|
Faraday Paradox
The Faraday paradox or Faraday's paradox is any experiment in which Michael Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction appears to predict an incorrect result. The paradoxes fall into two classes: * Faraday's law appears to predict that there will be zero electromotive force (EMF) but there is a non-zero EMF. * Faraday's law appears to predict that there will be a non-zero EMF but there is zero EMF. Faraday deduced his law of induction in 1831, after inventing the first electromagnetic generator or dynamo, but was never satisfied with his own explanation of the paradox. Faraday's law compared to the Maxwell–Faraday equation Faraday's law (also known as the ''Faraday–Lenz law'') states that the electromotive force (EMF) is given by the total derivative of the magnetic flux with respect to time ''t'': :\mathcal = -\frac, where \mathcal is the EMF and Φ''B'' is the magnetic flux through a loop of wire. The direction of the electromotive force is given by Lenz's law. An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M Faraday Th Phillips Oil 1842
M, or m, is the thirteenth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''em'' (pronounced ), plural ''ems''. History The letter M is derived from the Phoenician Mem, via the Greek Mu (Μ, μ). Semitic Mem is most likely derived from a " Proto-Sinaitic" (Bronze Age) adoption of the "water" ideogram in Egyptian writing. The Egyptian sign had the acrophonic value , from the Egyptian word for "water", ''nt''; the adoption as the Semitic letter for was presumably also on acrophonic grounds, from the Semitic word for "water", '' *mā(y)-''. Use in writing systems The letter represents the bilabial nasal consonant sound in the orthography of Latin as well as in that of many modern languages, and also in the International Phonetic Alphabet. In English, the Oxford English Dictionary (first edition) says that is sometimes a vowel, in words like ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partial Derivative
In mathematics, a partial derivative of a function of several variables is its derivative with respect to one of those variables, with the others held constant (as opposed to the total derivative, in which all variables are allowed to vary). Partial derivatives are used in vector calculus and differential geometry. The partial derivative of a function f(x, y, \dots) with respect to the variable x is variously denoted by It can be thought of as the rate of change of the function in the x-direction. Sometimes, for z=f(x, y, \ldots), the partial derivative of z with respect to x is denoted as \tfrac. Since a partial derivative generally has the same arguments as the original function, its functional dependence is sometimes explicitly signified by the notation, such as in: :f'_x(x, y, \ldots), \frac (x, y, \ldots). The symbol used to denote partial derivatives is ∂. One of the first known uses of this symbol in mathematics is by Marquis de Condorcet from 1770, who used it f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Homopolar Generator
A homopolar generator is a DC electrical generator comprising an electrically conductive disc or cylinder rotating in a plane perpendicular to a uniform static magnetic field. A potential difference is created between the center of the disc and the rim (or ends of the cylinder) with an electrical polarity that depends on the direction of rotation and the orientation of the field. It is also known as a unipolar generator, acyclic generator, disk dynamo, or Faraday disc. The voltage is typically low, on the order of a few volts in the case of small demonstration models, but large research generators can produce hundreds of volts, and some systems have multiple generators in series to produce an even larger voltage. They are unusual in that they can source tremendous electric current, some more than a million amperes, because the homopolar generator can be made to have very low internal resistance. Also, the homopolar generator is unique in that no other rotary electric machine can p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faraday Disk Dynamo
A homopolar generator is a DC electrical generator comprising an electrically conductive disc or cylinder rotating in a plane perpendicular to a uniform static magnetic field. A potential difference is created between the center of the disc and the rim (or ends of the cylinder) with an electrical polarity that depends on the direction of rotation and the orientation of the field. It is also known as a unipolar generator, acyclic generator, disk dynamo, or Faraday disc. The voltage is typically low, on the order of a few volts in the case of small demonstration models, but large research generators can produce hundreds of volts, and some systems have multiple generators in series to produce an even larger voltage. They are unusual in that they can source tremendous electric current, some more than a million amperes, because the homopolar generator can be made to have very low internal resistance. Also, the homopolar generator is unique in that no other rotary electric machine can pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Current
Direct current (DC) is one-directional flow of electric charge. An electrochemical cell is a prime example of DC power. Direct current may flow through a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through semiconductors, insulators, or even through a vacuum as in electron or ion beams. The electric current flows in a constant direction, distinguishing it from alternating current (AC). A term formerly used for this type of current was galvanic current. The abbreviations ''AC'' and ''DC'' are often used to mean simply ''alternating'' and ''direct'', as when they modify ''current'' or '' voltage''. Direct current may be converted from an alternating current supply by use of a rectifier, which contains electronic elements (usually) or electromechanical elements (historically) that allow current to flow only in one direction. Direct current may be converted into alternating current via an inverter. Direct current has many uses, from the charging of batteries to large power ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galvanometer
