|
Farangi-Sazi
Farangi-Sazi () was a style of Persian painting that originated in Safavid Iran in the second half of the 17th century. This style of painting emerged during the reign of Shah Abbas II (), but first became prominent under Shah Solayman II (). ''Farangi-sazi'' paintings depicted many types of different scenarios, varying from traditional Iranian scenes, such as portrayal of kings and aristocrats, to European depictions, sceneries, biblical, and mythological events. Only a few 17th-century artists made paintings in the style of ''Farangi-sazi'', the most prominent ones being Aliqoli Jebadar and Mohammad Zaman Mohammad Paolo Zaman Kermani known as Mohammad Zaman ( fl. 1680 – c. 1700), a famous Safavid calligrapher and painter. Life He was a native of Kerman, Persia. He received his education in Tabriz. He was sent to Rome under the reign of Shah .... References Sources * Further reading * * * * {{cite book, editor-last=Melville, editor-first=Charles, auth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suleiman Of Persia
Suleiman I (; born Sam Mirza, February or March 1648 – 29 July 1694) was the eighth and the penultimate Shah of Safavid Iran from 1666 to 1694. He was the eldest son of Abbas II and his concubine, Nakihat Khanum. Born as Sam Mirza, Suleiman spent his childhood in the harem among women and eunuchs and his existence was hidden from the public. When Abbas II died in 1666, his grand vizier, Mirza Mohammad Karaki, did not know that the shah had a son. The nineteen-years-old Sam Mirza was crowned king under the regnal name, Safi II, after his grandfather, Safi I. His reign as Safi II undergone troublesome events which led to a second coronation being held for him in 20 March 1668, simultaneously with Nowruz, in which he was crowned king as Suleiman I. After his second coronation, Suleiman retreated into his harem to enjoy sexual activities and excessive drinking. He was indifferent to the state affairs, and often would not appear in the public for months. As a result for his idlenes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shah Abbas II
Abbas II (; born Soltan Mohammad Mirza; 30 August 1632 – 26 October 1666) was the seventh Shah of Safavid Iran, ruling from 1642 to 1666. As the eldest son of Safi and his Circassian wife, Anna Khanum, he inherited the throne when he was nine, and had to rely on a regency led by Saru Taqi, the erstwhile grand vizier of his father, to govern in his place. During the regency, Abbas received formal kingly education that until then, he had been denied. In 1645, at age fifteen, he was able to remove Saru Taqi from power, and after purging the bureaucracy ranks, asserted his authority over his court and began his absolute rule. Abbas II's reign was marked by peacefulness and progression. He intentionally avoided a war with the Ottoman Empire, and his relations with the Uzbeks in the east were friendly. He enhanced his reputation as a military commander by leading his army during the war with the Mughal Empire, and successfully recovering the city of Kandahar. On his behest, Ros ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohammad Zaman
Mohammad Paolo Zaman Kermani known as Mohammad Zaman ( fl. 1680 – c. 1700), a famous Safavid calligrapher and painter. Life He was a native of Kerman, Persia. He received his education in Tabriz. He was sent to Rome under the reign of Shah Abbas II. He returned to Persia as a Catholic Christian with the name Paolo. Because of his conversion to Roman Catholicism he was obliged to escape from Persia to India where he obtained the protection of the Moghul dynasty. Mohammad Zaman was influenced by Italian painting techniques. However, as Ivanov suggests, Mohammad Zaman studied under a European artist in Isfahan Isfahan ( fa, اصفهان, Esfahân ), from its Achaemenid empire, ancient designation ''Aspadana'' and, later, ''Spahan'' in Sassanian Empire, middle Persian, rendered in English as ''Ispahan'', is a major city in the Greater Isfahan Regio ..., Persia, and the report of his being sent by Shah Abbas II to study in Italy, where he adopted Roman Catholic Christian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahram Gur And The Indian Princess On Saturday
Bahrām ( fa, بهرام) is a male given name. Other variants Behram, Bahran, Vahran, and Vahram ( uz, Баҳром, Bahrom and Tajik: Баҳром, Bahrom) The older form is Vahrām ( pal, 𐭥𐭫𐭧𐭫𐭠𐭭, in la, Varrames), also spelled Wahrām, literally meaning "smiting of resistance" or "victorious". It is name of several prominent figures in pre-Islamic Persia. In the Pahlavi language (Middle Persian), Bahram is another name of the Zoroastrian divinity Verethragna in Avestan language, that is the hypostasis of victory and represents the planet Mars. Historic people * One of the Sassanid kings by that name: ** Bahrām I, ''r.'' 273-276 ** Bahrām II, ''r.'' 276-293 ** Bahrām III, ''r.'' 293 ** Ardashir II, ''r.'' 379–383, who also went by the name 'Ardashir Vahram' ** Bahrām IV, ''r.'' 388–399 ** Bahrām V Gōr, ''r.'' 421–438 (often known as Bahram Gur) ** Bahrām VI Čōbīn, ''r.'' 590-591 ** Bahram VII * Bahram Khan, 14th-century governor based in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Art
Persian art or Iranian art () has one of the richest art heritages in world history and has been strong in many media including architecture, painting, weaving, pottery, calligraphy, metalworking and sculpture. At different times, influences from the art of neighbouring civilizations have been very important, and latterly Persian art gave and received major influences as part of the wider styles of Islamic art. This article covers the art of Persia up to 1925, and the end of the Qajar dynasty; for later art see Iranian modern and contemporary art, and for traditional crafts see arts of Iran. Rock art in Iran is its most ancient surviving art. Iranian architecture is covered at that article. From the Achaemenid Empire of 550 BC–330 BC for most of the time a large Iranian-speaking state has ruled over areas similar to the modern boundaries of Iran, and often much wider areas, sometimes called Greater Iran, where a process of cultural Persianization left enduring results even w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
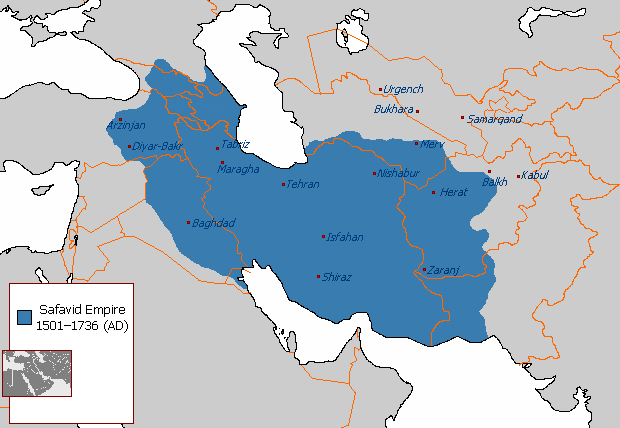
Safavid Iran
Safavid Iran or Safavid Persia (), also referred to as the Safavid Empire, '. was one of the greatest Iranian empires after the 7th-century Muslim conquest of Persia, which was ruled from 1501 to 1736 by the Safavid dynasty. It is often considered the beginning of modern Iranian history, as well as one of the gunpowder empires. The Safavid Shāh Ismā'īl I established the Twelver denomination of Shīʿa Islam as the official religion of the empire, marking one of the most important turning points in the history of Islam. An Iranian dynasty rooted in the Sufi Safavid order founded by Kurdish sheikhs, it heavily intermarried with Turkoman, Georgian, Circassian, and Pontic GreekAnthony Bryer. "Greeks and Türkmens: The Pontic Exception", ''Dumbarton Oaks Papers, Vol. 29'' (1975), Appendix II "Genealogy of the Muslim Marriages of the Princesses of Trebizond" dignitaries and was Turkish-speaking and Turkified. From their base in Ardabil, the Safavids established control ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aliquli Jabbadar
Aliquli Jabbadar (‘Alī-qolī Jabbadār) () was an Iranian artist, one of the first to have incorporated European influences in the traditional Safavid-era miniature painting. He is known for his scenes of the Safavid courtly life, especially his careful rendition of the physical setting and of details of dress."‘Aliquli Jabbadar", in: Bloom, Jonathan M. and Blair, Sheila S. (2009), The ''Grove encyclopedia of Islamic art and architecture'', Volume 2, pp. 55-56. Oxford University Press, . Jabbadar's name appears on a number of miniatures dating from the 17th century, including four from the State Hermitage in Russia and four from the Metropolitan Museum of Arts in the United States. In one of the signatures, the artist refers himself to as ''farangi'', "the Frank Frank or Franks may refer to: People * Frank (given name) * Frank (surname) * Franks (surname) * Franks, a medieval Germanic people * Frank, a term in the Muslim world for all western Europeans, particularly duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
17th Century In Art
17 (seventeen) is the natural number following 16 and preceding 18. It is a prime number. Seventeen is the sum of the first four prime numbers. In mathematics 17 is the seventh prime number, which makes seventeen the fourth super-prime, as seven is itself prime. The next prime is 19, with which it forms a twin prime. It is a cousin prime with 13 and a sexy prime with 11 and 23. It is an emirp, and more specifically a permutable prime with 71, both of which are also supersingular primes. Seventeen is the sixth Mersenne prime exponent, yielding 131,071. Seventeen is the only prime number which is the sum of four consecutive primes: 2, 3, 5, 7. Any other four consecutive primes summed would always produce an even number, thereby divisible by 2 and so not prime. Seventeen can be written in the form x^y + y^x and x^y - y^x, and, as such, it is a Leyland prime and Leyland prime of the second kind: :17=2^+3^=3^-4^. 17 is one of seven lucky numbers of Euler which produc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Art
Persian art or Iranian art () has one of the richest art heritages in world history and has been strong in many media including architecture, painting, weaving, pottery, calligraphy, metalworking and sculpture. At different times, influences from the art of neighbouring civilizations have been very important, and latterly Persian art gave and received major influences as part of the wider styles of Islamic art. This article covers the art of Persia up to 1925, and the end of the Qajar dynasty; for later art see Iranian modern and contemporary art, and for traditional crafts see arts of Iran. Rock art in Iran is its most ancient surviving art. Iranian architecture is covered at that article. From the Achaemenid Empire of 550 BC–330 BC for most of the time a large Iranian-speaking state has ruled over areas similar to the modern boundaries of Iran, and often much wider areas, sometimes called Greater Iran, where a process of cultural Persianization left enduring results eve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)