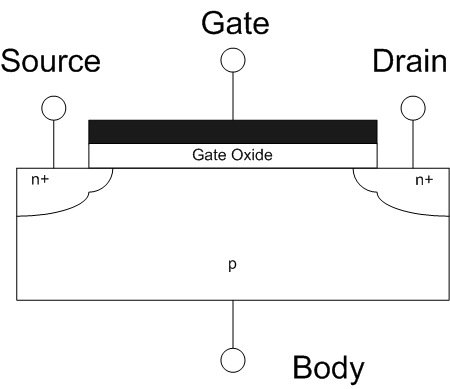
FeFET
A ferroelectric field-effect transistor (Fe FET) is a type of field-effect transistor that includes a ferroelectric material sandwiched between the gate electrode and source-drain conduction region of the device (the channel). Permanent electrical field polarisation in the ferroelectric causes this type of device to retain the transistor's state (on or off) in the absence of any electrical bias. FeFET based devices are used in FeFET memory - a type of single transistor non-volatile memory. Description In 1955, Ian Munro Ross filed a patent for a FeFET or MFSFET. Its structure was like that of a modern inversion channel MOSFET, but ferroelectric material was used as a dielectric/insulator instead of oxide. Use of a ferroelectric (triglycine sulfate) in a solid state memory was proposed by Moll and Tarui in 1963 using a thin film transistor. Further research occurred in the 1960s, but the retention characteristics of the thin film based devices was unsatisfactory. Early field e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FeFET
A ferroelectric field-effect transistor (Fe FET) is a type of field-effect transistor that includes a ferroelectric material sandwiched between the gate electrode and source-drain conduction region of the device (the channel). Permanent electrical field polarisation in the ferroelectric causes this type of device to retain the transistor's state (on or off) in the absence of any electrical bias. FeFET based devices are used in FeFET memory - a type of single transistor non-volatile memory. Description In 1955, Ian Munro Ross filed a patent for a FeFET or MFSFET. Its structure was like that of a modern inversion channel MOSFET, but ferroelectric material was used as a dielectric/insulator instead of oxide. Use of a ferroelectric (triglycine sulfate) in a solid state memory was proposed by Moll and Tarui in 1963 using a thin film transistor. Further research occurred in the 1960s, but the retention characteristics of the thin film based devices was unsatisfactory. Early field e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-volatile Memory
Non-volatile memory (NVM) or non-volatile storage is a type of computer memory that can retain stored information even after power is removed. In contrast, volatile memory needs constant power in order to retain data. Non-volatile memory typically refers to storage in semiconductor memory chips, which store data in floating-gate memory cells consisting of floating-gate MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors), including flash memory storage such as NAND flash and solid-state drives (SSD). Other examples of non-volatile memory include read-only memory (ROM), EPROM (erasable programmable ROM) and EEPROM (electrically erasable programmable ROM), ferroelectric RAM, most types of computer data storage devices (e.g. disk storage, hard disk drives, optical discs, floppy disks, and magnetic tape), and early computer storage methods such as punched tape and cards. Overview Non-volatile memory is typically used for the task of secondary storage or long-term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-volatile Memory
Non-volatile memory (NVM) or non-volatile storage is a type of computer memory that can retain stored information even after power is removed. In contrast, volatile memory needs constant power in order to retain data. Non-volatile memory typically refers to storage in semiconductor memory chips, which store data in floating-gate memory cells consisting of floating-gate MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors), including flash memory storage such as NAND flash and solid-state drives (SSD). Other examples of non-volatile memory include read-only memory (ROM), EPROM (erasable programmable ROM) and EEPROM (electrically erasable programmable ROM), ferroelectric RAM, most types of computer data storage devices (e.g. disk storage, hard disk drives, optical discs, floppy disks, and magnetic tape), and early computer storage methods such as punched tape and cards. Overview Non-volatile memory is typically used for the task of secondary storage or long-term ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hafnium Dioxide
Hafnium(IV) oxide is the inorganic compound with the formula . Also known as hafnium dioxide or hafnia, this colourless solid is one of the most common and stable compounds of hafnium. It is an electrical insulator with a band gap of 5.3~5.7 eV. Hafnium dioxide is an intermediate in some processes that give hafnium metal. Hafnium(IV) oxide is quite inert. It reacts with strong acids such as concentrated sulfuric acid and with strong bases. It dissolves slowly in hydrofluoric acid to give fluorohafnate anions. At elevated temperatures, it reacts with chlorine in the presence of graphite or carbon tetrachloride to give hafnium tetrachloride. Structure Hafnia typically adopts the same structure as zirconia (ZrO2). Unlike TiO2, which features six-coordinate Ti in all phases, zirconia and hafnia consist of seven-coordinate metal centres. A variety of other crystalline phases have been experimentally observed, including cubic fluorite (Fmm), tetragonal (P42/nmc), monoclinic (P21/c) an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field-effect Transistor
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs (JFETs or MOSFETs) are devices with three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since they involve single-carrier-type operation. That is, FETs use either electrons (n-channel) or holes (p-channel) as charge carriers in their operation, but not both. Many different types of field effect transistors exist. Field effect transistors generally display very high input impedance at low frequencies. The most widely used field-effect transistor is the MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor). History The concept of a field-effect transistor (FET) was first patented by Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 192 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field Effect Transistor
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs (JFETs or MOSFETs) are devices with three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since they involve single-carrier-type operation. That is, FETs use either electrons (n-channel) or holes (p-channel) as charge carriers in their operation, but not both. Many different types of field effect transistors exist. Field effect transistors generally display very high input impedance at low frequencies. The most widely used field-effect transistor is the MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor). History The concept of a field-effect transistor (FET) was first patented by Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferroelectric RAM
Ferroelectric RAM (FeRAM, F-RAM or FRAM) is a random-access memory similar in construction to DRAM but using a ferroelectric layer instead of a dielectric layer to achieve non-volatility. FeRAM is one of a growing number of alternative non-volatile random-access memory technologies that offer the same functionality as flash memory. An FeRAM chip contains a thin film of ferroelectric material, often lead zirconate titanate, commonly referred to as PZT. The atoms in the PZT layer change polarity in an electric field, thereby producing a power-efficient binary switch. However, the most important aspect of the PZT is that it is not affected by power disruption or magnetic interference, making FeRAM a reliable nonvolatile memory. FeRAM's advantages over Flash include: lower power usage, faster write performance and a much greater maximum read/write endurance (about 1010 to 1015 cycles). FeRAMs have data retention times of more than 10 years at +85 °C (up to many decades at lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field-effect Transistors
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs (JFETs or MOSFETs) are devices with three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since they involve single-carrier-type operation. That is, FETs use either electrons (n-channel) or holes (p-channel) as charge carriers in their operation, but not both. Many different types of field effect transistors exist. Field effect transistors generally display very high input impedance at low frequencies. The most widely used field-effect transistor is the MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor). History The concept of a field-effect transistor (FET) was first patented by Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ian Munro Ross
Ian Munro Ross FREng (15 August 1927 – 10 March 2013) was an early pioneer in transistors, and for 12 years President of Bell Labs. Ross was born in Southport, England, and in 1948 received his bachelor's degree in electrical engineering from Gonville and Caius College, Cambridge University. In 1952 he received his M.A. and PhD degrees in electrical engineering from Cambridge. In 1952 William Shockley hired him to work in semiconductors at Bell Labs, and he arrived in Murray Hill just after John Bardeen and Walter Houser Brattain had left. Shockley's group focused exclusively on transistor improvements, and Ross and G. C. Dacey were instrumental in the early stages of development of the field-effect transistor. In 1960 Ross and others invented epitaxy. He subsequently rose through managerial ranks, ultimately serving as the sixth President of Bell Labs 1979–1991 and overseeing its reorganization following the breakup of the Bell System. In 1979, he was a resident of Rumson, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Channel (semiconductor)
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs (JFETs or MOSFETs) are devices with three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control the flow of current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since they involve single-carrier-type operation. That is, FETs use either electrons (n-channel) or holes (p-channel) as charge carriers in their operation, but not both. Many different types of field effect transistors exist. Field effect transistors generally display very high input impedance at low frequencies. The most widely used field-effect transistor is the MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor). History The concept of a field-effect transistor (FET) was first patented by Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thin Film Transistor
A thin-film transistor (TFT) is a special type of field-effect transistor (FET) where the transistor is thin relative to the plane of the device. TFTs are grown on a supporting (but non-conducting) substrate. A common substrate is glass, because the traditional application of TFTs is in liquid-crystal displays (LCDs). This differs from the conventional bulk metal oxide field effect transistor (MOSFET), where the semiconductor material typically ''is'' the substrate, such as a silicon wafer. Design and Manufacture TFTs can be fabricated with a wide variety of semiconductor materials. Because it is naturally abundant and well understood, amorphous or polycrystalline silicon was historically used as the semiconductor layer. However, because of the low mobility of amorphous silicon and the large device-to-device variations found in polycrystalline silicon, other materials have been studied for use in TFTs. These include cadmium selenide, metal oxides such as indium gallium zinc o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bismuth Titanate
Bismuth titanate or bismuth titanium oxide is a solid inorganic compound of bismuth, titanium and oxygen with the chemical formula of Bi12TiO20, Bi 4Ti3O12 or Bi2Ti2O7. Synthesis Bismuth titanate ceramics can be produced by heating a mixture of bismuth and titanium oxides. Bi12TiO20 forms at 730–850 °C, and melts when the temperature is raised above 875 °C, decomposing in the melt to Bi4Ti3O12 and Bi2O3. Millimeter-sized single crystals of Bi12TiO20 can be grown by the Czochralski process, from the molten phase at 880–900 °C. Properties and applications Bismuth titanates exhibit electrooptical effect and photorefractive effect, that is, a reversible change in the refractive index under applied electric field or illumination, respectively. Consequently, they have potential applications in reversible recording media for real-time holography Holography is a technique that enables a wavefront to be recorded and later re-constructed. Holography is best kn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