A galvanometer is an electromechanical measuring instrument for electric current. Early galvanometers were uncalibrated, but improved versions, called ammeters, were calibrated and could measure the flow of current more precisely. A galvanometer works by deflecting a pointer in response to an electric current flowing through a coil in a constant magnetic field. Galvanometers can be thought of as a kind of actuator. Galvanometers came from the observation, first noted by Hans Christian Ørsted in 1820, that a magnetic compass's needle deflects when near a wire having electric current. They were the first instruments used to detect and measure small amounts of current. André-Marie Ampère, who gave mathematical expression to Ørsted's discovery, named the instrument after the Italian electricity researcher Luigi Galvani, who in 1791 discovered the principle of the frog galvanoscope – that electric current would make the legs of a dead frog jerk. Galvanometers have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnet
A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is invisible but is responsible for the most notable property of a magnet: a force that pulls on other ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, steel, nickel, cobalt, etc. and attracts or repels other magnets. A permanent magnet is an object made from a material that is magnetized and creates its own persistent magnetic field. An everyday example is a refrigerator magnet used to hold notes on a refrigerator door. Materials that can be magnetized, which are also the ones that are strongly attracted to a magnet, are called ferromagnetic (or ferrimagnetic). These include the elements iron, nickel and cobalt and their alloys, some alloys of rare-earth metals, and some naturally occurring minerals such as lodestone. Although ferromagnetic (and ferrimagnetic) materials are the only ones attracted to a magnet strongly enough to be commonly considered magnetic, all other substances respond wea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Faraday Disc
Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and plasma). The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount of kinetic energy. A solid is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to a force applied to the surface. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire available volume like a gas. The atoms in a solid are bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice ( crystalline solids, which include metals and ordinary ice), or irregularly (an amorphous solid such as common window glass). Solids cannot be compressed with little pressure whereas gases can be compressed with little pressure because the molecules in a gas are loosely packed. The branch of physics that deals with solids is called solid-state physics, and is the main branch of condensed matter physics (which also includes liquids). Materials sci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
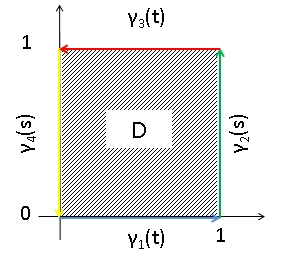
Kelvin–Stokes Theorem
Stokes's theorem, also known as the Kelvin–Stokes theorem Nagayoshi Iwahori, et al.:"Bi-Bun-Seki-Bun-Gaku" Sho-Ka-Bou(jp) 1983/12Written in Japanese)Atsuo Fujimoto;"Vector-Kai-Seki Gendai su-gaku rekucha zu. C(1)" :ja:培風館, Bai-Fu-Kan(jp)(1979/01) [] (Written in Japanese) after Lord Kelvin and Sir George Stokes, 1st Baronet, George Stokes, the fundamental theorem for curls or simply the curl theorem, is a theorem in vector calculus on . Given a vector field, the theorem relates the integral of the curl of the vector field over some surface, to the line integral of the vector field around the boundary of the surface. The classical Stokes' theorem can be stated in one sentence: The line integral of a vector field over a loop is equal to the ''flux of its curl'' through the enclosed surface. Stokes' theorem is a special case of the generalized Stokes' theorem. In particular, a vector field on can be considered as a 1-form in which case its curl is its exterior derivati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Classical Electromagnetism
Classical electromagnetism or classical electrodynamics is a branch of theoretical physics that studies the interactions between electric charges and currents using an extension of the classical Newtonian model; It is, therefore, a classical field theory. The theory provides a description of electromagnetic phenomena whenever the relevant length scales and field strengths are large enough that quantum mechanical effects are negligible. For small distances and low field strengths, such interactions are better described by quantum electrodynamics, which is a quantum field theory. Fundamental physical aspects of classical electrodynamics are presented in many texts, such as those by Feynman, Leighton and Sands, Griffiths, Panofsky and Phillips, and Jackson. History The physical phenomena that electromagnetism describes have been studied as separate fields since antiquity. For example, there were many advances in the field of optics centuries before light was understood to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maxwell's Equations
Maxwell's equations, or Maxwell–Heaviside equations, are a set of coupled partial differential equations that, together with the Lorentz force law, form the foundation of classical electromagnetism, classical optics, and electric circuits. The equations provide a mathematical model for electric, optical, and radio technologies, such as power generation, electric motors, wireless communication, lenses, radar etc. They describe how electric and magnetic fields are generated by charges, currents, and changes of the fields.''Electric'' and ''magnetic'' fields, according to the theory of relativity, are the components of a single electromagnetic field. The equations are named after the physicist and mathematician James Clerk Maxwell, who, in 1861 and 1862, published an early form of the equations that included the Lorentz force law. Maxwell first used the equations to propose that light is an electromagnetic phenomenon. The modern form of the equations in their most common formu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to the magnetic field. A permanent magnet's magnetic field pulls on ferromagnetic materials such as iron, and attracts or repels other magnets. In addition, a nonuniform magnetic field exerts minuscule forces on "nonmagnetic" materials by three other magnetic effects: paramagnetism, diamagnetism, and antiferromagnetism, although these forces are usually so small they can only be detected by laboratory equipment. Magnetic fields surround magnetized materials, and are created by electric currents such as those used in electromagnets, and by electric fields varying in time. Since both strength and direction of a magnetic field may vary with location, it is described mathematically by a function assigning a vector to each point of space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |